|
Anahit (film 1947)
Anahit ( hy, Անահիտ, fa, آناهید) was the goddess of fertility and healing, wisdom and water in Armenian mythology. In early periods she was the goddess of war. By the 5th century BCE she was the main deity in Armenia along with Aramazd. The Armenian goddess Anahit is related to the similar Iranian goddess Anahita. Anahit's worship, most likely borrowed from the Iranians during the Median invasion or the early Achaemenid period, was of paramount significance in Armenia. Artaxias I erected statues of Anahit, and promulgated orders to worship them.. Armenian Anahit and Persian Anahita According to Strabo, the "Armenians shared in the religion of the Perses and the Medes and particularly honored Anaitis". The kings of Armenia were "steadfast supporters of the cult". and Tiridates III, before his conversion to Christianity, "prayed officially to the triad Aramazd-Anahit-Vahagn but is said to have shown a special devotion to 'the great lady Anahit, ... the benefactres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aramazd
Aramazd ( arm, Արամազդ) was the chief and creator god in the Armenian version of Zoroastrianism.; ; ; ; ; The deity and his name were derived from the deity Ahura Mazda after the Median conquest of Armenia in the 6th century BC. Aramazd was regarded as a generous god of fertility, rain, and abundance, as well as the father of the other gods, including Anahit, Mihr, and Nane. Like Ahura Mazda, Aramazd was seen as the father of the other gods, rarely with a wife, though sometimes husband to Anahit or Spandaramet. Aramazd was the Parthian form of Ahura Mazda. Name The merging of the two words of Ahura Mazda first appears in the Old Persian section of the Behistun Inscription, carved by the Achaemenid King of Kings Darius the Great (), who refers to the deity as Auramazdāha. Avestan documents continued to spell the name with two words, a form which may have been accepted in Armenia. Aramazd is the Parthian form of Ahura Mazda. History Aramazd, Mihr, Anahit, Vahagn and T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark Antony
Marcus Antonius (14 January 1 August 30 BC), commonly known in English as Mark Antony, was a Roman politician and general who played a critical role in the transformation of the Roman Republic from a constitutional republic into the autocratic Roman Empire. Antony was a relative and supporter of Julius Caesar, and served as one of his generals during the conquest of Gaul and the Civil War. Antony was appointed administrator of Italy while Caesar eliminated political opponents in Greece, North Africa, and Spain. After Caesar's assassination in 44 BC, Antony joined forces with Marcus Aemilius Lepidus, another of Caesar's generals, and Octavian, Caesar's great-nephew and adopted son, forming a three-man dictatorship known to historians as the Second Triumvirate. The Triumvirs defeated Caesar's killers, the ''Liberatores'', at the Battle of Philippi in 42 BC, and divided the government of the Republic between themselves. Antony was assigned Rome's eastern provinces, includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregory The Illuminator
Gregory the Illuminator ( Classical hy, Գրիգոր Լուսաւորիչ, reformed: Գրիգոր Լուսավորիչ, ''Grigor Lusavorich'';, ''Gregorios Phoster'' or , ''Gregorios Photistes''; la, Gregorius Armeniae Illuminator, cu, Svyashchennomuchenik Grigory Armyansky, prosvetitel’ Velikoy Armenii, episkop Священномученик Григорий Армянский, просветитель Великой Армении, эпископ – ) was the 12th Catholicos-Patriarch and the first official head of the Armenian Apostolic Church. He was a religious leader who converted Armenia from paganism to Christianity in 301. He is also the patron saint of the church. Early life Gregory was the son of the Armenian Parthian nobles Anak the Parthian and Okohe. His father, Anak, was a Prince said to be related to the Arsacid Kings of Armenia or was from the House of Suren, one of the seven branches of the ruling Arsacid dynasty of Sakastan. Anak was char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Principate, which is the first phase of the Roman Empire, and Augustus is considered one of the greatest leaders in human history. The reign of Augustus initiated an imperial cult as well as an era associated with imperial peace, the ''Pax Romana'' or ''Pax Augusta''. The Roman world was largely free from large-scale conflict for more than two centuries despite continuous wars of imperial expansion on the empire's frontiers and the year-long civil war known as the "Year of the Four Emperors" over the imperial succession. Originally named Gaius Octavius, he was born into an old and wealthy equestrian branch of the plebeian ''gens'' Octavia. His maternal great-uncle Julius Caesar was assassinated in 44 BC, and Octavius was named in Caesar' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', a series of biographies of illustrious Greeks and Romans, and ''Moralia'', a collection of essays and speeches. Upon becoming a Roman citizen, he was possibly named Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus (). Life Early life Plutarch was born to a prominent family in the small town of Chaeronea, about east of Delphi, in the Greek region of Boeotia. His family was long established in the town; his father was named Autobulus and his grandfather was named Lamprias. His name is derived from Pluto (πλοῦτον), an epithet of Hades, and Archos (ἀρχός) meaning "Master", the whole name meaning something like "Whose master is Pluto". His brothers, Timon and Lamprias, are frequently mentioned in his essays and dialogues, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
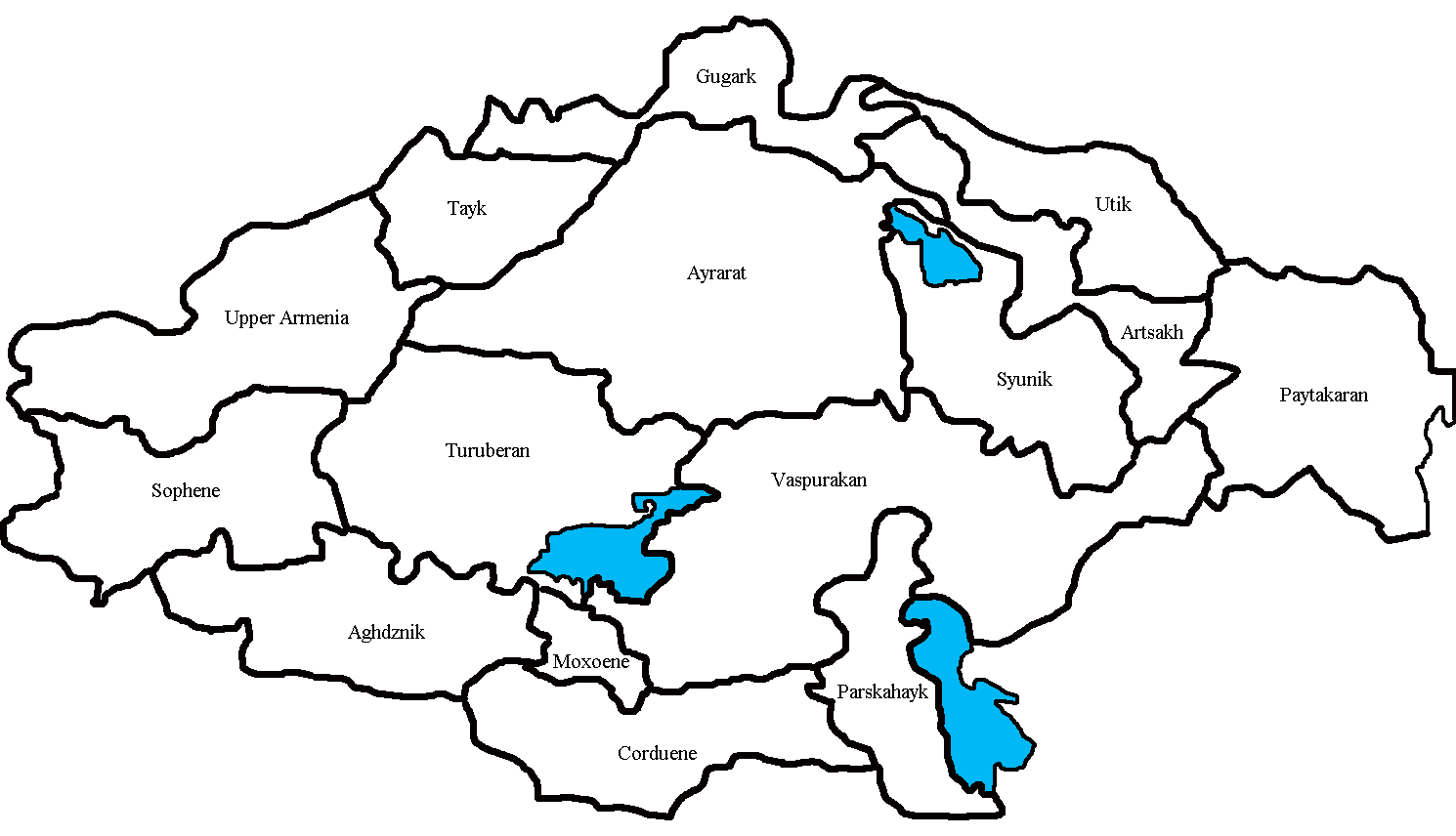
Sophene
Sophene ( hy, Ծոփք, translit=Tsopkʻ, grc, Σωφηνή, translit=Sōphēnē or hy, Չորրորդ Հայք, lit=Fourth Armenia) was a province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, located in the south-west of the kingdom, and of the Roman Empire. The region lies in what is now southeastern Turkey. The region that was to become Sophene was part of the kingdom of Ararat (Urartu) in the 8th-7th centuries BC. After unifying the region with his kingdom in the early 8th century BC, king Argishtis I of Urartu resettled many of its inhabitants in his newly built city of Erebuni (modern day Armenian capital Yerevan). Around 600 BC, Sophene became part of the newly emerged ancient Armenian Kingdom of the Orontids. This dynasty acted as satraps of Armenia first under the Median Empire, later under the Achaemenid Empire. After Alexander the Great's campaigns in 330s BC and the subsequent collapse of the Achaemenid Empire, Sophene remained part of the newly independent kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashtishat
Ashtishat (, ''Aštišat''; Western Armenian: ''Ashdishad'') is a locality and archaeological site in Muş Province of eastern Turkey. It is located near the village of Yücetepe, Muş at 38° 58' 20"N and 41° 27' 04" E on the Murat river east of Lake Van and north of the city of Muş. In antiquity the village was an important site of early Armenian Christianity and the ruins of several ancient church's and the monastery of Saint Daniel of Gop still occupy the town. The site also hosts the tombs of several early saints and patriotic leaders of the ancient Armenian kingdom.Ashdishad or the Tomb of Catholicos Saint Sahag - Union Internationale des Organisations Terre et Culture. History According to Armenian tradition, Ashtishat ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artashat (ancient City)
Artashat ( hy, Արտաշատ); Hellenized as Artaxata ( el, Ἀρτάξατα) and Artaxiasata ( grc, Ἀρταξιάσατα), was a large commercial city and the capital of ancient Armenia during the reign of king Artaxias I; the founder of the Artaxiad Dynasty of the ancient Kingdom of Armenia. The name of the city is derived from Iranian languages and means the "joy of Arta" (see also; '' -shat''). Founded by King Artaxias I in 176 BC, Artaxata served as the capital of the Kingdom of Armenia from 185 BC until 120 AD, and was known as the "Vostan Hayots" ("court/seal of the Armenians"). History Antiquity King Artashes I founded Artashat in 176 BC in the Vostan Hayots canton within the historical province of Ayrarat, at the point where Araks river was joined by Metsamor river during that ancient eras, near the heights of Khor Virap. The story of the foundation is given by the Armenian historian Movses Khorenatsi of the fifth century: "Artashes traveled to the location of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armavir, Armenia
Armavir ( hy, Արմավիր), is a town and urban municipal community located in the west of Armenia serving as the administrative centre of Armavir Province. It was founded in 1931 by the government of the Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic. As of the 2011 census, the population of the town is 29,319, declined from 46,900 reported at the 1989 census. Currently, the town has a population of 37,053 as per the 2019 official estimate. The town was known as Sardarabad before 1935, and Hoktemberyan from 1935 to 1995. Currently, Armavir is the seat of the Diocese of Armavir of the Armenian Apostolic Church. Etymology Founded in 1931 as Sardarabad, the town was known as Hoktemberyan (meaning the ''city of October'') between 1935 and 1995, named in honor of the October Revolution. In 1992, the town was named Armavir by the government of independent Armenia, after the nearby ancient city of Armavir, that was founded in the 8th century BC by King Argishti I of Urartu, and became the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erzincan
Erzincan (; ku, Erzîngan), historically Yerznka ( hy, Երզնկա), is the capital of Erzincan Province in Eastern Turkey. Nearby cities include Erzurum, Sivas, Tunceli, Bingöl, Elazığ, Malatya, Gümüşhane, Bayburt, and Giresun. The city is majority Sunni Turkish with a significant Alevi Kurdish minority. History Acilisene, the ancient city that is now Erzincan, was the site of the Peace of Acilisene by which in AD 387 Armenia was divided into two vassal states, a smaller one dependent on the Byzantine Empire and a larger one dependent on Persia. This is the name (Ἀκιλισηνή in Greek) by which it is called by Strabo in his ''Geography'', 11.4.14. The etymological origin of the word is disputed, but it is agreed that the city was once called Erez. For a while it was called Justinianopolis in honour of Emperor Justinian. In more recent Greek it has been called as Κελτζηνή (''Keltzene'') and Κελεζηνή (''Kelezene'')Raymond Janin, ''v. Celtzene ou Ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Iberia (antiquity)
In Greco-Roman geography, Iberia (Ancient Greek: ''Iberia''; la, Hiberia) was an exonym for the Georgian kingdom of Kartli ( ka, ქართლი), known after its core province, which during Classical Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages was a significant monarchy in the Caucasus, either as an independent state or as a dependent of larger empires, notably the Sassanid and Roman empires. Iberia, centered on present-day Eastern Georgia, was bordered by Colchis in the west, Caucasian Albania in the east and Armenia in the south. Its population, the Iberians, formed the nucleus of the Kartvelians (i.e. Georgians). Iberia, ruled by the Pharnavazid, Artaxiad, Arsacid and Chosroid royal dynasties, together with Colchis to its west, would form the nucleus of the unified medieval Kingdom of Georgia under the Bagrationi dynasty. In the 4th century, after the Christianization of Iberia by Saint Nino during the reign of King Mirian III, Christianity was made the state religion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caucasian Albania
Caucasian Albania is a modern exonym for a former state located in ancient times in the Caucasus: mostly in what is now Azerbaijan (where both of its capitals were located). The modern endonyms for the area are ''Aghwank'' and ''Aluank'', among the Udi people, who regard themselves as descended from the inhabitants of Caucasian Albania. However, its original endonym is unknown.Robert H. Hewsen. "Ethno-History and the Armenian Influence upon the Caucasian Albanians", in: Samuelian, Thomas J. (Ed.), ''Classical Armenian Culture. Influences and Creativity''. Chicago: 1982, pp. 27-40. Bosworth, Clifford E.br>Arran ''Encyclopædia Iranica''. The name Albania is derived from the Ancient Greek name and Latin .James Stuart Olson. An Ethnohistorical Dictionary of the Russian and Soviet Empires. The prefix "Caucasian" is used purely to avoid confusion with modern Albania of the Balkans, which has no known geographical or historical connections to Caucasian Albania. Little is known of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |









.jpg)