|
Anael
Haniel (, ''Ḥannīʾēl'', "God is my grace"; ''Ananiēl''; , '), also known as Hananel, Anael, Hanael or Aniel, is an angel in Jewish lore and angelology, and he is often included in lists as being one of the seven archangels. Haniel is generally associated with the planet Venus, and is the archangel of the sephirah Netzach. The name Haniel derives from the Hebrew ''Ḥēn'' (חֵן), meaning "grace, favour, charm" (qualities associated with Venus) + the suffix ''-ʾĒl,'' "God". It is equivalent to the Phoenician name Hannibal. Haniel is one of the archangels encrypted in the Sigillum Dei Aemeth of Dr. John Dee and Edward Kelley.Dee, John. Five Books of Mystery. edt. Joseph H. Peterson. Weiser. ISBN 1-57863-178-5 Gallery File:Anael como el regente de la Luna.jpg, Anael as the regent of the moon, Museo Soumaya Plaza Loreto, Mexico City. File:Haniel memorial stained glass, Mainside Protestant Chapel.jpg, Archangel Haniel, stained-glass window at the Main Protestant Chapel i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
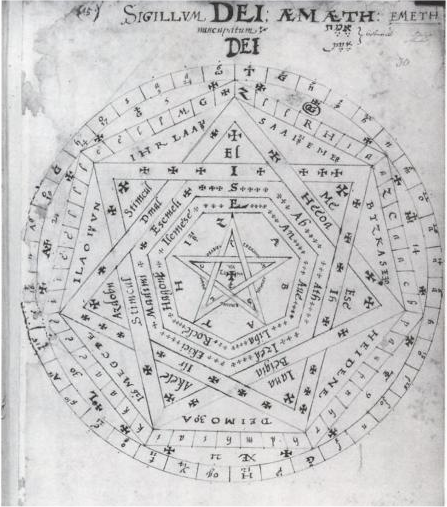
Sigillum Dei
The Sigillum Dei (seal of God, "Seal of Truth" or signum dei vivi, symbol of the ''Living God'', called by John Dee the Sigillum Dei Aemeth) is a magical diagram, composed of two circles, a pentagram, two heptagons, and one heptagram, and is labeled with the names of God and its angels. It is an angelic magic seal with the magical function that, according to one of the oldest sources ('' Liber Juratus''), allowed a destined intended magician to have the power to possess the Spirit of God and when activated can become the Living God; or The Lord God itself; amongst humanity and all creation itself, communicate with spirits as well as angels and archangels, control all elements, control every creature's holy spirit on the planet including the Spirit of God itself; all except for the Archangels, and to control light itself. The intended user also possesses the true benefic vision of God. Middle Ages Liber Juratus Probably the oldest known description and image of the ''Sigillum Dei' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Angels In Theology
This is a list of angels in religion, theology, astrology and magic, including both specific angels (e.g., Gabriel) and types of angels (e.g., seraphim A seraph ( ; pl.: ) is a Angelic being, celestial or heavenly being originating in Ancient Judaism. The term plays a role in subsequent Judaism, Islam and Christianity. Tradition places seraphim in the highest rank in Christian angelology and ...). List Groups Individual angels See also Notes References {{Angels in Abrahamic religions * Angels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Dee
John Dee (13 July 1527 – 1608 or 1609) was an English mathematician, astronomer, teacher, astrologer, occultist, and alchemist. He was the court astronomer for, and advisor to, Elizabeth I, and spent much of his time on alchemy, divination, and Hermetic philosophy. As an antiquarian, he had one of the largest libraries in England at the time. As a political advisor, he advocated the foundation of English colonies in the New World to form a "British Empire", a term he is credited with coining. Dee eventually left Elizabeth's service and went on a quest for additional knowledge in the deeper realms of the occult and supernatural. He aligned himself with several individuals who may have been charlatans, travelled through Europe, and was accused of spying for the English Crown. Upon his return to England, he found his home and library vandalised. He eventually returned to the Queen's service, but was turned away when she was succeeded by James I. He died in poverty in London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archangels In Christianity
Archangels () are the second lowest rank of angel in the Catholic hierarchy of angels, based on and put forward by Pseudo-Dionysius the Areopagite in the 5th or 6th century in his book ''De Coelesti Hierarchia'' (''On the Celestial Hierarchy''). The Bible itself uses the term “archangel” two times referring to the angel Michael only in the New Testament. The Bible does not mention a particular hierarchy of angels in any detail aside from this. The word is usually associated with the Abrahamic religions and many offshoots they are historically associated with. ''Archangel'' is derived from Greek (), with the Greek prefix meaning 'chief'. In Catholic theology, archangels constitute the second-lowest rank of angel; much of modernized imaging of Archangels as we have today likely stems from the etymology of their name, as well as their presentation in John Milton's ''Paradise Lost''. In many offshoots of Judaism, with the oldest text coming from Enoch 1, the highest ranking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Corps Base Camp Lejeune
Marine Corps Base Camp Lejeune ( or ) is a United States Armed Forces, United States military training facility in Jacksonville, North Carolina. Its of beaches make the base a major area for Amphibious warfare, amphibious assault training, and its location between two deep-water ports (Wilmington, North Carolina, Wilmington and Morehead City, North Carolina, Morehead City) allows for fast deployments. The main base is supplemented by six satellite facilities: Marine Corps Air Station New River, Camp Geiger, Stone Bay, Courthouse Bay, Camp Gilbert H. Johnson, Camp Johnson, and the Marine Corps Outlying Field Camp Davis, Greater Sandy Run Training Area. The Marine Corps port facility is in Beaufort, North Carolina, Beaufort, at the southern tip of Radio Island (between the NC State Port in Morehead City, and the marine science laboratories on Pivers Island in Beaufort). It is occupied only during military port operations. Facilities Camp Lejeune encompasses 156,000 acres, with 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museo Soumaya
The Museo Soumaya is a private museum in Mexico City and a non-profit cultural institution with two museum buildings in Mexico City — Plaza Carso and Plaza Loreto. It has over 66,000 works from 30 centuries of art including sculptures from Pre-Hispanic Mesoamerica, 19th- and 20th-century Mexican art and an extensive repertoire of works by European old masters and masters of modern western art such as Auguste Rodin, Salvador Dalí, Bartolomé Esteban Murillo and Tintoretto. It is called one of the most complete collections of its kind. The museum is named after Soumaya Domit, who died in 1999, and was the wife of the founder of the museum Carlos Slim. The museum received an attendance of 1,095,000 in 2013, making it the most visited art museum in Mexico and the 56th in the world that year. In October 2015, the museum welcomed its five millionth visitor. The museum was designed by Slim's son-in-law, Fernando Romero's practice, fr·ee. Collection The Museo Soumaya has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Kelley
Sir Edward Kelley or Kelly, also known as Edward Talbot (; 1 August 1555 – 1597/8), was an English Renaissance occultist and scryer. He is known for working with John Dee in his magical investigations. Besides the professed ability to see spirits or angels in a "shew-stone" or mirror, which John Dee so valued, Kelley also said that he possessed the secret of transmuting base metals into gold, a goal of alchemy, as well as the philosopher's stone itself. Legends began to surround Kelley shortly after his death. His flamboyant biography, his relationships with Queen Elizabeth I's royal magus Sir John Dee and Emperor Rudolf II, and his repute of having great alchemical skill and the ability to communicate with angels have all led to his relative notoriety among historians. Biography Birth and early career Much of Kelley's early life is obscure. He said he was descended from the family of Ui Maine in Ireland. He was born at Worcester on 1 August 1555, at 4 P.M. according ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archangel Haniel
Archangels () are the second lowest rank of angel in the Catholic hierarchy of angels, based on and put forward by Pseudo-Dionysius the Areopagite in the 5th or 6th century in his book ''De Coelesti Hierarchia'' (''On the Celestial Hierarchy''). The Bible itself uses the term “archangel” two times referring to the angel Michael only in the New Testament. The Bible does not mention a particular hierarchy of angels in any detail aside from this. The word is usually associated with the Abrahamic religions and many offshoots they are historically associated with. ''Archangel'' is derived from Greek (), with the Greek prefix meaning 'chief'. In Catholic theology, archangels constitute the second-lowest rank of angel; much of modernized imaging of Archangels as we have today likely stems from the etymology of their name, as well as their presentation in John Milton's ''Paradise Lost''. In many offshoots of Judaism, with the oldest text coming from Enoch 1, the highest ranking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angel
An angel is a spiritual (without a physical body), heavenly, or supernatural being, usually humanoid with bird-like wings, often depicted as a messenger or intermediary between God (the transcendent) and humanity (the profane) in various traditions like the Abrahamic religions. Other roles include protectors and guides for humans, such as guardian angels and servants of God. In Western belief-systems the term is often used to distinguish benevolent from malevolent intermediary beings. Emphasizing the distance between God and mankind, revelation-based belief-systems require angels to bridge the gap between the earthly and the transcendent realm. Angels play a lesser role in monistic belief-systems, since the gap is non-existent. However, angelic beings might be conceived as aid to achieve a proper relationship with the divine. Abrahamic religions describe angelic hierarchies, which vary by religion and sect. Some angels have specific names (such as Gabriel or Mich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hannibal (given Name)
Hannibal is a latinization (, ''Hanníbas'') of the Carthaginian masculine given name (), meaning "Baal is Gracious". Its continued use in later times and cultures ever since is caused mainly by the historical fame of the Carthaginian leader Hannibal, who commanded its forces during the Second Punic War. "Hannibal" may refer to: Carthaginians * Hannibal (247–183/182 BC), general who fought the Roman Republic in the Second Punic War * Hannibal Gisco (died 258 BC), military commander in the First Punic War * Hannibal Mago (died 406 BC), shofet (magistrate) of Carthage in 410 BC * Hannibal Monomachus, friend and staff officer of the Second Punic War general Hannibal * Hannibal the Rhodian, ship captain during the siege of Lilybaeum in the First Punic War * Hannibal (Mercenary War) (died 238 BC), general during the Mercenary War Others * Hannibal Mejbri (born 2003), Tunisian footballer * Hannibal Buress (born 1983), American comedian from Chicago * Hannibal Day (1804� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenicians
Phoenicians were an ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syrian coast. They developed a maritime civilization which expanded and contracted throughout history, with the core of their culture stretching from Arwad in modern Syria to Mount Carmel. The Phoenicians extended their cultural influence through trade and colonization throughout the Mediterranean, from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula, evidenced by thousands of Phoenician inscriptions. The Phoenicians directly succeeded the Bronze Age Canaanites, continuing their cultural traditions after the decline of most major Mediterranean basin cultures in the Late Bronze Age collapse and into the Iron Age without interruption. They called themselves Canaanites and referred to their land as Canaan, but the territory they occupied was notably smaller than that of Bronze Age Canaan. The name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |