|
Anabasis (plant)
''Anabasis'' is a genus of plants in the subfamily Salsoloideae of the family Amaranthaceae. It is distributed in southern Europe, North Africa, and Asia. Description The species of genus ''Anabasis'' are annual or perennial herbs or subshrubs. Their stems are fleshy and articulated, mostly glabrous with the exception of hairy tufts at the nodes, rarely with papillae-like trichomes or woolly. The opposite leaves may be reduced to small scales or normally developed. The inflorescences are elongated or condensed spikes. The bisexual flowers are sitting solitary or in groups of up to 4 in the axils of upper leaves (bracts), with 2 paired bracteoles. Flowers consist of 5 subequal membranous perianth segments, that are free nearly from base; 3-5 stamens without appendages; and an ovary with 2-3 thick and short stigmas. In fruit, prominent membranous wings develop on the back of the perianth segments, usually 2-3 of them larger than the others. Rarely, the perianth remains unwinge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anabasis Articulata
''Anabasis articulata'' is a plant of the genus ''Anabasis''. It a salt-tolerant xerophyte that is found in the Syrian desert. Bedouins often use the plant's ashes as a soap substitute. The plant is also known for its medical properties. Algerian traditional medicine practitioners use the plants leaves to make anti-diabetic decoction Decoction is a method of extraction by boiling herbal or plant material (which may include stems, roots, bark and rhizomes) to dissolve the chemicals of the material. It is the most common preparation method in various herbal-medicine systems. Dec .... References Amaranthaceae Flora of Syria Barilla plants {{Amaranthaceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stigma (botany)
The stigma () is the receptive tip of a carpel, or of several fused carpels, in the gynoecium of a flower. Description The stigma, together with the style and ovary (typically called the stigma-style-ovary system) comprises the pistil, which is part of the gynoecium or female reproductive organ of a plant. The stigma itself forms the distal portion of the style, or stylodia, and is composed of , the cells of which are receptive to pollen. These may be restricted to the apex of the style or, especially in wind pollinated species, cover a wide surface. The stigma receives pollen and it is on the stigma that the pollen grain germinates. Often sticky, the stigma is adapted in various ways to catch and trap pollen with various hairs, flaps, or sculpturings. The pollen may be captured from the air (wind-borne pollen, anemophily), from visiting insects or other animals ( biotic pollination), or in rare cases from surrounding water (hydrophily). Stigma can vary from long and sle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salsoleae
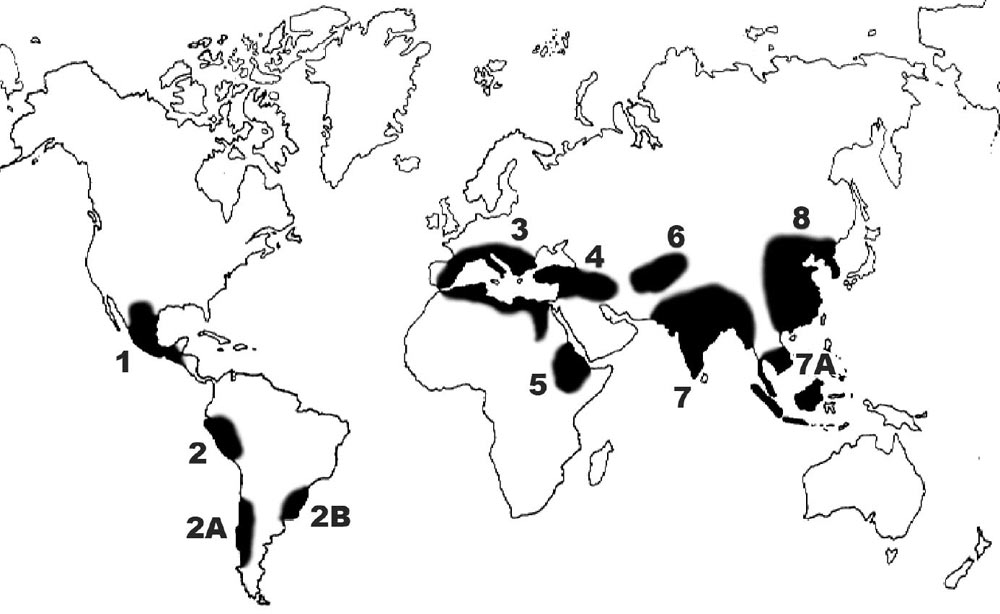
The Salsoloideae are a subfamily of the Amaranthaceae, formerly in family Chenopodiaceae. Description These are herbs, subshrubs, shrubs and some trees. Stems and leaves are often succulent. The ovary contains a spiral embryo. In most genera, scarious wings develop at the outside of the fruiting perianth, allowing for dispersal by the wind (anemochory). In tribe Caroxyleae, the stamens have vesiculose anther appendages, discolor with anthers, that probably play a role for insect pollination. In tribe Salsoleae the anther appendages are absent or small and inconspicuous. Distribution The area with most species (center of diversity) are the deserts and semideserts of Central-Asia and the Middle East. Distribution of the subfamily extends to the Mediterranean, to Middle-Europe, north and south Africa, and Australia, some species have also been introduced to America. Many species grow in dry habitats (xerophytes) or tolerate salty soils (halophytes), some are ruderals. Photos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribe (biology)
In biology, a tribe is a taxonomic rank above genus, but below family and subfamily. It is sometimes subdivided into subtribes. By convention, all taxonomic ranks from genus upwards are capitalized, including both tribe and subtribe. In zoology, the standard ending for the name of a zoological tribe is "-ini". Examples include the tribes Caprini (goat-antelopes), Hominini (hominins), Bombini (bumblebees), and Thunnini (tunas). The tribe Hominini is divided into subtribes by some scientists; subtribe Hominina then comprises "humans". The standard ending for the name of a zoological subtribe is "-ina". In botany, the standard ending for the name of a botanical tribe is "-eae". Examples include the tribes Acalypheae and Hyacintheae. The tribe Hyacintheae is divided into subtribes, including the subtribe Massoniinae. The standard ending for the name of a botanical subtribe is "-inae". In bacteriology, the form of tribe names is as in botany, e.g., Pseudomonadeae, based on the ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anabasis Aphylla
''Anabasis aphylla'' is a species of flowering plant in the family Amaranthaceae, native to the region surrounding the Caspian Sea, Central Asia, and Xinjiang and western Gansu provinces of China. A many-branched shrub usually found growing in alluvial fans and dune swales, it is sometimes planted to catch blowing soil and stabilize sand dunes. The alkaloid anabasine was named for this toxic species, from which it was first isolated by Orechoff and Menschikoff in the year 1931. Anabasine was widely used as an insecticide in the former Soviet Union The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ... until 1970.Ujváry, István, ''Pest Control Agents from Natural Products'' - Chapter 3 of Hayes' ''Handbook of Pesticide Toxicology (Third Edition)'', ed. Robert Krieger, pub. Academic Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Plantarum
' (Latin for "The Species of Plants") is a book by Carl Linnaeus, originally published in 1753, which lists every species of plant known at the time, classified into genera. It is the first work to consistently apply binomial names and was the starting point for the naming of plants. Publication ' was published on 1 May 1753 by Laurentius Salvius in Stockholm, in two volumes. A second edition was published in 1762–1763, and a third edition in 1764, although this "scarcely differed" from the second. Further editions were published after Linnaeus' death in 1778, under the direction of Karl Ludwig Willdenow, the director of the Berlin Botanical Garden; the fifth edition (1800) was published in four volumes. Importance ' was the first botanical work to consistently apply the binomial nomenclature system of naming to any large group of organisms (Linnaeus' tenth edition of ' would apply the same technique to animals for the first time in 1758). Prior to this work, a plant spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Von Linné
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to collect and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semidesert
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-arid climates, depending on variables such as temperature, and they give rise to different biomes. Defining attributes of semi-arid climates A more precise definition is given by the Köppen climate classification, which treats steppe climates (''BSk'' and ''BSh'') as intermediates between desert climates (BW) and humid climates (A, C, D) in ecological characteristics and agricultural potential. Semi-arid climates tend to support short, thorny or scrubby vegetation and are usually dominated by either grasses or shrubs as it usually can't support forests. To determine if a location has a semi-arid climate, the precipitation threshold must first be determined. The method used to find the precipitation threshold (in millimeters): *multiply by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes. Steppe biomes may include: * the montane grasslands and shrublands biome * the temperate grasslands, savannas and shrublands biome A steppe may be semi-arid or covered with grass or with shrubs or with both, depending on the season and latitude. The term " steppe climate" denotes the climate encountered in regions too dry to support a forest but not dry enough to be a desert. Steppe soils are typically of the chernozem type. Steppes are usually characterized by a semi-arid or continental climate. Extremes can be recorded in the summer of up to and in winter, . Besides this major seasonal difference, fluctuations between day and night are also very great. In both the highlands of Mongolia and northern Nevada, can be reached during the day with sub-freezing readings at night. Mid-latitude steppes feature hot summers and cold wint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Center Of Diversity
A center of origin is a geographical area where a group of organisms, either domesticated or wild, first developed its distinctive properties. They are also considered centers of diversity. Centers of origin were first identified in 1924 by Nikolai Vavilov. Plants Locating the origin of crop plants is basic to plant breeding. This allows one to locate wild relatives, related species, and new genes (especially dominant genes, which may provide resistance to diseases). Knowledge of the origins of crop plants is important in order to avoid genetic erosion, the loss of germplasm due to the loss of ecotypes and landraces, loss of habitat (such as rainforests), and increased urbanization. Germplasm preservation is accomplished through gene banks (largely seed collections but now frozen stem sections) and preservation of natural habitats (especially in centers of origin). Vavilov centers A Vavilov Center (of Diversity) is a region of the world. First indicated by Nikolai Vavilov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former Soviet Union, Soviet republics of the Soviet Union, republics of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan, which are colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as the countries all have names ending with the Persian language, Persian suffix "-stan", meaning "land of". The current geographical location of Central Asia was formerly part of the historic region of Turkestan, Turkistan, also known as Turan. In the pre-Islamic and early Islamic eras ( and earlier) Central Asia was inhabited predominantly by Iranian peoples, populated by Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian-speaking Bactrians, Sogdians, Khwarezmian language, Chorasmians and the semi-nomadic Scythians and Dahae. After expansion by Turkic peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwest Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian highlands, Armenian Highlands, the Levant, the island of Cyprus, the Sinai Peninsula, and partly the Caucasus, Caucasus Region (Transcaucasia). The region is considered to be separated from Africa by the Isthmus of Suez in Egypt, and separated from Europe by the waterways of the Turkish Straits and the watershed of the Greater Caucasus. Central Asia lies to its northeast, while South Asia lies to its east. Twelve seas surround the region (clockwise): the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, the Persian Gulf, the Gulf of Oman, the Arabian Sea, the Gulf of Aden, the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, the Gulf of Suez, and the Mediterranean Sea. Western Asia cove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.png)
