|
Anabar Plateau
The Anabar Plateau ( rus, Анабарское плато) is a mountain plateau in Krasnoyarsk Krai and the Sakha Republic (Yakutia), Siberia, Russia. The plateau is in a latitude dominated by permafrost. The permafrost thickness under the Anabar Plateau reaches . Geography The Anabar Plateau is located north of the Arctic Circle in northeastern Krasnoyarsk Krai and northwestern Sakha Republic, SSE of the Taymyr Depression, the central part of the North Siberian Lowland. It is located north of the Vilyuy Plateau and is the northernmost feature of the Central Siberian Plateau, to which it is connected in the southeast. To the southwest it runs into the higher Putorana Mountains, the border between both not being well-defined. The average height of the plateau surface is around . There are slightly higher tableland type elevations running across the plateau area, mostly in a roughly east to west direction. The highest point is a high unnamed summit. The Big Kuonamka, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kotuykan River
The Kotuykan () is a river in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. It is a right hand tributary of the Kotuy. The Kotuykan is long, and the area of its basin is . It freezes up in late September and breaks up in late May or early June. Course The Kotuykan has its source in the highest part of the Anabar Plateau. It is a fast-flowing river that flows westwards in a deep valley, often surrounded by picturesque cliffs of marine sediments exposed by erosion that are 1.5 billion years old. The Kotuykan joins the right bank of the Kotuy as the latter flows from the south across the western side of the Anabar Plateau, from its mouth and from the mouth of the Khatanga in the Laptev Sea. Google Earth Its main tributaries are the long Ilya (Илья) and the long Dyogdyo (Дёгдё). See also *List of rivers of Russia Russia can be divided into a European Russia, European and an North Asia, Asian part. The dividing line is generally considered to be the Ural Mountains. The European part is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Siberian Lowland
The North Siberian Lowland (russian: Северо-Сибирская низменность; sah, Хотугу Сибиир намтала), also known as Taymyr Lowland (Таймырская низменность), is a plain with a relatively flat relief separating the Byrranga Mountains of the Taymyr Peninsula in the north from the Central Siberian Plateau in the south.John Kimble (ed.), ''Cryosols: Permafrost-Affected Soils'' To the southeast of the Olenyok basin the lowland merges with the Central Yakutian Lowland. The territory of the lowland is one of the Great Russian Regions. Administratively it is mostly part of the Krasnoyarsk Krai, with a small section in the Sakha Republic (Yakutia). The main towns are Dudinka, Norilsk and Khatanga.Google Earth Geography The North Siberian Lowland lies between the lower reaches of the Yenisey and Olenyok rivers in Krasnoyarsk Krai and Yakutia. It is 1,400 km long and up to 600 km wide. This lowland plain features flat-topp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lena River
The Lena (russian: Ле́на, ; evn, Елюенэ, ''Eljune''; sah, Өлүөнэ, ''Ölüöne''; bua, Зүлхэ, ''Zülkhe''; mn, Зүлгэ, ''Zülge'') is the easternmost of the three great Siberian rivers that flow into the Arctic Ocean (the other two being the Ob and the Yenisey). Permafrost underlies most of the catchment, 77% of which is continuous. It is long, and has a drainage basin of . The Lena is the eleventh-longest river in the world, and the longest river entirely within Russia. Course Originating at an elevation of at its source in the Baikal Mountains south of the Central Siberian Plateau, west of Lake Baikal, the Lena flows northeast across the Lena-Angara Plateau, being joined by the Kirenga, Vitim and Olyokma. From Yakutsk it enters the Central Yakutian Lowland and flows north until joined by its right-hand tributary the Aldan and its most important left-hand tributary, the Vilyuy. After that, it bends westward and northward, flowing between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
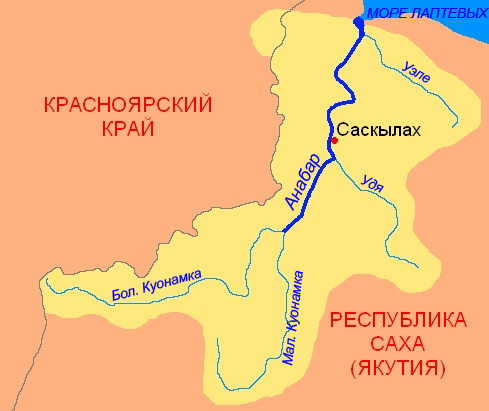
Anabar (river)
The Anabar ( rus, Анабар, r=Anabar, in its upper course: Большая Куонамка ''Bolshaya Kuonamka''; sah, Анаабыр, translit=Anaabyr) is a river in Sakha, Russia. It is long ( counting the long Bolshaya Kuonamka ("Big Kuonamka") stretch of its upper course) and has a drainage basin of . Course The Anabar is formed at the confluence of the Malaya Kuonamka and Bolshaya Kuonamka at the edge of the North Siberian Lowland. The length of the Anabar proper is . The two rivers forming it have their sources in the northeastern part of the Anabar Plateau, part of the Central Siberian Plateau. There are many lakes in its basin. The Anabar basin is located between rivers Khatanga and Olenyok. The mouth of the river is in the Anabar Bay. Its mean annual discharge is , concentrated heavily in early summer when the ice that covers the river for most of the year thaws. The Uele river flows into the Laptev Sea close to the mouth of the Anabar, but it is not its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaya Kuonamka
The Malaya Kuonamka (russian: Малая Куонамка; sah, Кыра Куонамка) is a river in Yakutia (Sakha Republic), Russia. It is a right tributary of the Anabar with a length of . Its drainage basin area is . The river flows north of the Arctic Circle, in the northern limits of the Central Siberian Plateau and the North Siberian Lowland. The area is very cold and desolate, devoid of settlements. The Kuonamka Formation is a Cambrian large igneous province in the northeastern Siberian platform. Course The Malaya Kuonamka "Little Kuonamka" is the second largest tributary of the Anabar. The river has its source in an elevated swamp at an altitude of in the eastern side of the Anabar Plateau. Together with the long Bolshaya Kuonamka "Big Kuonamka" to the west, it is one of the two rivers that form the Anabar at their confluence. In their last stretch both rivers flow roughly northwards. Finally they meet where the Anabar river proper begins, from its mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khatanga River
The Khatanga (russian: Хатанга) is a river in Krasnoyarsk Krai in Russia. The river is navigable. The river port of Khatanga is located on the river. Course It begins at the confluence of the rivers Kotuy and Kheta. The Khatanga is long ( including its headwater Kotuy); the area of its basin is . It flows into the Khatanga Gulf of the , forming an |
Kyuyonelekeen
The Kyuyonelekeen (russian: Кюёнэлэкээн; sah, Күөнэлэкээн), also spelled as ''Kyuyonelekyan'' and ''Kyuenelekyan'', is a river in Yakutia (Sakha Republic) and Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. It is the third longest tributary of the Arga-Sala, of the Olenyok basin, and has a length of and a drainage basin area of . The river and its tributaries flow across uninhabited areas. The nearest settlement is Olenyok village, Olenyoksky District, located to the east of its mouth. Course The Kyuyonelekeen is a left tributary of the Arga-Sala. Its sources are in the southern end of the Anabar Plateau, Central Siberian Plateau, south of the basin of the Bolshaya Kuonamka, part of the Anabar basin. The river flows roughly southwards across mountainous taiga, to the west of the Kengeede. In mid course it turns eastwards and, after a stretch, southeastwards. Finally it joins the left bank of the Arga-Sala river from its mouth in the Olenyok. Google Earth The river is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kengeede
The Kengeede (russian: Кэнгээдэ; sah, Күҥгэдэ), also spelled as ''Kengede'', ''Kengyade'' or ''Kende'', is a river in Yakutia (Sakha Republic) and Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. It is the second longest tributary of the Arga-Sala, of the Olenyok basin, and has a length of and a drainage basin area of . The river basin is a lonely, desolate area devoid of settlements. Course The Kengeede is a left tributary of the Arga-Sala. Its sources are in the southern end of the Anabar Plateau, south of the basin of the Bolshaya Kuonamka. The river flows roughly southwards , to the east of the Kyuyonelekeen. It heads across mountainous taiga areas with rapids and riffles in numerous sections. In its upper course it bends eastwards, then for a stretch northeastwards, and then again southwards, heading in that direction for the remainder of its course. Finally it joins the left bank of the Arga-Sala river from its mouth, not far upstream of Olenyok village, Olenyoksky District, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olenyok River
The Olenyok (russian: Оленёк, sometimes spelled ''Оленек'', ''Olenek''; sah, Өлөөн, Ölöön) is a major river in northern Siberian Russia, west of the lower Lena and east of the Anabar. It is long, of which around is navigable. Average water discharge is . The Olenyok is known for its abundance in fish. It is frozen for over eight months every year and the climate in its area is harsh because of the direct influence of the Arctic. History In 1633 Ivan Rebrov reached the Olenyok from the Lena delta and built a fort. In 1642–44 Rebrov and Fedot Alekseyev Popov reached the river but were driven out by the natives. Pioneering Russian Arctic explorer Vasili Pronchishchev and his wife Tatiana (Maria) died of scurvy in the area of the river in September 1736, while mapping the coasts of the Laptev Sea. After their deaths, husband and wife were interred at Ust-Olenyok, near the mouth of the Olenyok. Their tomb was moved after the bodies were exhumed in 1999. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kotuy River
The Kotuy () is a river in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. It is one of the two rivers that form the Khatanga; the other one being the Kheta. The Kotuy is long, and the area of its basin is . It freezes up in late September or early October and breaks up in late May or early June. Course The Kotuy has its source in the Putorana Mountains and flows north, cutting from the south across the western side of the Anabar Plateau. After leaving the plateau area it flows northwestwards until the confluence with the Kheta to form the Khatanga, a little distance upstream from Khatanga town. Google Earth Its main tributaries are the Moyero, the Tukalan, the Eriyechka, the Changada, and the Kotuykan, which has its source in the highest part of the Anabar Plateau. Lake Yessey is part of the river basin. See also *List of rivers of Russia Russia can be divided into a European Russia, European and an North Asia, Asian part. The dividing line is generally considered to be the Ural Mountains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popigay River
The Popigay (russian: Попигай) is a river in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. It s a right tributary of the Khatanga. The length of the river is . The area of its drainage basin is . The river has its source in the Anabar Plateau. It freezes up in October and breaks up in June. Its main tributaries are the Rassokha and Fomich. The river passes by the Popigay crater, about northeast of . See also * |
Anabar River
The Anabar ( rus, Анабар, r=Anabar, in its upper course: Большая Куонамка ''Bolshaya Kuonamka''; sah, Анаабыр, translit=Anaabyr) is a river in Sakha, Russia. It is long ( counting the long Bolshaya Kuonamka ("Big Kuonamka") stretch of its upper course) and has a drainage basin of . Course The Anabar is formed at the confluence of the Malaya Kuonamka and Bolshaya Kuonamka at the edge of the North Siberian Lowland. The length of the Anabar proper is . The two rivers forming it have their sources in the northeastern part of the Anabar Plateau, part of the Central Siberian Plateau. There are many lakes in its basin. The Anabar basin is located between rivers Khatanga and Olenyok. The mouth of the river is in the Anabar Bay. Its mean annual discharge is , concentrated heavily in early summer when the ice that covers the river for most of the year thaws. The Uele river flows into the Laptev Sea close to the mouth of the Anabar, but it is not its tribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)