|
Amyzon (city)
Amyzon ( grc, Ἀμυζών) in Caria (now Mazin, Aydın Province between the villages of Akmescit and Gaffarlar, in Aegean Turkey) was an ancient city 30 km south of modern Koçarlı. History The city was in the Athenian alliance in 405BC Under the Seleucids, Amyzon was one of the cities in the Chrysaorian League of Carian cities that lasted at least until 203 BC, when Antiochus III confirmed the privileges of Amyzon. The League had a form of reciprocal citizenship whereby a citizen of a member city was entitled to certain rights and privileges in any other member city. The city was dismissed by Strabo as a mere ''peripolion'' ('suburb' or 'township') of Alabanda; Amyzon was mentioned by Pliny, Ptolemy and Hierocles. In the wars among the successors of Alexander, in the 3rd century BC, the city allied with the less immediately threatening power, first with the Ptolemies, then with the Seleucids. In the second city it concluded an alliance with Heracleia under Latmos. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionians, Ionian and Dorians, Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joined the Carian population in forming Greek-dominated states there. Carians were described by Herodotus as being of Minoan civilization, Minoan descent,''The Histories'', Book I Section 171. while he reports that the Carians themselves maintained that they were Anatolian mainlanders intensely engaged in seafaring and were akin to the Mysians and the Lydians. The Carians spoke Carian language, Carian, a native Anatolian language closely related to Luwian language, Luwian. Also closely associated with the Carians were the Leleges, which could be an earlier name for Carians. Municipalities of Caria Cramer's detailed catalog of Carian towns in classical Greece is based entirely on ancient sources. The multiple names of towns and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucid
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire originally founded by Alexander the Great. After receiving the Mesopotamian region of Babylonia in 321 BC, Seleucus I began expanding his dominions to include the Near Eastern territories that encompass modern-day Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Syria, all of which had been under Macedonian control after the fall of the former Persian Achaemenid Empire. At the Seleucid Empire's height, it had consisted of territory that had covered Anatolia, Persia, the Levant, and what are now modern Iraq, Kuwait, Afghanistan, and parts of Turkmenistan. The Seleucid Empire was a major center of Hellenistic culture. Greek customs and language were privileged; the wide variet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Robert (historian)
Louis Robert (Laurière, 15 February 1904 - Paris, 31 May 1985) was a professor of Greek history and Epigraphy at the Collège de France, and author of many volumes and articles on Greek epigraphy (of all periods, from the archaic period to Late Antiquity), numismatics, and the historical geography of Greek lands. Robert studied at the École Normale Supérieure from 1924 to 1927, was a member of the École française d'Athènes from 1927 to 1932, and taught at the École pratique des hautes études (IVth section) in Paris from 1932. He was made full professor at the Collège de France in 1939, where he remained until his retirement in 1974. He continued to publish on Greek epigraphy with his wife, Jeanne Robert, as co-author, as he had done since their marriage and until his death in 1985. Selected bibliography * ''Villes d' Asie Mineure'', 1935 (second edition, with an ample postface, 1962) * ''Collection Froehner, Inscriptions grecques'', 1936. * ''Études Anatoliennes, Sur d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idrieus
Idrieus, or Hidrieus ( grc, Ἱδριεύς, Hidrieús; died 344 BC) was a ruler of Caria as a Satrap under the Achaemenid Empire. Alongside his sister and wife Ada, he enjoyed the status of king or dynast by virtue of the powerful position he inherited from his predecessors of the House of Hecatomnus (the Hecatomnids). Biography Idrieus was the second son of Hecatomnus, and was married to his sister Ada. Alongside Ada, he succeeded to the throne on the death of his sister Artemisia II of Caria in 351 BC. Shortly after his accession he was required by the Persian king, Artaxerxes III Ochus, to provide arms and troops for the capture of Cyprus, a request with which he readily complied. He equipped a fleet of 40 triremes and assembled an army of 8000 mercenary troops. These were despatched for use against Cyprus under the command of Evagoras and the Athenian general Phocion. This is the only recorded event preserved from his reign. However; it can be inferred from Isocrates th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hecatomnids
The Hecatomnid dynasty or Hecatomnids were the rulers of Caria and surrounding areas BCE. The Hecatomnids were satraps (governors) under the Achaemenid Empire, although they ruled with considerable autonomy, and established a hereditary dynasty. The first satrap of the dynasty was Hecatomnus. He was appointed as the first Carian satrap of Caria in the late 390s BCE. Previously, Caria had been governed as part of Lydia, by the satrap Tissaphernes based in Sardis. Tissaphernes was executed by Tithraustes on the orders of Artaxerxes II Memnon in 395 BCE. If Hecatomnus did not become satrap immediately upon the death of Tissaphernes, he was in office by 392 BCE, when he made war on Evagoras of Salamis on the orders of Artaxerxes II Memnon. Hecatomnus therefore became satrap of Caria BCE. He was previously one of many minor dynasts in Caria. The Hecatomnid dynasty's seat was originally Mylasa, in central Caria. Hecatomnus' father, Hyssaldomus, was also an independent dynast based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
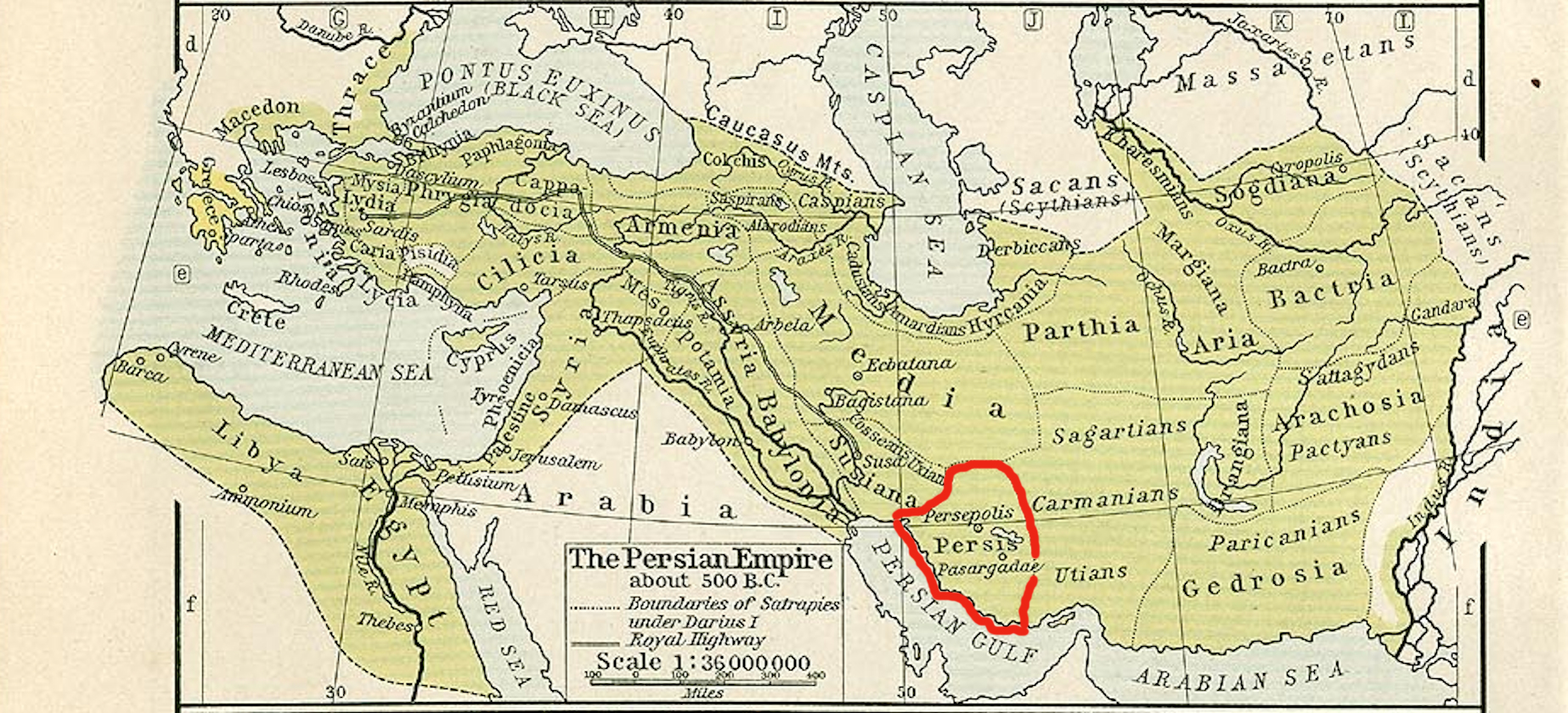
Bagadates I
Baydad (also spelled Bagdates), was a dynast (''frataraka'') of Persis from 164 to 146 BC. Background Since the end of the 3rd or the beginning of the 2nd century BCE, Persis had been ruled by local dynasts subject to the Seleucid Empire. They held the ancient Persian title of ''frataraka'' ("leader, governor, forerunner"), which is also attested in the Achaemenid-era. The Achaemenid Empire, which had a century earlier ruled most of the Near East, originated from the region. The ''frataraka'' themselves emphasized their close affiliation with the prominent Achaemenid King of Kings, and their court was probably at the former Achaemenid capital of Persepolis, where they financed construction projects on and near the Achaemenid plateau. The ''frataraka'' had traditionally been regarded as priestly dynasts or advocates of religious (and political) opposition to Hellenism, however, this is no longer considered the case. Chronology of the ''frataraka'' The traditional view of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artemis
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Artemis (; grc-gre, Ἄρτεμις) is the goddess of the hunt, the wilderness, wild animals, nature, vegetation, childbirth, care of children, and chastity. She was heavily identified with Selene, the Moon, and Hecate, another Moon goddess, and was thus regarded as one of the most prominent lunar deities in mythology, alongside the aforementioned two.Smiths.v. Artemis/ref> She would often roam the forests of Greece, attended by her large entourage, mostly made up of nymphs, some mortals, and hunters. The goddess Diana is her Roman equivalent. In Greek tradition, Artemis is the daughter of the sky god and king of gods Zeus and Leto, and the twin sister of Apollo. In most accounts, the twins are the products of an extramarital liaison. For this, Zeus' wife Hera forbade Leto from giving birth anywhere on land. Only the island of Delos gave refuge to Leto, allowing her to give birth to her children. Usually, Artemis i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doric Order
The Doric order was one of the three orders of ancient Greek and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of columns. Originating in the western Doric region of Greece, it is the earliest and, in its essence, the simplest of the orders, though still with complex details in the entablature above. The Greek Doric column was fluted or smooth-surfaced, and had no base, dropping straight into the stylobate or platform on which the temple or other building stood. The capital was a simple circular form, with some mouldings, under a square cushion that is very wide in early versions, but later more restrained. Above a plain architrave, the complexity comes in the frieze, where the two features originally unique to the Doric, the triglyph and gutta, are skeuomorphic memories of the beams and retaining pegs of the wooden constructions that preceded stone Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt the following year. The Ancient Greek word ''Hellas'' (, ''Hellás'') was gradually recognized as the name for Greece, from which the word ''Hellenistic'' was derived. "Hellenistic" is distinguished from "Hellenic" in that the latter refers to Greece itself, while the former encompasses all ancient territories under Greek influence, in particular the East after the conquests of Alexander the Great. After the Macedonian invasion of the Achaemenid Empire in 330 BC and its disintegration shortly after, the Hellenistic kingdoms were established throughout south-west Asia ( Seleucid Empire, Kingdom of Pergamon), north-east Africa ( Ptolemaic Kingdom) and South Asia ( Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, Indo-Gree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mint (coin)
A mint is an industrial facility which manufactures coins that can be used as currency. The history of mints correlates closely with the history of coins. In the beginning, hammered coinage or cast coinage were the chief means of coin minting, with resulting production runs numbering as little as the hundreds or thousands. In modern mints, coin dies are manufactured in large numbers and planchets are made into milled coins by the billions. With the mass production of currency, the production cost is weighed when minting coins. For example, it costs the United States Mint much less than 25 cents to make a quarter (a 25 cent coin), and the difference in production cost and face value (called seigniorage) helps fund the minting body. Conversely, a U.S. penny ($0.01) cost $0.015 to make in 2016. History The first minted coins The earliest metallic money did not consist of coins, but of unminted metal in the form of rings and other ornaments or of weapons, which were used for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)