|
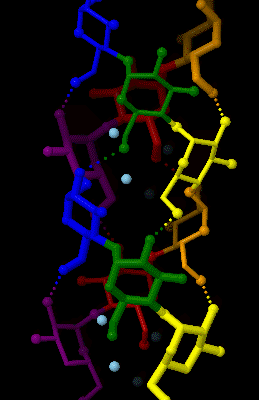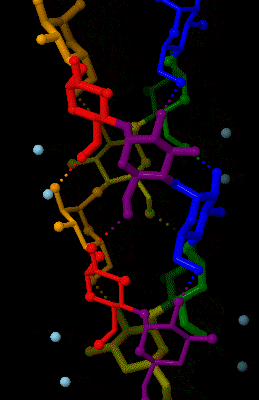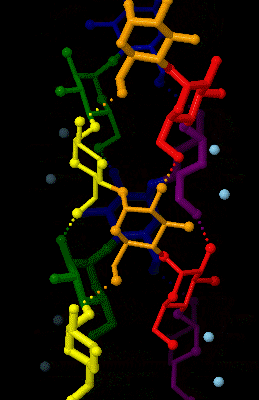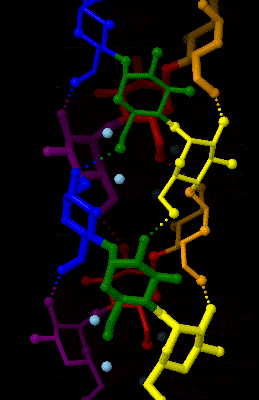
Amylose 3Dprojection
Amylose is a polysaccharide made of α-D-glucose units, bonded to each other through α(1→4) glycosidic bonds. It is one of the two components of starch, making up approximately 20–30%. Because of its tightly packed helical structure, amylose is more resistant to digestion than other starch molecules and is therefore an important form of resistant starch. Structure Amylose is made up of α(1→4) bound glucose molecules. The carbon atoms on glucose are numbered, starting at the aldehyde (C=O) carbon, so, in amylose, the 1-carbon on one glucose molecule is linked to the 4-carbon on the next glucose molecule (α(1→4) bonds). The structural formula of amylose is pictured at right. The number of repeated glucose subunits (n) is usually in the range of 300 to 3000, but can be many thousands. There are three main forms of amylose chains can take. It can exist in a disordered amorphous conformation or two different helical forms. It can bind with itself in a double helix (A or B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysaccharide
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with water (hydrolysis) using amylase enzymes as catalyst, which produces constituent sugars (monosaccharides, or oligosaccharides). They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Examples include storage polysaccharides such as starch, glycogen and galactogen and structural polysaccharides such as cellulose and chitin. Polysaccharides are often quite heterogeneous, containing slight modifications of the repeating unit. Depending on the structure, these macromolecules can have distinct properties from their monosaccharide building blocks. They may be amorphous or even insoluble in water. When all the monosaccharides in a polysaccharide are the same type, the polysaccharide is called a homopolysaccharide or homoglycan, but when more t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maltotriose
Maltotriose is a trisaccharide (three-part sugar) consisting of three glucose molecules linked with α-1,4 glycosidic bonds. It is most commonly produced by the digestive enzyme alpha-amylase (a common enzyme in human saliva) on amylose in starch. The creation of both maltotriose and maltose during this process is due to the random manner in which alpha amylase hydrolyses α-1,4 glycosidic bonds. It is the shortest chain oligosaccharide that can be classified as maltodextrin Maltodextrin is a polysaccharide that is used as a food ingredient. It is produced from vegetable starch by partial hydrolysis and is usually found as a white hygroscopic spray-dried powder. Maltodextrin is easily digestible, being absorbed as r .... References Trisaccharides {{Organic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorimeter (chemistry)
A colorimeter is a device used in Colorimetry (chemical method), colorimetry that measures the absorbance of particular wavelengths of light by a specific Solution (chemistry), solution. It is commonly used to determine the concentration of a known solute in a given solution by the application of the Beer–Lambert law, which states that the concentration of a solute is proportional to the absorbance. Construction The essential parts of a colorimeter are: * a light source (often an ordinary low-voltage filament lamp); * an adjustable aperture; * a set of colored Filter (optics), filters; * a cuvette to hold the working solution; * a detector (usually a photoresistor) to measure the transmitted light; * a meter to display the output from the detector. In addition, there may be: * a voltage regulator, to protect the instrument from fluctuations in Mains power systems, mains voltage; * a second light path, cuvette and detector. This enables comparison between the working solut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine Test
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a violet gas at . The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811 and was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, after the Ancient Greek 'violet-coloured'. Iodine occurs in many oxidation states, including iodide (I−), iodate (), and the various periodate anions. It is the least abundant of the stable halogens, being the sixty-first most abundant element. As the heaviest essential mineral nutrient, iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency affects about two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disabilities. The dominant producers of iodine today are Chile and Japan. Due to its high atomic number and ease of attachment to organic compounds, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelengths
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The inverse of the wavelength is called the spatial frequency. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek letter ''lambda'' (λ). The term ''wavelength'' is also sometimes applied to modulated waves, and to the sinusoidal envelopes of modulated waves or waves formed by interference of several sinusoids. Assuming a sinusoidal wave moving at a fixed wave speed, wavelength is inversely proportional to frequency of the wave: waves with higher frequencies have shorter wavelengths, and lower frequencies have longer wavelengths. Wavelength depends on the medium (for example, vacuum, air, or water) that a wave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iodine
Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a semi-lustrous, non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at , and boils to a violet gas at . The element was discovered by the French chemist Bernard Courtois in 1811 and was named two years later by Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac, after the Ancient Greek 'violet-coloured'. Iodine occurs in many oxidation states, including iodide (I−), iodate (), and the various periodate anions. It is the least abundant of the stable halogens, being the sixty-first most abundant element. As the heaviest essential mineral nutrient, iodine is required for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine deficiency affects about two billion people and is the leading preventable cause of intellectual disabilities. The dominant producers of iodine today are Chile and Japan. Due to its high atomic number and ease of attachment to organic compound ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xanthan Gum
Xanthan gum () is a polysaccharide with many industrial uses, including as a common food additive. It is an effective thickening agent, emulsifier, and stabilizer that prevents ingredients from separating. It can be produced from simple sugars using a fermentation process and derives its name from the species of bacteria used, ''Xanthomonas campestris''. History Xanthan gum was discovered by Allene Rosalind Jeanes and her research team at the United States Department of Agriculture, and brought into commercial production by CP Kelco under the trade name Kelzan in the early 1960s. It was approved for use in foods in 1968 and is accepted as a safe food additive in the USA, Canada, European countries, and many other countries, with E number E415, and CAS number 11138-66-2. Xanthan gum derives its name from the species of bacteria used during the fermentation process, ''Xanthomonas campestris''. Uses Xanthan gum, 1%, can produce a significant increase in the viscosity of a liquid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alginate
Alginic acid, also called algin, is a naturally occurring, edible polysaccharide found in brown algae. It is hydrophilic and forms a viscous gum when hydrated. With metals such as sodium and calcium, its salts are known as alginates. Its colour ranges from white to yellowish-brown. It is sold in filamentous, granular, or powdered forms. It is a significant component of the biofilms produced by the bacterium ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', a major pathogen found in the lungs of some people who have cystic fibrosis. The biofilm and ''P. aeruginosa'' have a high resistance to antibiotics, but susceptible to inhibition by macrophages. Structure Alginic acid is a linear copolymer with homopolymeric blocks of (1→4)-linked β-D- mannuronate (M) and α-L- guluronate (G) residues, respectively, covalently linked together in different sequences or blocks. The monomers may appear in homopolymeric blocks of consecutive G-residues (G-blocks), consecutive M-residues (M-blocks) or alterna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
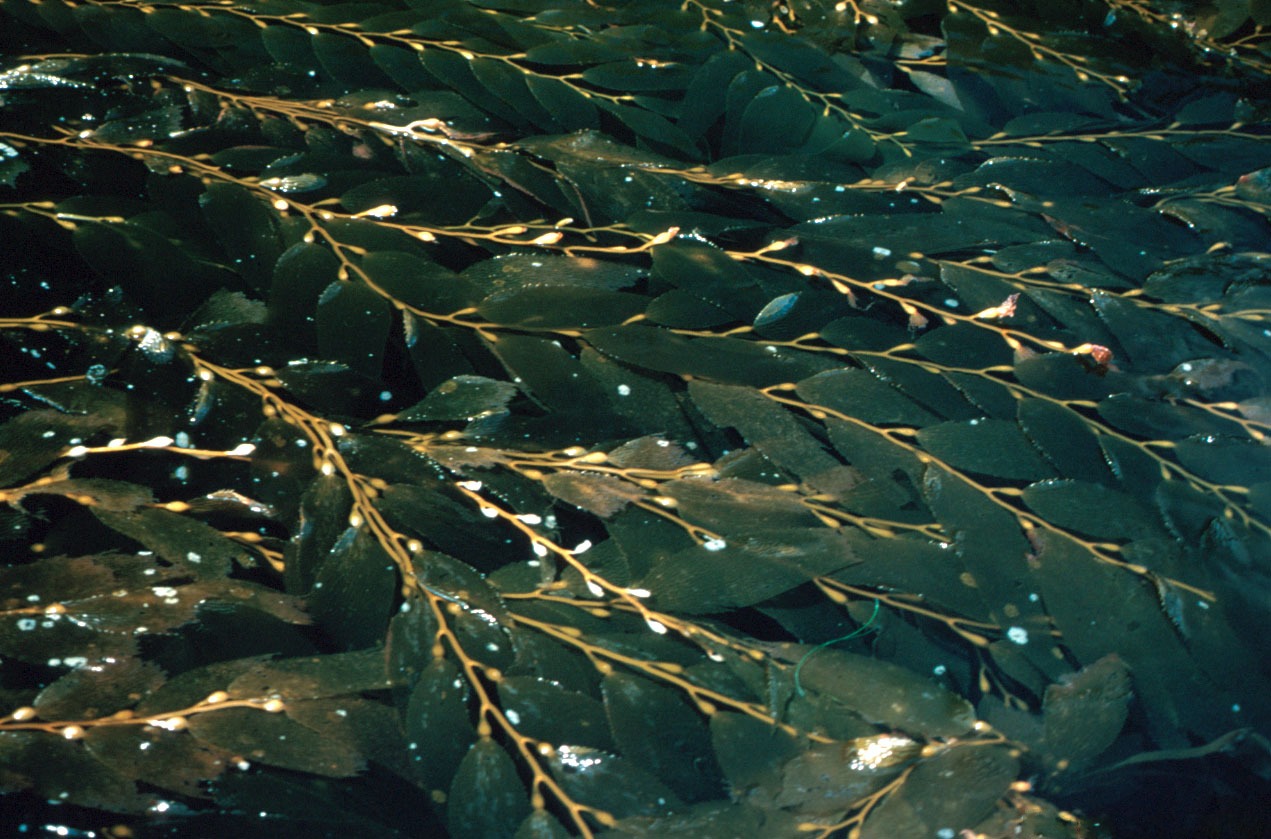
Carrageenan
Carrageenans or carrageenins ( ; ) are a family of natural linear sulfated polysaccharides that are extracted from red edible seaweeds. Carrageenans are widely used in the food industry, for their gelling, thickening, and stabilizing properties. Their main application is in dairy and meat products, due to their strong binding to food proteins. In recent years, carrageenans have emerged as a promising candidate in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine applications as they resemble native glycosaminoglycans (GAGs). They have been mainly used for tissue engineering, wound coverage and drug delivery. Carrageenans contain 15-40% ester-sulfate content, which makes them anionic polysaccharides. They can be mainly categorized into three different classes based on their sulfate content. Kappa-carrageenan has one sulfate group per disaccharide, iota-carrageenan has two, and lambda-carrageenan has three. The most well-known and most important red seaweed used for manufacturing the hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Viscosity quantifies the internal frictional force between adjacent layers of fluid that are in relative motion. For instance, when a viscous fluid is forced through a tube, it flows more quickly near the tube's axis than near its walls. Experiments show that some stress (such as a pressure difference between the two ends of the tube) is needed to sustain the flow. This is because a force is required to overcome the friction between the layers of the fluid which are in relative motion. For a tube with a constant rate of flow, the strength of the compensating force is proportional to the fluid's viscosity. In general, viscosity depends on a fluid's state, such as its temperature, pressure, and rate of deformation. However, the dependence on some of these properties is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syneresis (chemistry)
Syneresis (also spelled 'synæresis' or 'synaeresis'), in chemistry, is the extraction or expulsion of a liquid from a gel, such as when serum drains from a contracting clot of blood. Another example of syneresis is the collection of whey on the surface of yogurt. Syneresis can also be observed when the amount of diluent in a swollen polymer exceeds the solubility limit as the temperature changes. A household example of this is the counterintuitive expulsion of water from dry gelatin when the temperature increases. Syneresis has also been proposed as the mechanism of formation for the amorphous silicate composing the frustule of diatoms. Examples In the processing of dairy milk, for example during cheese making, syneresis is the formation of the curd due to the sudden removal of the hydrophilic macropeptides, which causes an imbalance in intermolecular forces. Bonds between hydrophobic sites start to develop and are enforced by calcium bonds, which form as the water molecules ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatic Compounds
Aromatic compounds, also known as "mono- and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons", are organic compounds containing one or more aromatic rings. The parent member of aromatic compounds is benzene. The word "aromatic" originates from the past grouping of molecules based on smell, before their general chemical properties are understood. The current definition of aromatic compounds does not have any relation with their smell. Heteroarenes are closely related, since at least one carbon atom of CH group is replaced by one of the heteroatoms oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur. Examples of non-benzene compounds with aromatic properties are furan, a heterocyclic compound with a five-membered ring that includes a single oxygen atom, and pyridine, a heterocyclic compound with a six-membered ring containing one nitrogen atom. Hydrocarbons without an aromatic ring are called aliphatic. Benzene ring model Benzene, C6H6, is the least complex aromatic hydrocarbon, and it was the first one named as suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |