|
Amstrad CPC 464
The CPC 464 is the first personal home computer built by Amstrad in 1984. It was one of the bestselling and best produced microcomputers, with more than 2 million units sold in Europe. The British microcomputer boom had already peaked before Amstrad announced the CPC 464 (which stood for Colour Personal Computer) which they then released a mere 9 months later. Amstrad was known for cheap hi-fi products but had not broken into the home computer market until the CPC 464. Their consumer electronic sales were starting to plateau and owner and founder Alan Sugar stated "We needed to move on and find another sector or product to bring us back to profit growth". Work started on the Amstrad home computer in 1983 with engineer Ivor Spital who concluded that Amstrad should enter the home computer market, offering a product that integrated low-cost hardware to be sold at an affordable "impulse-purchase price". Spital wanted to offer a device that would not commandeer the family TV but in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amstrad CPC
The Amstrad CPC (short for ''Colour Personal Computer'') is a series of 8-bit home computers produced by Amstrad between 1984 and 1990. It was designed to compete in the mid-1980s home computer market dominated by the Commodore 64 and the Sinclair ZX Spectrum, where it successfully established itself primarily in the United Kingdom, France, Spain, and the German-speaking parts of Europe. The series spawned a total of six distinct models: The ''CPC464'', ''CPC664'', and ''CPC6128'' were highly successful competitors in the European home computer market. The later ''464plus'' and ''6128plus'', intended to prolong the system's lifecycle with hardware updates, were considerably less successful, as was the attempt to repackage the ''plus'' hardware into a game console as the ''GX4000''. The CPC models' hardware is based on the Zilog Z80A CPU, complemented with either 64 or 128 KB of RAM. Their computer-in-a-keyboard design prominently features an integrated storage device, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcomputer
A microcomputer is a small, relatively inexpensive computer having a central processing unit (CPU) made out of a microprocessor. The computer also includes memory and input/output (I/O) circuitry together mounted on a printed circuit board (PCB). Microcomputers became popular in the 1970s and 1980s with the advent of increasingly powerful microprocessors. The predecessors to these computers, mainframes and minicomputers, were comparatively much larger and more expensive (though indeed present-day mainframes such as the IBM System z machines use one or more custom microprocessors as their CPUs). Many microcomputers (when equipped with a keyboard and screen for input and output) are also personal computers (in the generic sense). An early use of the term ''personal computer'' in 1962 predates microprocessor-based designs. ''(See "Personal Computer: Computers at Companies" reference below)''. A ''microcomputer'' used as an embedded control system may have no human-readable input ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tape Drive
A tape drive is a data storage device that reads and writes data on a magnetic tape. Magnetic tape data storage is typically used for offline, archival data storage. Tape media generally has a favorable unit cost and a long archival stability. A tape drive provides sequential access storage, unlike a hard disk drive, which provides direct access storage. A disk drive can move to any position on the disk in a few milliseconds, but a tape drive must physically wind tape between reels to read any one particular piece of data. As a result, tape drives have very large average access times. However, tape drives can stream data very quickly off a tape when the required position has been reached. For example, Linear Tape-Open (LTO) supports continuous data transfer rates of up to 360 MB/s, a rate comparable to hard disk drives. Design Magnetic tape drives with capacities of less than one megabyte were first used for data storage on mainframe computers in the 1950s. , capaci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of processor time, mass storage, printing, and other resources. For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computer from cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers. The dominant general-purpose personal computer operating system is Microsoft Windows with a market share of around 74.99%. macOS by Apple Inc. is in second place (14.84%), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMSDOS
AMSDOS is a disk operating system for the 8-bit Amstrad CPC Computer (and various clones). The name is a contraction of Amstrad Disk Operating System. AMSDOS first appeared in 1984 on the CPC 464, with added 3 inch disk drive, and then on the CPC 664 and CPC 6128. Relatively fast and efficient for its time, AMSDOS was quicker and more effective than most of its contemporaries. AMSDOS was provided built into ROM (either supplied with the external disk drive or in the machine ROM, depending on model) and was accessible through the built-in Locomotive BASIC as well as through firmware routines. Its main function was to map the cassette access routines (which were built into every CPC model) through to a disk drive. This enabled the majority of cassette-based programs to work with a disk drive with no modification. AMSDOS was able to support up to two connected disk drives. Commands AMDOS extends the AMSTRAD BASIC by the addition of a number of external commands which are identif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple II
The Apple II (stylized as ) is an 8-bit home computer and one of the world's first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products. It was designed primarily by Steve Wozniak; Jerry Manock developed the design of Apple II's foam-molded plastic case, Rod Holt developed the switching power supply, while Steve Jobs's role in the design of the computer was limited to overseeing Jerry Manock's work on the plastic case. It was introduced by Jobs and Wozniak at the 1977 West Coast Computer Faire, and marks Apple's first launch of a personal computer aimed at a consumer market—branded toward American households rather than businessmen or computer hobbyists. ''Byte'' magazine referred to the Apple II, Commodore PET 2001, and TRS-80 as the "1977 Trinity". As the Apple II had the defining feature of being able to display color graphics, the Apple logo was redesigned to have a spectrum of colors. The Apple II is the first model in the Apple II series, followed by Apple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
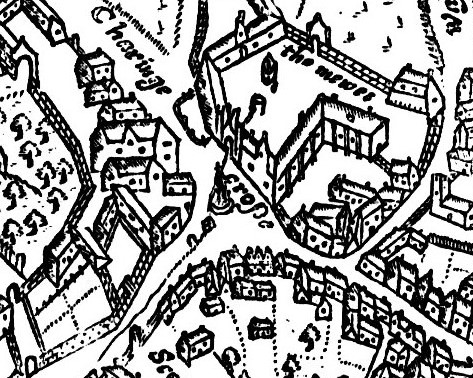
Trafalgar Square
Trafalgar Square ( ) is a public square in the City of Westminster, Central London, laid out in the early 19th century around the area formerly known as Charing Cross. At its centre is a high column bearing a statue of Admiral Nelson commemorating the victory at the Battle of Trafalgar. The battle of 21 October 1805, established the British navy's dominance at sea in the Napoleonic Wars over the fleets of France and Spain. The site around Trafalgar Square had been a significant landmark since the 1200s. For centuries, distances measured from Charing Cross have served as location markers. The site of the present square formerly contained the elaborately designed, enclosed courtyard of the King's Mews. After George IV moved the mews to Buckingham Palace, the area was redeveloped by John Nash, but progress was slow after his death, and the square did not open until 1844. The Nelson's Column at its centre is guarded by four lion statues. A number of commemorative statues and sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Sugar
Alan Michael Sugar, Baron Sugar (born 24 March 1947) is a British business magnate, media personality, author, politician and political adviser. In 1968, he started what would later become his largest business venture, consumer electronics company Amstrad. In 2007, he sold his remaining interest in the company in a deal to BSkyB for £125m. Sugar was the chairman and part-owner of Tottenham Hotspur F.C., Tottenham Hotspur from 1991 to 2001, selling his remaining stake in the club in 2007 as well, for £25m. He is also known for being the host and "Boss" for the BBC reality competition series ''The Apprentice (British TV series), The Apprentice'', which has been broadcast every year, with the exception of 2020, since 2005. He also assumed the role for ''The Celebrity Apprentice Australia'' for Australia's Nine Network in 2021. According to the Sunday Times Rich List 2015, ''Sunday Times'' Rich List, Sugar became a billionaire in 2015. In 2021, his fortune was estimated at £1.2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amstrad
Amstrad was a British electronics company, founded in 1968 by Alan Sugar at the age of 21. The name is a contraction of Alan Michael Sugar Trading. It was first listed on the London Stock Exchange in April 1980. During the late 1980s, Amstrad had a substantial share of the PC market in the UK. Amstrad was once a FTSE 100 Index constituent, but since 2007 has been wholly owned by Sky UK. , Amstrad's main business was manufacturing Sky UK interactive boxes. In 2010, Sky integrated Amstrad's satellite division as part of Sky so they could make their own set-top boxes in-house. The company had offices in Kings Road, Brentwood, Essex. History 1960s and 1970s Amstrad (also known as AMSTrad) was founded in 1968 by Alan Sugar at the age of 21, the name of the original company being AMS Trading (Amstrad) Limited, derived from its founder's initials (Alan Michael Sugar). Amstrad entered the market in the field of consumer electronics. During the 1970s they were at the forefront ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or technician. Unlike large, costly minicomputers and mainframes, time-sharing by many people at the same time is not used with personal computers. Primarily in the late 1970s and 1980s, the term home computer was also used. Institutional or corporate computer owners in the 1960s had to write their own programs to do any useful work with the machines. While personal computer users may develop their own applications, usually these systems run commercial software, free-of-charge software ("freeware"), which is most often proprietary, or free and open-source software, which is provided in "ready-to-run", or binary, form. Software for personal computers is typically developed and distributed independently from the hardware or operating system ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |