|
Amratian
The Amratian culture, also called Naqada I, was an archaeological culture of prehistoric Upper Egypt. It lasted approximately from 4000 to 3500 BC. Overview The Amratian culture is named after the archaeological site of el-Amra, located around south of Badari in Upper Egypt. El-Amra was the first site where this culture group was found without being mingled with the later Gerzeh culture (Naqada II). However, this period is better attested at the Nagada site, thus it also is referred to as the Naqada I culture. Black-topped pottery continued to be produced, but white cross-line pottery, a type which has been decorated with close parallel white lines being crossed by another set of close parallel white lines, begins to be produced during this time. The Amratian falls between S.D. 30 and 39 in Flinders Petrie's sequence dating system. The Amratians possessed slaves and constructed rowboats of bundled papyrus in which they could sail the Nile. Trade between the Amratian culture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Egypt
Prehistoric Egypt and Predynastic Egypt span the period from the earliest human settlement to the beginning of the Early Dynastic Period around 3100 BC, starting with the first Pharaoh, Narmer for some Egyptologists, Hor-Aha for others, with the name Menes also possibly used for one of these kings. At the end of prehistory, "Predynastic Egypt" is traditionally defined as the period from the final part of the Neolithic period beginning c. 6000 BC to the end of the Naqada III period c. 3000 BC. The dates of the Predynastic period were first defined before widespread archaeological excavation of Egypt took place, and recent finds indicating very gradual Predynastic development have led to controversy over when exactly the Predynastic period ended. Thus, various terms such as " Protodynastic period", "Zero Dynasty" or "Dynasty 0" are used to name the part of the period which might be characterized as Predynastic by some and Early Dynastic by others. The Predynastic period is genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
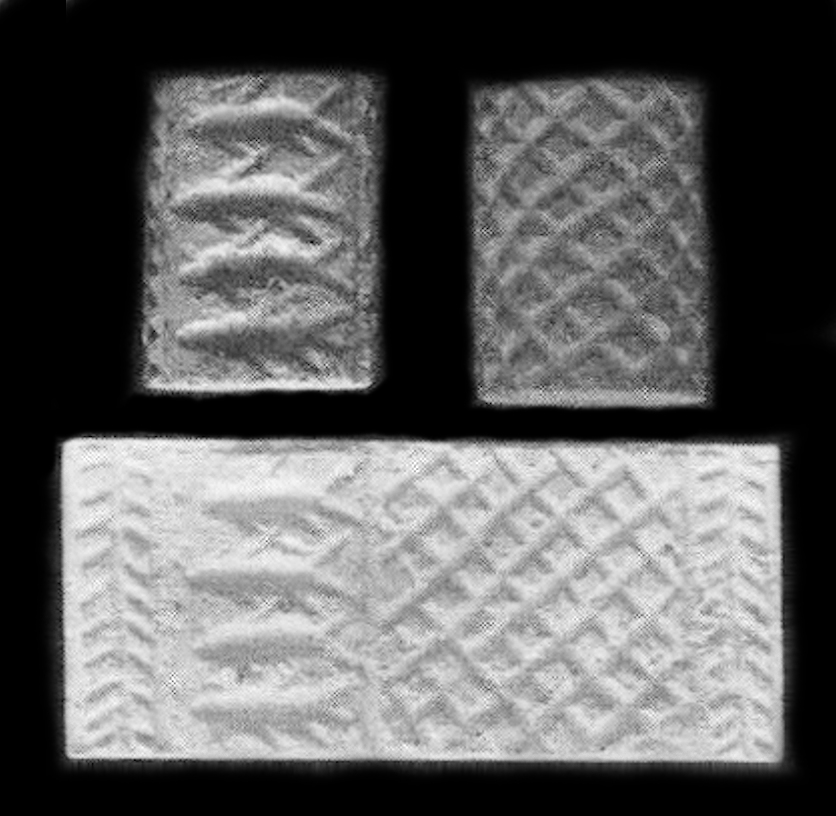
Naqada II
The Gerzeh culture, also called Naqada II, refers to the archaeological stage at Gerzeh (also Girza or Jirzah), a prehistoric Egyptian cemetery located along the west bank of the Nile. The necropolis is named after el-Girzeh, the nearby contemporary town in Egypt. Gerzeh is situated only several miles due east of the oasis of Faiyum. The Gerzeh culture is a material culture identified by archaeologists. It is the second of three phases of the prehistoric Naqada cultures and so is also known as Naqada II. The Gerzeh culture was preceded by the Amratian culture ("Naqada I") and followed by the Naqada III ("protodynastic" or "Semainian culture"). Historical context Sources differ on dating, some saying use of the culture distinguishes itself from the Amratian and begins circa 3500 BC lasting through circa 3200 BC. Accordingly, some authorities place the onset of the Gerzeh coincident with the Amratian or Badari cultures, i.e. c.3800 BC to 3650 BC even thoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerzeh Culture
The Gerzeh culture, also called Naqada II, refers to the archaeological stage at Gerzeh (also Girza or Jirzah), a prehistoric Egyptian cemetery located along the west bank of the Nile. The necropolis is named after el-Girzeh, the nearby contemporary town in Egypt. Gerzeh is situated only several miles due east of the oasis of Faiyum. The Gerzeh culture is a material culture identified by archaeologists. It is the second of three phases of the prehistoric Naqada cultures and so is also known as Naqada II. The Gerzeh culture was preceded by the Amratian culture ("Naqada I") and followed by the Naqada III ("protodynastic" or "Semainian culture"). Historical context Sources differ on dating, some saying use of the culture distinguishes itself from the Amratian and begins circa 3500 BC lasting through circa 3200 BC. Accordingly, some authorities place the onset of the Gerzeh coincident with the Amratian or Badari cultures, i.e. c.3800 BC to 3650 BC even thoug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tasian Culture
The Tasian culture is possibly one of the oldest-known Predynastic culture in Upper Egypt, which evolved around 4500 BC. It is named for the burials found at Deir Tasa, a site on the east bank of the Nile located between Asyut and Akhmim. There is no general agreement about the proposed "Tasian culture", and some scholars since Baumgartel in 1955 have suggested it is a part of the Badarian culture, rather than a separate entity. The Tasian culture group is notable for producing the earliest black-topped pottery, a type of red and brown pottery, which has been painted black on its top and interior. This pottery is vital to the dating of the various predynastic Egyptian civilizations. Since all dates for the Predynastic period are tenuous at best, Flinders Petrie developed a system called Sequence Dating through which the relative date, if not the absolute date, of any given Predynastic site can be ascertained by examining the handles on pottery. As the Predynastic period in anc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merimde Culture
The Merimde culture (also Merimde Beni-Salame or Benisalam) ( ar, مرمدة بني سلامة) was a Neolithic culture in the West Nile Delta in Lower Egypt, which corresponds in its later phase to the Faiyum A culture and the Badari culture in Predynastic Egypt. It is estimated that the culture evolved between 4800 and 4300 BC. Merimde also refers to the archaeological site of the same name. Archaeological work The culture was concentrated around Merimde Beni Salama, the main settlement site, located in the West delta of the Nile in Lower Egypt 45 km northwest of Cairo. The site was discovered by German archaeologist Hermann Junker, who excavated 6,400 m2 of the site during his West Nile Delta expedition in 1928. Early on, the settlement had been considered to be ca. 25 hectares, but recent research expanded this to at least 40 hectares. Later excavations in the 1970s performed by the Egyptian Antiquities Organization and the German Institute of Archaeology led to the es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El-Amrah, Egypt
El-Amrah is a site about south of Badari, Upper Egypt. Archaeological discoveries in 1901 at El-Amrah, were the basis of what is now known as the Amratian culture, a Naqada I culture of predynastic Upper Egypt Upper Egypt ( ar, صعيد مصر ', shortened to , , locally: ; ) is the southern portion of Egypt and is composed of the lands on both sides of the Nile that extend upriver from Lower Egypt in the north to Nubia in the south. In ancient E ..., that lasted from 4400 BC to 3500 BC.Shaw, Ian, ed. (2000). The Oxford History of Ancient Egypt. Oxford University Press. p. 479. File:Model cattle, El-Amra, Naqada I, British Museum EA 35506.jpg, Model cattle, El-Amra, Naqada I, British Museum EA 35506 File:Pre-Dynastic model house, El-Amra, Naqada IIC until 3200 BCE, British Museum EA35505.jpg, Pre-Dynastic model house, El-Amra, Naqada IIC until 3200 BCE, British Museum EA35505 References {{Authority control Neolithic cultures of Africa Predynastic Egypt 4t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmetic Palette
Cosmetic palettes are archaeological Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, originally used in predynastic Egypt, predynastic ancient Egypt, Egypt to grind and apply ingredients for facial or body cosmetics. The decorative palettes of the late 4th millennium BC, 4th millennium BCE appear to have lost this function and became commemorative, ornamental, and possibly ceremonial. They were made almost exclusively out of siltstone with a few exceptions. The siltstone originated from quarries in the Wadi Hammamat. Many of the palettes were found at Hierakonpolis, a centre of power in Predynastic Egypt, pre-dynastic Upper Egypt. After the unification of the country, the palettes ceased to be included in tomb assemblages. Notable palettes Notable decorative palettes are: * The Cosmetic palette in the form of a Nile tortoise * The Narmer Palette, often thought to depict the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the pharaoh Narmer, Egyptian Museum, Cairo * Libyan Palette, Egyptian Museum, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Egypt
Upper Egypt ( ar, صعيد مصر ', shortened to , , locally: ; ) is the southern portion of Egypt and is composed of the lands on both sides of the Nile that extend upriver from Lower Egypt in the north to Nubia in the south. In ancient Egypt, Upper Egypt was known as ''tꜣ šmꜣw'', literally "the Land of Reeds" or "the Sedgeland". It is believed to have been united by the rulers of the supposed Thinite Confederacy who absorbed their rival city states during the Naqada III period (c. 3200–3000 BC), and its subsequent unification with Lower Egypt ushered in the Early Dynastic period. Upper and Lower Egypt became intertwined in the symbolism of pharaonic sovereignty such as the Pschent double crown. Upper Egypt remained as a historical region even after the classical period. Geography Upper Egypt is between the Cataracts of the Nile beyond modern-day Aswan, downriver (northward) to the area of El-Ayait, which places modern-day Cairo in Lower Egypt. The northern (d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagada
Naqada (Egyptian Arabic: ; Coptic language: ; Ancient Greek: ) is a town on the west bank of the Nile in Qena Governorate, Egypt, situated ca. 20 km north of Luxor. It includes the villages of Tukh, Khatara, Danfiq, and Zawayda. According to 1960 census, it is one of the most uninhabited areas and had only 3,000 inhabitants, mostly of Christian faith who preserved elements of the Coptic language up until the 1930s. Archaeology Naqada stands near the site of a prehistoric Egyptian necropolis: The town was the centre of the cult of Set and large tombs were built there 3500 BCE. The large quantity of remains from Naqada have enabled the dating of the entire archeological period throughout Egypt and environs, hence the town name Naqada is used for the pre-dynastic Naqada culture 4400–3000 BCE. Other Naqada culture archeological sites include el Badari, the Gerzeh culture, and Nekhen. In Popular Culture In the Stargate franchise, alien civilizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal in a pure form. Chemically, gold is a transition metal and a group 11 element. It is one of the least reactive chemical elements and is solid under standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental ( native state), as nuggets or grains, in rocks, veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to most acids, though it does dissolve in aqua regia (a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid), forming a soluble tetrachloroaurate anion. Gold is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adobe
Adobe ( ; ) is a building material made from earth and organic materials. is Spanish for ''mudbrick''. In some English-speaking regions of Spanish heritage, such as the Southwestern United States, the term is used to refer to any kind of earthen construction, or various architectural styles like Pueblo Revival or Territorial Revival. Most adobe buildings are similar in appearance to cob and rammed earth buildings. Adobe is among the earliest building materials, and is used throughout the world. Adobe architecture has been dated to before 5,100 B.C. Description Adobe bricks are rectangular prisms small enough that they can quickly air dry individually without cracking. They can be subsequently assembled, with the application of adobe mud to bond the individual bricks into a structure. There is no standard size, with substantial variations over the years and in different regions. In some areas a popular size measured weighing about ; in other contexts the size is weighi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_1.jpg)