|
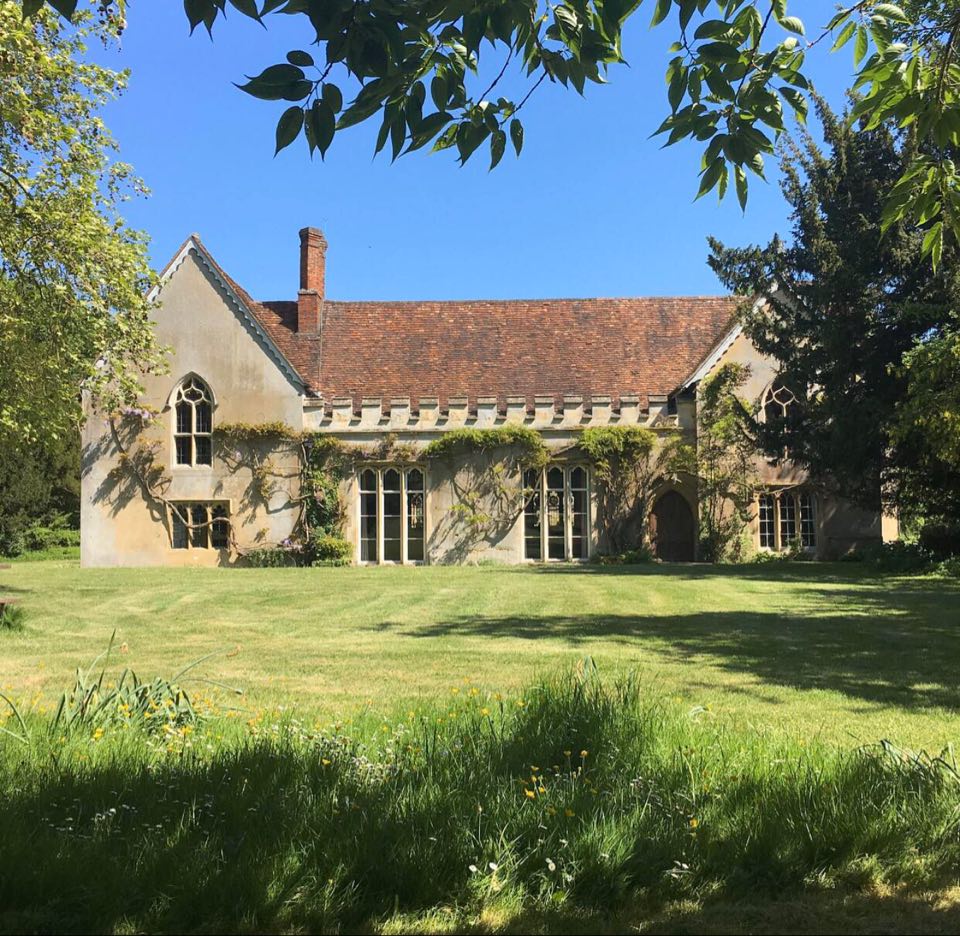
Ampton Hall In The Sunlight - Geograph
Ampton is a village and civil parish in the West Suffolk (district), West Suffolk District of Suffolk, England, about five miles north of Bury St Edmunds. According to Eilert Ekwall the meaning of the village name is 'Amma's homestead'. According to the 2001 census the parish had a population of 63, including Little Livermere and Timworth, increasing to 171 at the 2011 Census. The parish is grouped with Little Livermere and Timworth to form a parish meeting. Ampton currently has 13 listed structures within it, 12 of them Grade II listed and SS Peter & Paul's church being Grade I listed. At the church hang four bells, with the heaviest weighing 8-1 cwt and dating from 1405.Dove's Guide Retrieved 2012-03-21. Most of the village was designated as a Conservation area (United Kingdom), cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Livermere
Little Livermere is a village and civil parish in England situated about north of Bury St Edmunds, in an area of Suffolk known as the Breckland. The population at the 2011 Census is included in the civil parish of Ampton. In 1688 the Rector, James Paston, published a 39 page pamphlet supporting the repeal of the penal laws. The village was almost entirely demolished in the 18th century when a park and mere were created in the grounds of the stately home, Livermere Hall, which was itself destroyed in 1923. Livermere Hall is thought to be the setting M.R. James had in mind for Castringham Hall in his ghost story " The Ash-tree", published in '' Ghost Stories of an Antiquary'' in 1904. James was the son of the Rector of nearby Great Livermere Great Livermere is a village and civil parish in the West Suffolk district of Suffolk in eastern England. It is located around four miles north-east of the borough's largest town Bury St Edmunds. Great Livermere also has a village ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Gazetteer Of England And Wales
The ''Imperial Gazetteer of England and Wales'' is a substantial topographical dictionary first published between 1870 and 1872, edited by the Reverend John Marius Wilson. It contains a detailed description of England and Wales. Its six volumes have a brief article on each county, city, borough, civil parish, and diocese, describing their political and physical features and naming the principal people of each place. The publishers were A. Fullarton and Co., of London & Edinburgh. The work is a companion to Wilson's ''Imperial Gazetteer of Scotland'', published in parts between 1854 and 1857. The text of the Imperial Gazetteer is available online in two forms, as images you pay for on the Ancestry web site,Gazetteers at ukgenealogy.co.uk (accessed 4 November 2007) and as freely accessible searchable text on '' |
Sheriff Of Suffolk
This is a list of Sheriffs and High Sheriffs of Suffolk. The Sheriff is the oldest secular office under the Crown and is appointed annually (in March) by the Crown. The Sheriff was originally the principal law enforcement officer in the county and presided at the Assizes and other important county meetings. Most of the responsibilities associated with the post have been transferred elsewhere or are now defunct, so that its functions are now largely ceremonial. There was a single Sheriff serving the two counties of Norfolk and Suffolk until 1576. On 1 April 1974, under the provisions of the Local Government Act 1972, the title of Sheriff of Suffolk was retitled High Sheriff of Suffolk. Sheriff Pre-17th century 17th century 18th century 19th century 20th century High Sheriff 20th century 21st century See also High Sheriff of Norfolk and Suffolk References British History Online-List of Sheriffs for Suffolk {{DEFAULTSORT:High Sheriff Of Suffolk Suff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roundhead
Roundheads were the supporters of the Parliament of England during the English Civil War (1642–1651). Also known as Parliamentarians, they fought against King Charles I of England and his supporters, known as the Cavaliers or Royalists, who claimed rule by absolute monarchy and the principle of the divine right of kings. The goal of the Roundheads was to give to Parliament the supreme control over executive administration of the country/kingdom. Beliefs Most Roundheads sought constitutional monarchy in place of the absolute monarchy sought by Charles; however, at the end of the English Civil War in 1649, public antipathy towards the king was high enough to allow republican leaders such as Oliver Cromwell to abolish the monarchy completely and establish the Commonwealth of England. The Roundhead commander-in-chief of the first Civil War, Thomas Fairfax, remained a supporter of constitutional monarchy, as did many other Roundhead leaders such as Edward Montagu, 2nd Earl of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National School (England And Wales)
A National school was a school founded in 19th century England and Wales by the National Society for Promoting Religious Education. These schools provided elementary education, in accordance with the teaching of the Church of England, to the children of the poor. Together with the less numerous British schools of the British and Foreign School Society, they provided the first near-universal system of elementary education in England and Wales. The schools were eventually absorbed into the state system, either as fully state-run schools or as faith schools funded by the state. History Prior to 1800, education for poorer children was limited to isolated charity schools. In 1808 the Royal Lancastrian Society (later the British and Foreign School Society) was created to promote schools using the Monitorial System of Joseph Lancaster. The National Society was set up in 1811 to establish similar schools using the system of Dr Andrew Bell, but based on the teachings of the Church of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grade II Listed Building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Ireland Environment Agency in Northern Ireland. The term has also been used in the Republic of Ireland, where buildings are protected under the Planning and Development Act 2000. The statutory term in Ireland is " protected structure". A listed building may not be demolished, extended, or altered without special permission from the local planning authority, which typically consults the relevant central government agency, particularly for significant alterations to the more notable listed buildings. In England and Wales, a national amenity society must be notified of any work to a listed building which involves any element of demolition. Exemption from secular listed building control is provided for some buildings in current use for worship, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manor House
A manor house was historically the main residence of the lord of the manor. The house formed the administrative centre of a manor in the European feudal system; within its great hall were held the lord's manorial courts, communal meals with manorial tenants and great banquets. The term is today loosely applied to various country houses, frequently dating from the Late Middle Ages, which formerly housed the landed gentry. Manor houses were sometimes fortified, albeit not as fortified as castles, and were intended more for show than for defencibility. They existed in most European countries where feudalism was present. Function The lord of the manor may have held several properties within a county or, for example in the case of a feudal baron, spread across a kingdom, which he occupied only on occasional visits. Even so, the business of the manor was directed and controlled by regular manorial courts, which appointed manorial officials such as the bailiff, granted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacobean Style
The Jacobean style is the second phase of Renaissance architecture in England, following the Elizabethan style. It is named after King James VI and I, with whose reign (1603–1625 in England) it is associated. At the start of James' reign there was little stylistic break in architecture, as Elizabethan trends continued their development. However, his death in 1625 came as a decisive change towards more classical architecture, with Italian influence, was in progress, led by Inigo Jones; the style this began is sometimes called Stuart architecture, or English Baroque (though the latter term may be regarded as starting later). Courtiers continued to build large prodigy houses, even though James spent less time on summer progresses round his realm than Elizabeth had. The influence of Flemish and German Northern Mannerism increased, now often executed by immigrant craftsmen and artists, rather than obtained from books as in the previous reign. There continued to be very little buildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grade II-listed
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Ireland Environment Agency in Northern Ireland. The term has also been used in the Republic of Ireland, where buildings are protected under the Planning and Development Act 2000. The statutory term in Ireland is " protected structure". A listed building may not be demolished, extended, or altered without special permission from the local planning authority, which typically consults the relevant central government agency, particularly for significant alterations to the more notable listed buildings. In England and Wales, a national amenity society must be notified of any work to a listed building which involves any element of demolition. Exemption from secular listed building control is provided for some buildings in current use for worship, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Bartholomew
John Bartholomew (25 December 1831 – 29 March 1893) was a Scottish cartographer. Life Bartholomew was born in Edinburgh, Scotland. His father, John Bartholomew Sr., started a cartographical establishment in Edinburgh, and he was educated in the work. He was subsequently assistant to the German geographer August Petermann, until in 1856 he took up the management of his father's firm. For this establishment, now known as the Edinburgh Geographical Institute, Bartholomew built up a reputation unsurpassed in Great Britain for the production of the finest cartographical work. Bartholomew was an in-house cartographer for George Philip. He is best known for the development of colour contouring (or hypsometric tints), the system of representing altitudes on a graduated colour scale, with areas of high altitude in shades of brown and areas of low altitude in shades of green. He first showcased his colour contouring system at the Paris Exhibition of 1878; although it initially me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Calthorpe (Roundhead)
James Calthorpe (died 1658) of Ampton who was Sheriff of Suffolk, in 1656, during the Protectorate of Oliver Cromwell, by whom he was knighted at Whitehall, 10 December, in the same year. Biography Calthorpe was the third son, and the only one of ten children of Sir Henry Calthorpe and his wife Dorothy (daughter and heiress of Edward Humphrey) to survive to adulthood. He was educated at Catherine Hall, Cambridge. He and was Sheriff of Suffolk, in 1656, during the Protectorate of Oliver Cromwell, by whom he was knighted at Whitehall, 10 December, in the same year. James Calthorpe survived his father by twenty-one years, being interred in the chancel of Ampton Church the same day of the month on which Sir Henry died, 1 August 1658. Family Calthorpe married Dorothy, second daughter of Sir James Reynolds, of Castle Camps, Cambridgeshire, and sister to Sir John Reynolds, Commissary-General in Ireland, on whose death she became his sole heiress). They had three sons and six dau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Ely
The Diocese of Ely is a Church of England diocese in the Province of Canterbury. It is headed by the Bishop of Ely, who sits at Ely Cathedral in Ely. There is one suffragan (subordinate) bishop, the Bishop of Huntingdon. The diocese now covers the modern ceremonial county of Cambridgeshire (excluding the Soke of Peterborough) and western Norfolk. The diocese was created in 1109 out of part of the Diocese of Lincoln. The diocese is ancient, and the area of Ely was part of the patrimony of Saint Etheldreda. A religious house was founded in the city in 673. After her death in 679 she was buried outside the church, and her remains were later reburied inside, the foundress being commemorated as a great Anglian saint. The diocese has had its boundaries altered various times. From an original diocese covering the historic county of Cambridgeshire and the Isle of Ely, Bedfordshire and Huntingdonshire were added in 1837 from the Diocese of Lincoln, as was the Sudbury archdeaconry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |