|
Amorpha Juglandis
''Amorpha juglandis'', the walnut sphinx, is the only species in the monotypic moth genus ''Amorpha'', which is in the family Sphingidae, erected by Jacob Hübner in 1809. The species was first described by James Edward Smith in 1797. Distribution It is native to North America, where it is distributed from the Atlantic Ocean to the Rocky Mountains in Canada and the United States. Description The wingspan is 45–75 mm. Amorpha juglandis MHNT CUT 2010 0 266 Edgard, St. John Par. Louisiana USA female dorsal.jpg, Female Amorpha juglandis MHNT CUT 2010 0 266 Edgard, St. John Par. Louisiana female ventral.jpg, Female underside Amorpha juglandis MHNT CUT 2010 0 266 Sank City Sank Co Wisconsin male dorsal.jpg, Male Amorpha juglandis MHNT CUT 2010 0 266 Sank City Sank Co Wisconsin male ventral.jpg, Male underside Biology The adult moth is nocturnal, active mainly during the early hours of the night. The caterpillar feeds on alder (''Alnus''), hickory (''Carya''), hazelnut (''Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Edward Smith (botanist)
__NOTOC__ Sir James Edward Smith (2 December 1759 – 17 March 1828) was an English botanist and founder of the Linnean Society. Early life and education Smith was born in Norwich in 1759, the son of a wealthy wool merchant. He displayed a precocious interest in the natural world. During the early 1780s he enrolled in the medical course at the University of Edinburgh where he studied chemistry under Joseph Black and natural history under John Walker. He then moved to London in 1783 to continue his studies. Smith was a friend of Sir Joseph Banks, who was offered the entire collection of books, manuscripts and specimens of the Swedish natural historian and botanist Carl Linnaeus following the death of his son Carolus Linnaeus the Younger. Banks declined the purchase, but Smith bought the collection for the bargain price of £1,000. The collection arrived in London in 1784, and in 1785 Smith was elected Fellow of the Royal Society. Academic career Between 1786 and 1788 Smit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hickory
Hickory is a common name for trees composing the genus ''Carya'', which includes around 18 species. Five or six species are native to China, Indochina, and India (Assam), as many as twelve are native to the United States, four are found in Mexico, and two to four are native to Canada. A number of hickory species are used for products like edible nuts or wood. Hickories are temperate forest trees with pinnately compound leaves and large nuts. Hickory flowers are small, yellow-green catkins produced in spring. They are wind-pollinated and self-incompatible. The fruit is a globose or oval nut, long and diameter, enclosed in a four-valved husk, which splits open at maturity. The nut shell is thick and bony in most species, and thin in a few, notably the pecan (''C. illinoinensis''); it is divided into two halves, which split apart when the seed germinates. Etymology The name "hickory" derives from a Native American word in an Algonquian language (perhaps Powhatan). It is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Jacob Hübner
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smerinthini
Smerinthini is a tribe of moths of the family Sphingidae. The genus was erected by Augustus Radcliffe Grote and Herbert C. Robinson in 1865. Taxonomy *Genus '' Acanthosphinx'' Aurivillius, 1891 *Genus '' Afroclanis'' Carcasson, 1968 *Genus '' Afrosataspes'' Basquin & Cadiou, 1986 *Genus '' Afrosphinx'' Carcasson, 1968 *Genus ''Agnosia'' Rothschild & Jordan, 1903 *Genus ''Amorpha'' Hübner, 1809 *Genus '' Anambulyx'' Rothschild & Jordan, 1903 *Genus '' Andriasa'' Walker, 1856 *Genus '' Avinoffia'' Clark, 1929 *Genus '' Cadiouclanis'' Eitschberger, 2007 *Genus '' Callambulyx'' Rothschild & Jordan, 1903 *Genus '' Ceridia'' Rothschild & Jordan, 1903 *Genus ''Chloroclanis'' Carcasson, 1968 *Genus '' Clanidopsis'' Rothschild & Jordan, 1903 *Genus ''Clanis'' Hübner, 1819 *Genus '' Coequosa'' Walker, 1856 *Genus ''Craspedortha'' Mell, 1922 *Genus ''Cypa'' Walker, 1865 *Genus ''Cypoides'' Matsumura, 1921 *Genus ''Daphnusa'' Walker, 1856 *Genus ''Dargeclanis'' Eitschberger, 2007 *Genus ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
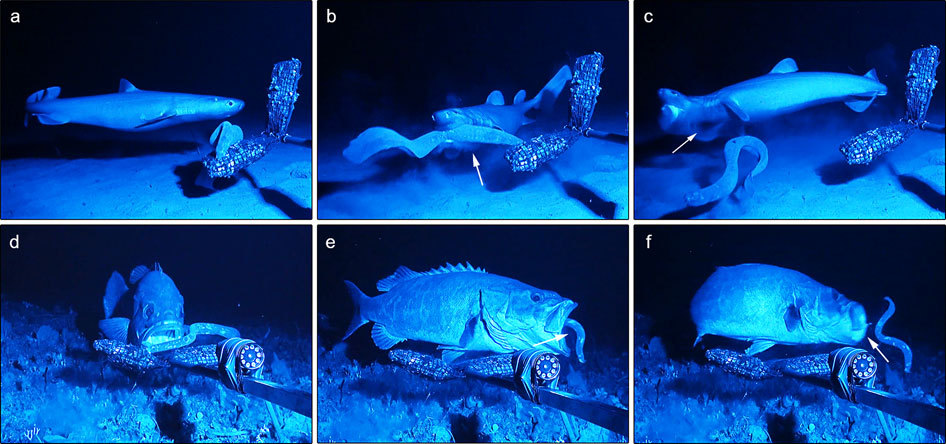
Antipredator Adaptation
Anti-predator adaptations are mechanisms developed through evolution that assist prey organisms in their constant struggle against predators. Throughout the animal kingdom, adaptations have evolved for every stage of this struggle, namely by avoiding detection, warding off attack, fighting back, or escaping when caught. The first line of defence consists in avoiding detection, through mechanisms such as camouflage, masquerade, apostatic selection, living underground, or nocturnality. Alternatively, prey animals may ward off attack, whether by advertising the presence of strong defences in aposematism, by mimicking animals which do possess such defences, by startling the attacker, by signalling to the predator that pursuit is not worthwhile, by distraction, by using defensive structures such as spines, and by living in a group. Members of groups are at reduced risk of predation, despite the increased conspicuousness of a group, through improved vigilance, predator confusion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiracle (arthropods)
A spiracle or stigma is the opening in the exoskeletons of insects and some spiders to allow air to enter the trachea. In the respiratory system of insects, the tracheal tubes primarily deliver oxygen directly into the animals' tissues. The spiracles can be opened and closed in an efficient manner to reduce water loss. This is done by contracting closer muscles surrounding the spiracle. In order to open, the muscle relaxes. The closer muscle is controlled by the central nervous system, but can also react to localized chemical stimuli. Several aquatic insects have similar or alternative closing methods to prevent water from entering the trachea. The timing and duration of spiracle closures can affect the respiratory rates of the organism. Spiracles may also be surrounded by hairs to minimize bulk air movement around the opening, and thus minimize water loss. Although all insects have spiracles, only some spiders have them, such as orb weavers and wolf spiders. Ancestrally, spiders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrya
''Ostrya'' is a genus of eight to 10 small deciduous trees belonging to the birch family Betulaceae. Common names include hop-hornbeam and hophornbeam. It may also be called ironwood, a name shared with a number of other plants. The genus is native in southern Europe, southwest and eastern Asia, and North and Central America. They have a conical or irregular crown and a scaly, rough bark. They have alternate and double-toothed birch-like leaves 3–10 cm long. The flowers are produced in spring, with male catkins 5–10 cm long and female aments 2–5 cm long. The fruit form in pendulous clusters 3–8 cm long with 6–20 seeds; each seed is a small nut 2–4 mm long, fully enclosed in a bladder-like involucre. The wood is very hard and heavy. The genus name ''Ostrya'' is derived from the Greek word (), which may be related to () "shell (of an animal)". Regarded as a weed tree by some foresters, this hard and stable wood was historically used to fashion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juglans
Walnut trees are any species of tree in the plant genus ''Juglans'', the type genus of the family Juglandaceae, the seeds of which are referred to as walnuts. All species are deciduous trees, tall, with pinnate leaves , with 5–25 leaflets; the shoots have chambered pith, a character shared with the wingnuts (''Pterocarya''), but not the hickories (''Carya'') in the same family. The 21 species in the genus range across the north temperate Old World from southeast Europe east to Japan, and more widely in the New World from southeast Canada west to California and south to Argentina. Edible walnuts, which are consumed worldwide, are usually harvested from cultivated varieties of the species ''Juglans regia''. China produces half of the world total of walnuts. Etymology The common name ''walnut'' derives from Old English ''wealhhnutu'', literally 'foreign nut' (from ''wealh'' 'foreign' + ''hnutu'' 'nut'), because it was introduced from Gaul and Italy. The Latin name for the wal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beech
Beech (''Fagus'') is a genus of deciduous trees in the family Fagaceae, native to temperate Europe, Asia, and North America. Recent classifications recognize 10 to 13 species in two distinct subgenera, ''Engleriana'' and ''Fagus''. The ''Engleriana'' subgenus is found only in East Asia, distinctive for its low branches, often made up of several major trunks with yellowish bark. The better known ''Fagus'' subgenus beeches are high-branching with tall, stout trunks and smooth silver-grey bark. The European beech (''Fagus sylvatica'') is the most commonly cultivated. Beeches are monoecious, bearing both male and female flowers on the same plant. The small flowers are unisexual, the female flowers borne in pairs, the male flowers wind-pollinating catkins. They are produced in spring shortly after the new leaves appear. The fruit of the beech tree, known as beechnuts or mast, is found in small burrs that drop from the tree in autumn. They are small, roughly triangular, and edible, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hazel
The hazel (''Corylus'') is a genus of deciduous trees and large shrubs native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. The genus is usually placed in the birch family Betulaceae,Germplasmgobills Information Network''Corylus''Rushforth, K. (1999). ''Trees of Britain and Europe''. Collins .Huxley, A., ed. (1992). ''New RHS Dictionary of Gardening''. Macmillan . though some botanists split the hazels (with the hornbeams and allied genera) into a separate family Corylaceae. The fruit of the hazel is the hazelnut. Hazels have simple, rounded leaves with double-serrate margins. The flowers are produced very early in spring before the leaves, and are monoecious, with single-sex catkins. The male catkins are pale yellow and long, and the female ones are very small and largely concealed in the buds, with only the bright-red, 1-to-3 mm-long styles visible. The fruits are nuts long and 1–2 cm diameter, surrounded by an involucre (husk) which partly to fully encloses the nut. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alder
Alders are trees comprising the genus ''Alnus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The genus comprises about 35 species of monoecious trees and shrubs, a few reaching a large size, distributed throughout the north temperate zone with a few species extending into Central America, as well as the northern and southern Andes. Description With a few exceptions, alders are deciduous, and the leaves are alternate, simple, and serrated. The flowers are catkins with elongate male catkins on the same plant as shorter female catkins, often before leaves appear; they are mainly wind-pollinated, but also visited by bees to a small extent. These trees differ from the birches (''Betula'', another genus in the family) in that the female catkins are woody and do not disintegrate at maturity, opening to release the seeds in a similar manner to many conifer cones. The largest species are red alder (''A. rubra'') on the west coast of North America, and black alder (''A. glutinosa''), native ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Taxon
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. In contrast, an oligotypic taxon contains more than one but only a very few subordinate taxa. Examples Just as the term ''monotypic'' is used to describe a taxon including only one subdivision, the contained taxon can also be referred to as monotypic within the higher-level taxon, e.g. a genus monotypic within a family. Some examples of monotypic groups are: Plants * In the order Amborellales, there is only one family, Amborellaceae and there is only one genus, '' Amborella'', and in this genus there is only one species, namely ''Amborella trichopoda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

