|
Amnon Biran
Amnon ( he, אַמְנוֹן ''’Amnōn'', "faithful") was, in the Hebrew Bible, the oldest son of King David and his second wife, Ahinoam of Jezreel. He was born in Hebron during his father's reign in Judah. He was the heir apparent to the throne of Israel until he was assassinated by his half-brother Absalom to avenge the rape of Absalom's sister Tamar. Biblical account Amnon's background Amnon was born in Hebron to Ahinoam and King David. As the presumptive heir to the throne of Israel, Amnon enjoyed a life of power and privilege. Rape of Tamar Although he was the heir-apparent to David's throne, Amnon is best remembered for the rape of his half-sister Tamar, daughter of David and Maachah. Despite the biblical prohibition on sexual relations between half siblings, Amnon had an overwhelming desire for her. He acted on advice from his cousin, Jonadab son of Shimeah, David's brother, to lure Tamar into his quarters by pretending to be sick and desiring her to cook ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kings Of Israel And Judah
This article is an overview of the kings of the United Kingdom of Israel as well as those of its successor states and classical period kingdoms ruled by the Hasmonean dynasty and Herodian dynasty. Kings of Ancient Israel and Judah The Hebrew Bible describes a succession of kings of a United Kingdom of Israel, and then of divided kingdoms, Israel and Judah. In contemporary scholarship, the united monarchy is debated, due to a lack of archaeological evidence for it. It is generally accepted that a "House of David" existed, but some scholars believe that David could have only been the king or chieftain of Judah, which was likely small, and that the northern kingdom was a separate development. There are some dissenters to this view, including those who support the traditional narrative, and those support the united monarchy's existence but believe that the Bible contains theological exaggerations. Overview table House of Gideon *Abimelech – the son of Gideon, was th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talmai
Talmai (; he, wikt:תלמי, תלמי 'my furrows') is a name in the Hebrew Bible, Bible referring to a number of minor people. Its Aramaic version was associated with the Greek Ptolemy (name), Ptolemy (see that article for the list of corresponding names and surnames), and is the origin of Bartholomew (name), Bartholomew. Talmai and his brothers, the Nephilim Talmai, Ahiman and Sheshai were Nephilim, three giant sons of Anak whom Caleb and the spies saw in Mount Hebron (Book of Numbers 13:22) when they went in to explore the land. They were afterwards driven out and slain (Joshua 15:14; Book of Judges, Judges 1:10). Talmai, father of Maacah King of Geshur. His daughter Maacah (מַעֲכָה) was a wife to the king David of Israel, mother of Tamar (David's daughter), Tamar and Absalom (). After slaying Amnon (for the rape of Tamar), Absalom fled to Talmai in Geshur for three years. Rephaites Monarchs of the Hebrew Bible Absalom Books of Samuel people Anakim Nephilim {{Heb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urethra
The urethra (from Greek οὐρήθρα – ''ourḗthrā'') is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in marsupials, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus. Females use their urethra only for urinating, but males use their urethra for both urination and ejaculation. The external urethral sphincter is a striated muscle that allows voluntary control over urination. The internal sphincter, formed by the involuntary smooth muscles lining the bladder neck and urethra, receives its nerve supply by the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system. The internal sphincter is present both in males and females. Structure The urethra is a fibrous and muscular tube which connects the urinary bladder to the external urethral meatus. Its length differs between the sexes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylonian Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the centerpiece of Jewish cultural life and was foundational to "all Jewish thought and aspirations", serving also as "the guide for the daily life" of Jews. The term ''Talmud'' normally refers to the collection of writings named specifically the Babylonian Talmud (), although there is also an earlier collection known as the Jerusalem Talmud (). It may also traditionally be called (), a Hebrew abbreviation of , or the "six orders" of the Mishnah. The Talmud has two components: the Mishnah (, 200 CE), a written compendium of the Oral Torah; and the Gemara (, 500 CE), an elucidation of the Mishnah and related Tannaitic writings that often ventures onto other subjects and expounds broadly on the Hebrew Bible. The term "Talmud" may refer to eith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eli (biblical Figure)
Eli (, ; grc, Ἠλί, translit=Ēli; la, Heli) was, according to the Books of Samuel, a high priest and Judge of the Israelites in the city of Shiloh, ancient Israel. When Hannah came to Shiloh to pray for a son, Eli initially accused her of drunkenness, but when she protested her innocence, Eli wished her well. Hannah's eventual child, Samuel, was raised by Eli in the tabernacle. When Eli failed to rein in the abusive behavior of his sons, God promised to punish his family, which resulted in the death of Eli and his sons. Later biblical passages mention the fortunes of several of his descendants, and he figures prominently in Samaritan religious tradition. Biblical narrative Eli was the high priest (''kohen gadol'') of Shiloh, the second-to-last Israelite judge (succeeded only by Samuel) before the rule of the Kings of Israel and Judah. Hannah This story of Hannah, with which the Books of Samuel begin, involves Eli. Hannah was the wife of Elkanah. She was childless. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Wesley
John Wesley (; 2 March 1791) was an English people, English cleric, Christian theology, theologian, and Evangelism, evangelist who was a leader of a Christian revival, revival movement within the Church of England known as Methodism. The societies he founded became the dominant form of the independent Methodist movement that continues to this day. Educated at Charterhouse School, Charterhouse and Christ Church, Oxford, Wesley was elected a fellow of Lincoln College, Oxford, in 1726 and ordination, ordained as an Anglican priest two years later. At Oxford, he led the "Holy Club", a society formed for the purpose of the study and the pursuit of a devout Christian life; it had been founded by his brother Charles Wesley, Charles and counted George Whitefield among its members. After an unsuccessful ministry of two years, serving at Christ Church (Savannah, Georgia), Christ Church, in the Georgia colony of Savannah, Georgia, Savannah, he returned to London and joined a religious so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methodism
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's brother Charles Wesley were also significant early leaders in the movement. They were named ''Methodists'' for "the methodical way in which they carried out their Christian faith". Methodism originated as a revival movement within the 18th-century Church of England and became a separate denomination after Wesley's death. The movement spread throughout the British Empire, the United States, and beyond because of vigorous missionary work, today claiming approximately 80 million adherents worldwide. Wesleyan theology, which is upheld by the Methodist churches, focuses on sanctification and the transforming effect of faith on the character of a Christian. Distinguishing doctrines include the new birth, assurance, imparted righteousness, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
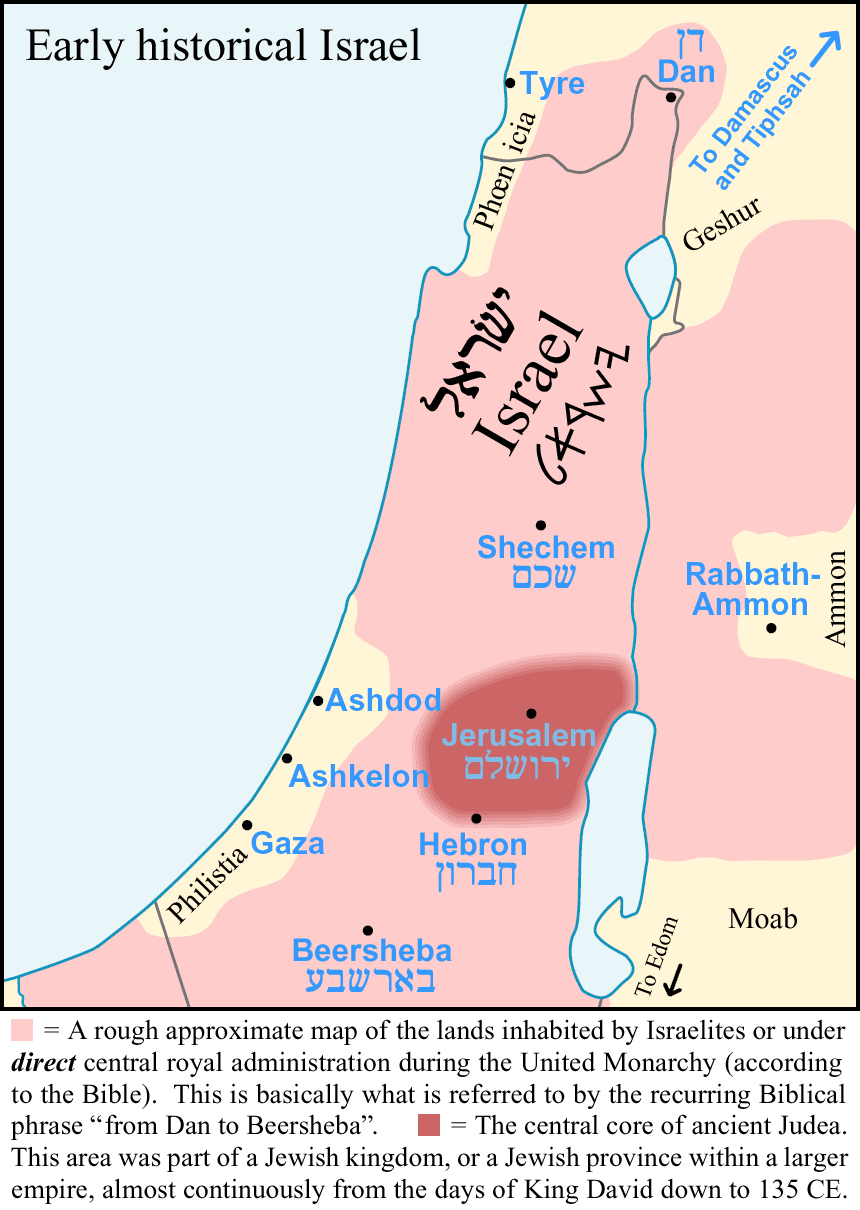
Geshur
Geshur was a territory in the ancient Levant mentioned in the early books of the Hebrew Bible and possibly in several other ancient sources, located in the region of the modern-day Golan Heights. Some scholars suggest it was established as an independent city-state from the middle of the tenth century BCE, maintained its autonomy for about a century until it was annexed in the third quarter of the ninth century by Hazael, the king of Aram. Location Geshur is identified with the area stretching along the eastern shore of the Sea of Galilee and reaching south to the Yarmuk River, in what is now called the Golan Heights. This location places it on one of the routes connecting the region of Bashan with the Phoenician coast. Tel Dover, located southeast of the Sea of Galilee on the Jarmuk (Yarmuk) River, may have been the kingdom's southern border. Surveys conducted within the Golan Heights have not discovered many settlements within the territory of Geshur. Religion Excavations of et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kareth
The Hebrew term ''kareth'' ("cutting off" he, כָּרֵת, ), or extirpation, is a form of punishment for sin, mentioned in the Hebrew Bible and later Jewish writings. Kareth in its simplistic meaning refers to an individual being expelled from the Nation of Israel. In the Talmud, ''kareth'' means not necessarily physical "cutting off" of life, but can also mean the extinction of the soul and denial of a share in the world to come. Etymology The word ''kareth'' is derived from the Hebrew verb ''karat'' ("to cut off"). The noun form ''kareth'' does not occur in the Hebrew Bible; rather, verb forms such as ''venichreta'' (" hat soulshall be cut off") are most common. Hebrew Bible In the Hebrew Bible, verbs that underlie the later use of the noun form ''kareth'' refer to forms of punishment including premature death, or else exclusion from the people. According to Richard C. Steiner, the phrase "to be cut off from one's people" is an antonym for "to be gathered to one's people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael D
Michael D may refer to: * Mike D (born 1965), founding member of the Beastie Boys Arts * Michael D. Cohen (actor) (born 1975), Canadian actor * Michael D. Ellison, African American recording artist * Michael D. Fay, American war artist * Michael D. Ford (1928–2018), English set decorator * Michael D. Roberts, American actor Business * Michael D. Dingman (1931–2017), American businessman * Michael D. Ercolino (1906–1982), American businessman * Michael D. Fascitelli, (born c. 1957), American businessman * Michael D. Penner (born 1969), Canadian lawyer and businessman Education * Michael D. Aeschliman (born 1948), American–Swiss educator * Michael D. Cohen (academic) (1945–2013), professor of complex systems, information and public policy at the University of Michigan * Michael D. Hanes, American music educator * Michael D. Hurley (born 1976), British Professor of Literature and Theology * Michael D. Johnson, a former President of John Carroll University * Mic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)