|
Amish In Illinois
The Amish (; pdc, Amisch; german: link=no, Amische), formally the Old Order Amish, are a group of traditionalist Anabaptist Christian church fellowships with Swiss German and Alsatian origins. They are closely related to Mennonite churches, another Anabaptist denomination. The Amish are known for simple living, plain dress, Christian pacifism, and slowness to adopt many conveniences of modern technology, with a view neither to interrupt family time, nor replace face-to-face conversations whenever possible, and a view to maintain self-sufficiency. The Amish value rural life, manual labor, humility and '' Gelassenheit'' (submission to God's will). The history of the Amish church began with a schism in Switzerland within a group of Swiss and Alsatian Mennonite Anabaptists in 1693 led by Jakob Ammann. Those who followed Ammann became known as Amish. In the second half of the 19th century, the Amish divided into Old Order Amish and Amish Mennonites; the latter do not abstain from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lancaster County, Pennsylvania
Lancaster County (; Pennsylvania Dutch: Lengeschder Kaundi), sometimes nicknamed the Garden Spot of America or Pennsylvania Dutch Country, is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. It is located in the south central part of Pennsylvania. As of the 2020 census, the population was 552,984. Its county seat is Lancaster. Lancaster County comprises the Lancaster, Pennsylvania metropolitan statistical area. Lancaster County is a tourist destination with its Amish community a major attraction. Contrary to popular belief, the word "Dutch" in "Pennsylvania Dutch" is not a mistranslation, but rather a corruption of the Pennsylvania German endonym ''Deitsch'', which means "Pennsylvania Dutch / German" or "German". Ultimately, the terms Deitsch, Dutch, Diets, and Deutsch are all cognates of the Proto-Germanic word meaning "popular" or "of the people". The continued use of "Dutch" instead of "German" was strengthened by the Pennsylvania Dutch in the 19th century as a way of distin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convenience
Convenient procedures, products and services are those intended to increase ease in accessibility, save resources (such as time, effort and energy) and decrease frustration. A modern convenience is a labor-saving device, service or substance which make a task easier or more efficient than a traditional method. Convenience is a relative concept, and depends on context. For example, automobiles were once considered a convenience, yet today are regarded as a normal part of life. Because differences in lifestyles around the world, the term is a relative term based upon the conveniences previously available to a person or group. For instance, an American definition of 'modern convenience' is likely different from that of an individual living in a developing country. Most of the time, the term 'modern convenience' is used to express personal lifestyle and home life. Examples Service conveniences are those that save shoppers time or effort, and includes variables such as credit av ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
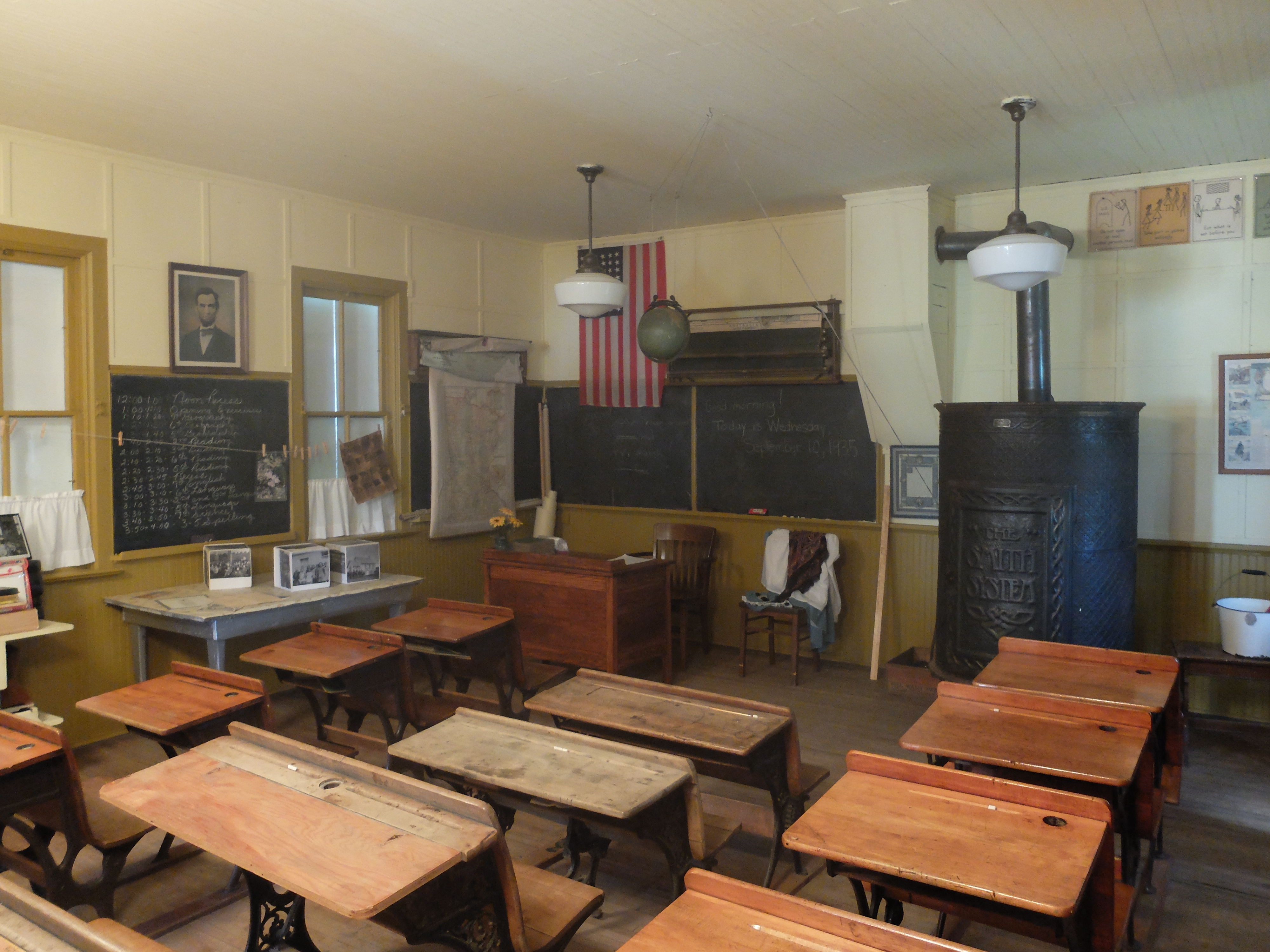
One-room School
One-room schools, or schoolhouses, were commonplace throughout rural portions of various countries, including Prussia, Norway, Sweden, the United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, the United Kingdom, Ireland, and Spain. In most rural and small town schools, all of the students met in a single room. There, a single teacher taught academic basics to several grade levels of elementary-age children. While in many areas one-room schools are no longer used, some remain in developing nations and rural or remote areas. In the United States, the concept of a "little red schoolhouse" is a stirring one, and historic one-room schoolhouses have widely been preserved and are celebrated as symbols of frontier values and of local and national development. When necessary, the schools were enlarged or replaced with two-room schools. More than 200 are listed on the U.S. National Register of Historic Places. In Norway, by contrast, one-room schools were viewed more as impositions upon conse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord's Day
The Lord's Day in Christianity is generally Sunday, the principal day of communal worship. It is observed by most Christians as the weekly memorial of the resurrection of Jesus Christ, who is said in the canonical Gospels to have been witnessed alive from the dead early on the first day of the week. The phrase appears in . According to some sources, Christians held corporate worship on Sunday in the 1st century. (''First Apology of Justin Martyr, First Apology''chapter 67, and by 361 AD it had become a mandated weekly occurrence. Before the Early Middle Ages, the Lord's Day became associated with Sabbath in Christianity, Sabbatarian (rest) practices legislated by Church Councils. Christian denominations such as the Reformed Churches, Methodist Churches, and Baptist Churches regard Sunday as Christian Sabbath, a practice known as first-day Sabbatarianism. First-day Sabbatarian (Sunday Sabbatarian) practices include attending morning and evening church services on Sundays, receiving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Believer's Baptism
Believer's baptism or adult baptism (occasionally called credobaptism, from the Latin word meaning "I believe") is the practice of baptizing those who are able to make a conscious profession of faith, as contrasted to the practice of baptizing infants. Credobaptists believe that infants incapable of consciously believing should not be baptized. The mode of believer's baptism depends on the Christian denomination, and is done either by pouring (the normative method in Mennonite, Amish, and Hutterite churches) or by immersion (the normative method practiced by Schwarzenau Brethren, River Brethren, Baptists, and the Churches of Christ, among others). Certain denominations of Methodism, including the Free Methodist Church and Evangelical Wesleyan Church, practice infant baptism for families who desire it for their children, but provide a rite for child dedication for those who have a preference for believer's baptism only after their child has made a personal acceptance of Jesus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allen County, Indiana
Allen County is a county in the U.S. state of Indiana. As of the 2020 Census, the population was 385,410, making it the third-most populous county in Indiana. The county seat and largest city is Fort Wayne, the second largest city in Indiana. Allen County is included in the Fort Wayne Metropolitan Statistical Area and the Fort Wayne– Huntington– Auburn Combined Statistical Area. Allen County is the cultural and economic center of northeastern Indiana. The county is within a radius of major population centers, including Chicago, Cincinnati, Cleveland, Columbus, Detroit, Indianapolis, Louisville, Milwaukee, and within a one-day drive of one-third of the U.S. population and one-fifth of Canadians. Occupied for thousands of years by cultures of indigenous peoples, Allen County was organized by European Americans on December 17, 1823, from Delaware and Randolph counties; and formed on April 1, 1824, at the Ewing Tavern. The county is named for Colonel John Allen, an att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adams County, Indiana
Adams County lies in northeastern Indiana in the United States and shares its eastern border with Ohio. It was officially established in 1836. The county seat is Decatur. According to the 2020 census, its population was 35,809, an increase of 4.1% from 34,387 in 2010. The county has four incorporated cities and towns with a total population of over 15,000, as well as many small unincorporated communities. The county is divided into 12 townships which provide local services. There are four Indiana state roads in the county, as well as three U.S. Routes and one railroad line. In 2017, about a quarter of the county's population (estimated 8,600) was Swiss Amish that settled in the Southern half of the county around Berne. History The statute that mandated creation of this county was passed on February 7, 1835, and the organization itself was authorized on March 1, 1836. Its name honors the sixth President of the United States, John Quincy Adams. Selection of the county seat was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alemannic German
Alemannic, or rarely Alemannish (''Alemannisch'', ), is a group of High German dialects. The name derives from the ancient Germanic tribal confederation known as the Alamanni ("all men"). Distribution Alemannic dialects are spoken by approximately ten million people in several countries: * In Europe: ** Switzerland: all German-speaking parts of the country except Samnaun ** Germany: centre and south of Baden-Württemberg, Swabia, and certain districts of Bavaria ** Austria: Vorarlberg, Reutte District of Tyrol ** Liechtenstein ** France: Alsace region ( Alsatian dialect) and in some villages of the Phalsbourg county, in Lorraine ** Italy: Gressoney-La-Trinité, Gressoney-Saint-Jean, Issime, Alagna Valsesia, Rimella and Formazza, in some other villages almost extinct *Outside Europe: ** United States: Allen and Adams County, Indiana, by the Amish there and also in their daughter settlements in Indiana and other U.S. states. ** Venezuela: Colonia Tovar (Colonia Tovar dialect) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Order Mennonite
Old Order Mennonites (Pennsylvania Dutch language, Pennsylvania German: ) form a branch of the Mennonite tradition. Old Order Movement, Old Order are those Mennonite groups of Swiss people, Swiss German and south Germans, German heritage who practice a lifestyle without some elements of modern technology, who still drive a horse and buggy rather than cars, wear very conservative and modest plain dress, dress plainly and who have retained the old forms of worship, baptism and communion. All Old Order Mennonites reject certain technologies (e.g., radio, television, Internet), but the extent of this rejection depends on the individual group. Old Order groups generally place great emphasis on a disciplined community instead of the individual's personal faith beliefs. The Pennsylvania Dutch language, Pennsylvania German language is spoken and vigorous among all horse-and-buggy groups except the Virginia Old Order Mennonites, who lost their original language before becoming Old Order. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Beachy Amish
The Old Beachy Amish or Old Beachy Amish Mennonites, also called Midwest Beachy Amish Mennonites, are a Plain, car-driving Beachy Amish group, that preserves the old ways of the Beachy Amish including the German language. They live in Kentucky and Illinois. They are part of the Amish Mennonite movement in a broader sense, but they are not an organized denomination. History In 1927 the Beachy church emerged from a division in the (Casselman) River Old Order Amish congregation in Somerset County, Pennsylvania. Bishop Moses M. Beachy led the new congregation during that time and his name became associated with this faction. The Beachys favored a milder discipline for members whose only offense was transferring membership to other Anabaptist churches, specifically the conservative Amish Mennonite congregation that broke away from Moses Beachy's congregation in 1895. The majority of the Beachy Amish transformed into Evangelical churches between 1946 and 1977. The Old Beachy Amish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Order Amish
The New Order Amish are a subgroup of Amish that split away from the Old Order Amish in the 1960s for a variety of reasons, which included a desire for "clean" youth courting standards, meaning they do not condone the practice of bundling, or non-sexually lying in bed together, during courtship. Tobacco and alcohol are also not allowed. They also wished to incorporate more evangelical elements into the church, including Sunday school and mission work. Some scholars see the group best characterized as a subgroup of Old Order Amish, despite the name. History The New Order Amish emerged mainly in two regions: Lancaster County, Pennsylvania, and Holmes/Wayne County, Ohio. Waldrep cites a New Order Amish man: Even though in Waldrep's opinion this seems "like a simplistic reading", he states that "in the final analysis the characterization appears accurate". In 1966, around one hundred families split with the Old Order Amish in Lancaster County, Pennsylvania, over differences r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subgroups Of Amish
Subgroups of Amish developed over the years, as Amish churches have divided many times over doctrinal disputes. The 'Old Order' Amish, a conservative faction that withdrew from fellowship with the wider body of Amish in the 1860s, are those that have most emphasized traditional practices and beliefs. There are many different subgroups of Amish with most belonging, in ascending order of conservatism, to the Beachy Amish, New Order, Old Order, or Swartzentruber Amish groups. Amish affiliations Donald B. Kraybill, Karen M. Johnson-Weiner and Steven M. Nolt speak in their book ''The Amish'' of different Amish ''affiliations''. They define an affiliation as "a cluster of two or more districts with at least twenty years of shared history". They continue: "affiliated congregations share similar Ordnungs, which specify distinctive lifestyles and visible symbols that set them apart from other affiliations". When referring to affiliations, Amish themselves speak of "our people" (''unser L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
