|
American 21 Inch Torpedo
There have been a number of 21-inch torpedoes in service with the United States. These have been used on ships and submarines of the U.S. Navy. American 21-inch torpedoes are in diameter. Ship classes that carried 21-inch torpedoes include: * ''Allen M. Sumner''-class destroyers * ''Atlanta''-class cruisers * ''Bagley''-class destroyers * ''Balao''-class submarines * ''Barbel''-class submarines * ''Barracuda''-class submarines * ''Benham''-class destroyers * ''Benjamin Franklin''-class submarines * ''Benson''-class destroyers * ''Cachalot''-class submarines * ''Caldwell''-class destroyers * ''Cassin''-class destroyers * ''Chester''-class cruisers * ''Clemson''-class destroyers * ''Colorado''-class battleships * ''Connecticut''-class battleships * ''Dealey''-class destroyer escorts * ''Ethan Allen''-class submarines * ''Farragut''-class destroyers * ''Forrest Sherman''-class destroyers * ''Fletcher''-class destroyers * ''Gato''-class submarines * ''Gearing''-class destroyers * ''Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, such a device was called an automotive, automobile, locomotive, or fish torpedo; colloquially a ''fish''. The term ''torpedo'' originally applied to a variety of devices, most of which would today be called naval mine, mines. From about 1900, ''torpedo'' has been used strictly to designate a self-propelled underwater explosive device. While the 19th-century battleship had evolved primarily with a view to engagements between armored warships with naval artillery, large-caliber guns, the invention and refinement of torpedoes from the 1860s onwards allowed small torpedo boats and other lighter surface combatant , surface vessels, submarines/submersibles, even improvised fishing boats or frogmen, and later light aircraft, to destroy large shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dealey-class Destroyer Escort
The ''Dealey''-class destroyer escorts were the first post-World War II escort ships built for the United States Navy. Slightly faster and larger than the escort destroyers they succeeded, the ''Dealey'' class were fitted with twin-mounted guns, anti-submarine (ASW) rockets, a depth charge rack and six depth charge launchers. There were later modernizations that removed the ASW rockets and the depth charges in favor of nuclear-capable anti-submarine rocket launchers and torpedo mounts which fired lighter homing torpedoes. A large SQS 23 sonar was refitted in a bow sonar dome and most of the class were also fitted with a hangar and landing pad for DASH drone helicopters to deliver MK 44 and Mk 46 torpedoes. The drone helicopters proved very unreliable and their failure contributed to the relatively short life of the class. They were decommissioned in 1972 and 1973 in favor of the . and were sold at surplus to other countries in 1972, with the remainder of the class being sold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Madison-class Submarine
The ''James Madison'' class of submarine was an evolutionary development from the of fleet ballistic missile submarine. They were identical to the ''Lafayette''s except for being initially designed to carry the Polaris A-3 missile instead of the earlier A-2. This class, together with the , , , and classes, composed the " 41 for Freedom" that was the Navy's primary contribution to the nuclear deterrent force through the late 1980s. This class and the ''Benjamin Franklin'' class are combined with the ''Lafayette''s in some references. Design In the early 1970s all were modified for the Poseidon C-3 missile. During the late 1970s and early 1980s, six boats were further modified to carry the Trident I C-4 missile, along with six ''Benjamin Franklin''-class boats. These were ''James Madison'', ''Daniel Boone'', ''John C. Calhoun'', ''Von Steuben'', ''Casimir Pulaski'', and ''Stonewall Jackson''. Fate The ''James Madison''s were decommissioned between 1986 and 1995 due to a combin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
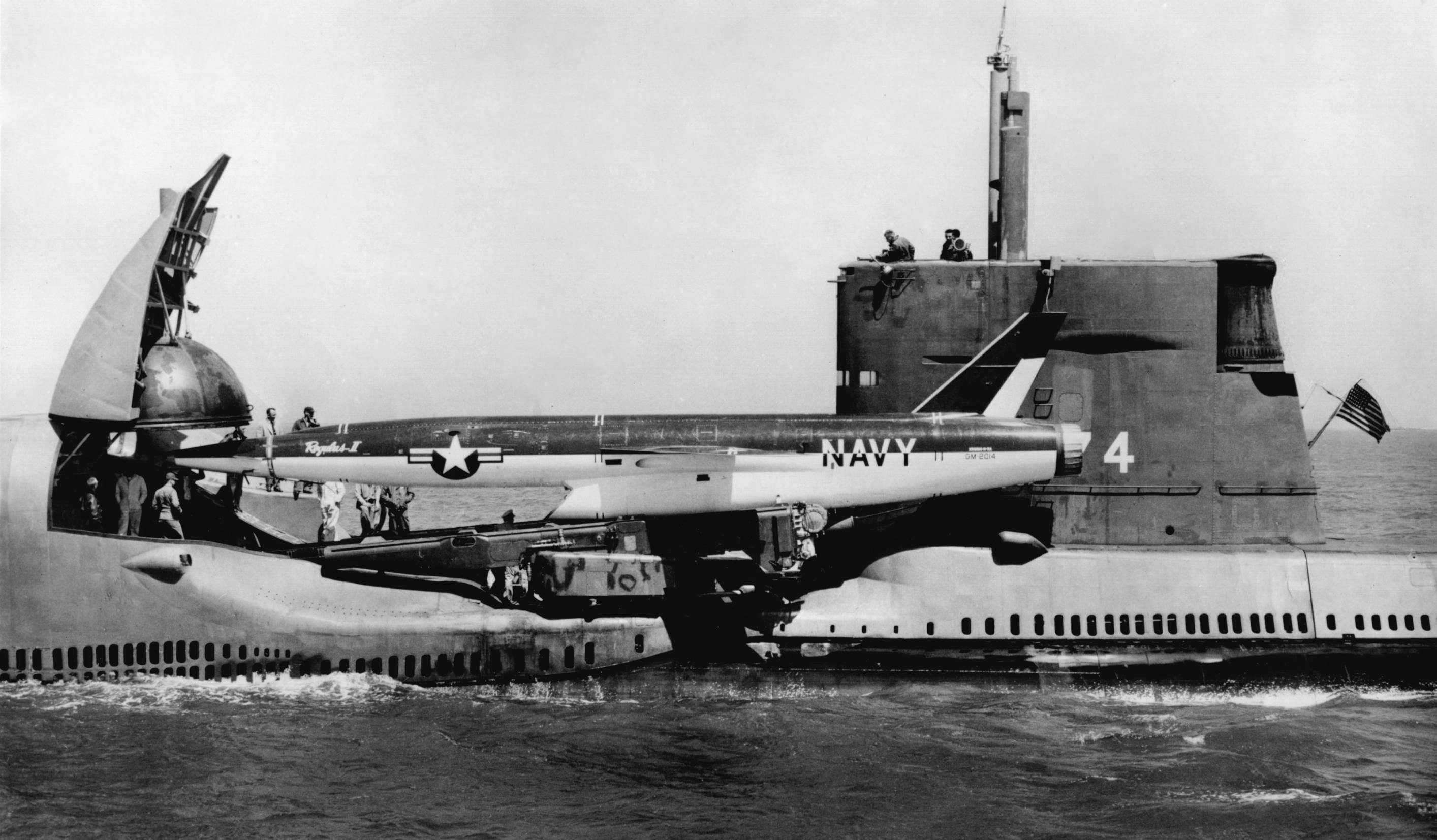
USS Halibut (SSGN-587)
USS ''Halibut'' (SSGN-587), a unique nuclear-powered guided missile submarine-turned-special operations platform, later redesignated as an attack submarine SSN-587, was the second ship of the United States Navy to be named after the halibut. Operational history ''Halibut''s keel was laid down by Mare Island Naval Shipyard at Vallejo, California, on 11 April 1957. She was launched on 9 January 1959, sponsored by Vernice Holifield, wife of Congressman Chet Holifield of California, and commissioned on 4 January 1960. Regulus deterrence patrols, 1960 – 1965 ''Halibut'' was originally designed under project SCB 137 as a diesel-electric submarine, but was completed with nuclear power under SCB 137A. She was the first submarine initially designed to launch guided missiles. Intended to carry the Regulus I and Regulus II nuclear cruise missiles, her main deck was high above the waterline to provide a dry "flight deck." Her missile system was completely automated, with hydrauli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gridley-class Destroyer
The ''Gridley''-class destroyers were a class of four 1500-ton destroyers in the United States Navy. They were part of a series of USN destroyers limited to 1,500 tons standard displacement by the London Naval Treaty and built in the 1930s.Comparison of 1500-ton classes a Destroyer History Foundation The first two ships were laid down on 3 June 1935 and commissioned in 1937. The second two were laid down in March 1936 and commissioned in 1938. Based on the preceding ''Mahan''-class destroyers with somewhat different machinery, they had the same hull but had only a sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grayback-class Submarine
The ''Grayback''-class submarine was a class of two guided missile-carrying submarines of the United States Navy. They carried the Regulus I and Regulus II nuclear cruise missiles, deployed 1957–64, that were rapidly phased out by Polaris Submarine Launched Ballistic Missiles (SLBMs). They and were the sole submarines designed specifically to carry Regulus missiles, and the only submarines capable of carrying Regulus II. However, and were modified earlier to carry two Regulus I missiles per boat. Design On the ''Grayback''s, two missile hangars allowed for a total of two Regulus II or four Regulus I missiles each. Since Regulus II was cancelled in December 1958 except for test firings, the class deployed with four Regulus I missiles. They were originally ordered as sisters of , similar to the last s, but were converted under project SCB 161 to missile submarines during construction.Gardiner and Chumbley, pp. 609–610 Torpedo armament was the same as the ''Tang''s, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gleaves-class Destroyer
The ''Gleaves''-class destroyers were a class of 66 destroyers of the United States Navy built 1938–42, designed by Gibbs & Cox. The first ship of the class was . They were the destroyer type that was in production for the US Navy when the United States entered World War II. The ''Gleaves'' class were initially specified as part of a 24-ship authorized in fiscal years 1938–40; however, Bethlehem Shipbuilding requested that the six ships designed by them use less complex machinery. Initially, ''Gleaves'' and , although designed by Gibbs & Cox and built by Bath Iron Works, were to follow the ''Benson'' design as modified by Bethlehem. This temporarily made the lead ship with more complex machinery, so the class was initially called the ''Livermore'' class, and this name persisted through World War II. However, it soon proved possible for ''Gleaves'' and ''Niblack'' to be built to the ''Livermore'' design. Since ''Gleaves'' was completed before ''Livermore'' and had a lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Washington-class Submarine
The ''George Washington'' class was a class of nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines deployed by the United States Navy. ''George Washington'', along with the later , , , and classes, comprised the "41 for Freedom" group of submarines that represented the Navy's main contribution to the nuclear deterrent force through the late 1980s. Development In 1957, the US Navy began using submarines in the nuclear deterrent role, when a pair of World War II vintage diesel-electric boats, and , converted to be able to carry a pair of Regulus cruise missiles, began operating deterrent patrols. These two were soon joined by a pair of purpose built diesel boats, and a nuclear powered boat, . However, the use of Regulus in the deterrent role showed a number of limitations; as a cruise missile, it was vulnerable to interception by fighter aircraft, it was limited to subsonic speed, and had a range of less than 1000 km, while the largest of the Regulus armed boats could carry a ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
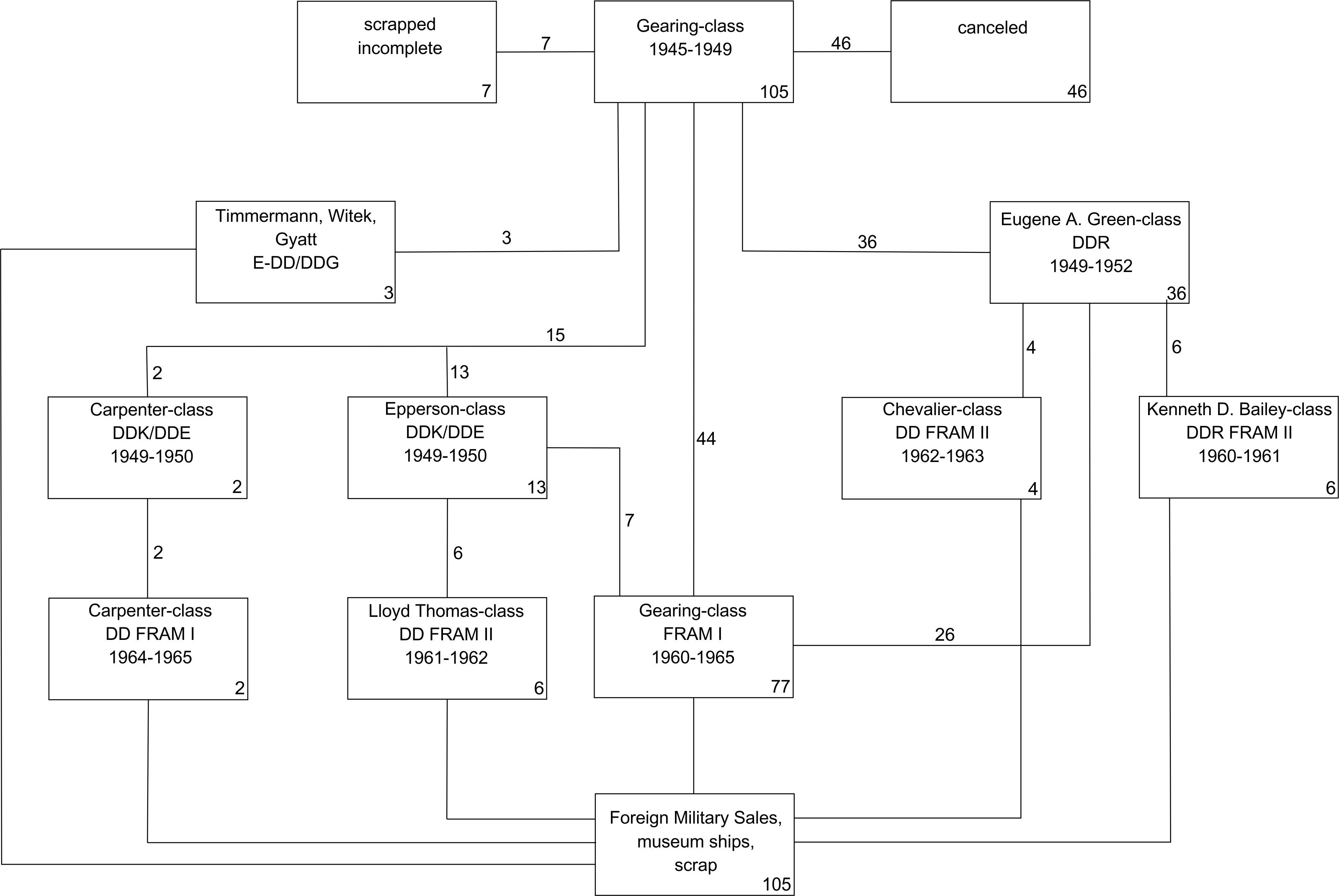
Gearing-class Destroyer
The ''Gearing'' class was a series of 98 destroyers built for the U.S. Navy during and shortly after World War II. The ''Gearing'' design was a minor modification of the , whereby the hull was lengthened by at amidships, which resulted in more fuel storage space and increased the operating range. The first ''Gearing''s were not ready for service until mid-1945 and saw little service in World War II. They continued serving, with a series of upgrades, until the 1970s. At that time many were sold to other nations, where they served many more years. Procurement and construction 31 vessels were authorized on 9 July 1942: * DD-710 to DD-721 awarded to Federal Shipbuilding, Kearny. * DD-742 to DD-743 awarded to Bath Iron Works, Bath, Maine. * DD-763 to DD-769 awarded to Bethlehem Steel, San Francisco. * DD-782 to DD-791 awarded to Todd Pacific Shipyards, Seattle. 4 vessels were authorized on 13 May 1942: * DD-805 to DD-808 awarded to Bath Iron Works, Bath, Maine. 3 vessels were a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gato-class Submarine
The ''Gato'' class of submarines was built for the United States Navy and launched in 1941–1943; they were the first mass-production U.S. submarine class of World War II. Together with their near-sisters the and es, their design formed the majority of the United States Navy's World War II submarine fleet.Typical Gato-class submarine diagram USS ''MacKinnon'' website Named after the of the class, , the ''Gato''s and their successors formed the core of the submarine service that was largely responsible for the destruction of the Japanese merchant marine and a large portion of the Imperial Japanese Navy in |
Fletcher-class Destroyer
The ''Fletcher'' class was a class of destroyers built by the United States during World War II. The class was designed in 1939, as a result of dissatisfaction with the earlier destroyer leader types of the and classes. Some went on to serve during the Korean War and into the Vietnam War. The United States Navy commissioned 175 ''Fletcher''-class destroyers between 1942 and 1944, more than any other destroyer class, and the design was generally regarded as highly successful. The ''Fletcher''s had a design speed of and a principal armament of five guns in single mounts with ten torpedo tubes in two quintuple centerline mounts. The and classes were ''Fletcher'' derivatives. The long-range ''Fletcher''-class ships performed every task asked of a destroyer, from anti-submarine warfare and anti-aircraft warfare to surface action.Friedman pp. 111–112. They could cover the vast distances required by fleet actions in the Pacific and served almost exclusively in the Pacific Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |