|
Ambush Rock
An ambush is a long-established military tactic in which a combatant uses an advantage of concealment or the element of surprise to attack unsuspecting enemy combatants from concealed positions, such as among dense underbrush or behind mountaintops. Ambushes have been used consistently throughout history, from ancient to modern warfare. In the 20th century, an ambush might involve thousands of soldiers on a large scale, such as over a choke point such as a mountain pass, or a small irregulars band or insurgent group attacking a regular armed force patrols. Theoretically, a single well-armed and concealed soldier could ambush other troops in a surprise attack. Sometimes an ambush can involve the exclusive or combined use of improvised explosive devices, that allow the attackers to hit enemy convoys or patrols while minimizing the risk of being exposed to return fire. History This use by early people of ambushing may date as far back as two million years when anthropolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bac Le Ambush
BAC or Bac may refer to: Places * Bac, Rožaje, Bac, a village in Montenegro * Baile Átha Cliath, Irish language name for Dublin city. * Bîc River, aka ''Bâc River'', a Moldovan river * Baç Bridge, bridge in Turkey * Barnes County Municipal Airport (ICAO airport code: KBAC; FAA airport code: BAC) Valley City, North Dakota, US; see List of airports in North Dakota Arts and entertainment * Baryshnikov Arts Center, in Manhattan, New York City * ''Batman: Arkham City'', a 2011 video game * Battersea Arts Centre, London, England * Benedicta Arts Center, St. Joseph, Minnesota, USA * Big Apple Chorus, New York based barbershop chorus * Boston Area Crusaders, former name of the Boston Crusaders Drum and Bugle Corps Organizations * BAC-Credomatic, a Central American financial company owned by Grupo Aval Acciones y Valores * Baltimore Aircoil Company, a manufacturer of Cooling tower, cooling towers * Bangabandhu Aeronautical Centre * Bank of America, which trades on the NYSE under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Improvised Explosive Devices
An improvised explosive device (IED) is a bomb constructed and deployed in ways other than in conventional military action. It may be constructed of conventional military explosives, such as an artillery shell, attached to a detonating mechanism. IEDs are commonly used as roadside bombs, or homemade bombs. IEDs are generally done in these terrorism operations or in asymmetric unconventional warfare by insurgent guerrillas or commando forces in a theatre of operations. In the Iraq War (2003–2011), insurgents used IEDs extensively against U.S.-led forces and, by the end of 2007, IEDs were responsible for approximately 63% of coalition deaths in Iraq. They were also used in Afghanistan by insurgent groups, and caused over 66% of coalition casualties in the 2001–2021 Afghanistan War. IEDs were also used frequently by the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) in Sri Lanka during the Sri Lankan Civil War. Background An IED is a bomb fabricated in an improvised manner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
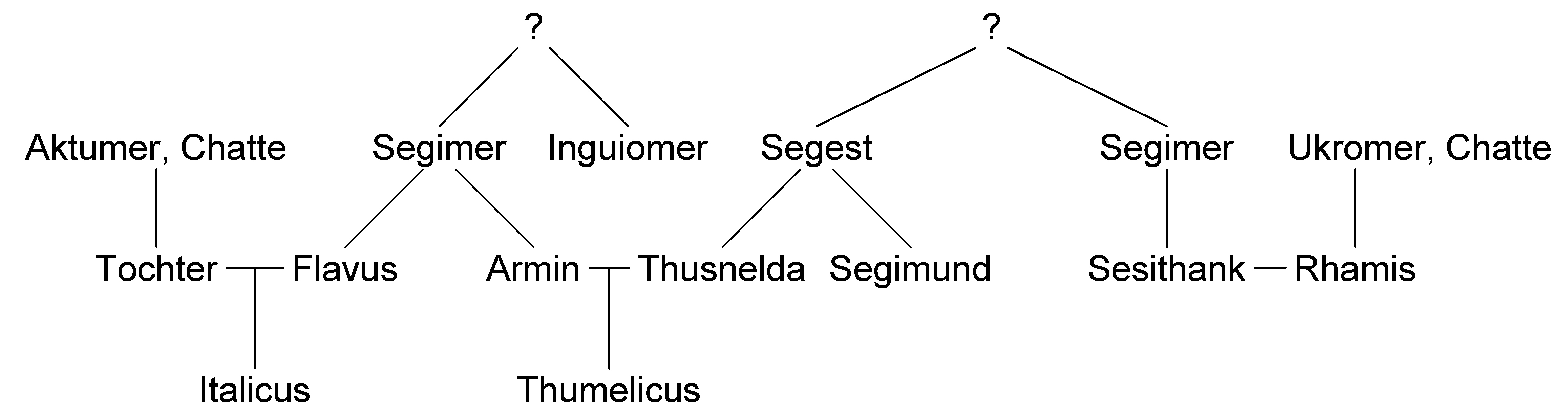
Arminius
Arminius ( 18/17 BC – 21 AD) was a chieftain of the Germanic Cherusci tribe who is best known for commanding an alliance of Germanic tribes at the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest in 9 AD, in which three Roman legions under the command of general Publius Quinctilius Varus were destroyed. His victory at Teutoburg Forest would precipitate the Roman Empire's permanent strategic withdrawal from Germania Magna. Modern historians have regarded Arminius' victory as one of Rome's greatest defeats. As it prevented the Romanization of Germanic peoples east of the Rhine, it has also been considered one of the most decisive battles in history and a turning point in human history. Born a prince of the Cherusci tribe, Arminius was part of the Roman friendly faction of the tribe. He learned Latin and served in the Roman military, which gained him Roman citizenship and the rank of ''eques''. After serving with distinction in the Great Illyrian Revolt, he was sent to Germania to aid the loc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Numidian Cavalry
Numidian cavalry was a type of light cavalry developed by the Numidians. After they were used by Hannibal during the Second Punic War, they were described by the Roman historian Livy as "by far the best horsemen in Africa." History Numidian cavalry is first mentioned by Polybius as part of the Carthaginian army during the First Punic War. The Numidian cavalry's horses, ancestors of the Berber horse, were small compared to other horses of the era, and were well adapted for faster movement over long distances.Epona Numidian horsemen rode without s or s, controlling their mounts with a simple rope around their hor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman War Elephants
Due to the Roman focus on infantry and its discipline, war elephants were rarely used. While the Romans did eventually adopt them, and used them occasionally after the Punic wars, especially during the conquest of Greece, they fell out of use by the time of Claudius, after which they were generally used for the purpose of demoralizing enemies instead of being used for tactical purposes. The Romans occasionally used them for transport. History History of elephants and Rome Although the use of war elephants in the Mediterranean is most famously associated with the wars between Carthage and Rome, the introduction of war elephants was primarily the result of the Greek kingdom of Epirus. King Pyrrhus of Epirus brought twenty elephants to attack the Romans at the battle of Heraclea in 280 BC, leaving some fifty additional animals, on loan from Pharaoh Ptolemy II, on the mainland. The Romans were unprepared for fighting elephants, and the Epirot forces routed the Romans. The next year, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quintus Fabius Maximus Servilianus (consul 142 BC)
Quintus Fabius Maximus Servilianus was the adoptive son of Quintus Fabius Maximus Aemilianus and the natural son of Gnaeus Servilius Caepio (consul in 169 BC)--hence the adoptive cognomen Servilianus. He was consul of the Roman Republic in 142 BC together with Lucius Caecilius Metellus Calvus. He was the brother of Gnaeus Servilius Caepio (consul of 141 BC and censor in 125) and Quintus Servilius Caepio (consul in 140 BC). All three brothers were commanders in the Roman Province of Hispania Ulterior (Further Spain) and fought in the Lusitanian War. Servilianus was born into the patrician gens Servilia before his adoption. His early career is unknown, but it is speculated that he would have been elected praetor by 145 BC. Servilianus was also a priest and member of the College of Pontiffs. He wrote twelve books on sacred laws. After his election as consul in 142 BC, Servilianus was sent to Hispania Ulterior and was given command of the Lusitanian War. He took with him two legion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curius And Apuleius
Curius and Apuleius were chieftains of the Lusitanians, a proto-Celtic tribe from western Hispania. They were active at the last phase of the Lusitanian War. Biography Sources describe them as heading a gang of robbers that fought Quintus Fabius Maximus Servilianus while he was entering Lusitania in the search of Viriathus. While it is generally agreed that they commanded Lusitanian forces, their nationality is disputed due to their ostensibly Roman names. It has been argued they might have been either Romanized Iberians or Roman deserters who had adopted local tribal customs. Their relation to Viriathus is also a blurred matter. Oral tradition have them serving as lieutenants to the Lusitanian leader, but it is more likely they were independent rebels from the lands south of the Tajo river, inspired by but not affiliated to Viriathus. In any case, the large size of their forces is considered proof that they were authentic military commanders and not mere bandits. In 140 BC, aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guadiaro (river)
The Guadiaro is a river in the Spanish provinces of Cádiz and Málaga in the autonomous community of Andalusia, Spain. It flows southward from the Sierra Bermeja through the Sierra de Grazalema and discharges into the Mediterranean at Sotogrande. The river is notable for having some of the only marshland on the Costa del Sol. This marsh is protected by a nature preserve. There are several towns and communities near its mouth, Pueblonuevo de Guadiaro, Guadiaro, Torreguadiaro, Sotogrande, San Enrique, and Venta Nueva, all located within the San Roque municipality. See also * List of rivers of Spain This is an incomplete list of rivers that are at least partially in Spain. The rivers flowing into the sea are sorted along the coast. Rivers flowing into other rivers are listed by the rivers they flow into. Rivers in the mainland Iberian Peninsu ... References External links News and Information about Río Guadiaro(Spanish) Rivers of Spain Rivers of Andalusia {{ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viriathus
Viriathus (also spelled Viriatus; known as Viriato in Portuguese and Spanish; died 139 BC) was the most important leader of the Lusitanian people that resisted Roman expansion into the regions of western Hispania (as the Romans called it) or western Iberia (as the Greeks called it), where the Roman province of Lusitania would be finally established after the conquest. Viriathus developed alliances with other Celtic groups, even far away from his usual theatres of war, inducing them to rebel against Rome. He led his army, supported by most of the Lusitanian and Vetton tribes as well as by other Celtic and Iberian allies, to several victories over the Romans between 147 BC and 139 BC before being betrayed by them and murdered while sleeping. Of him, Theodor Mommsen said, "It seemed as if, in that thoroughly prosaic age, one of the Homeric heroes had reappeared." Etymology There are several possible etymologies for the name Viriathus. The name can be composed of two elements: '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lusitanians
The Lusitanians ( la, Lusitani) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people living in the west of the Iberian Peninsula prior to its conquest by the Roman Republic and the subsequent incorporation of the territory into the Roman province of Lusitania. History Origins Frontinus mentions Lusitanian leader Viriathus as the leader of the Celtiberians, in their war against the Romans. The Greco-Roman historian Diodorus Siculus attributed them a name of another List of ancient Celtic peoples and tribes, Celtic tribe: "Those who are called Lusitanians are the bravest of all Cimbri", often thought of as Germanic. The Lusitanians were also called Belitanians, according to the diviner Artemidorus. . [S.l.]: Real Academia de la Historia, 2000. 33 p. vol. 6 of Bibliotheca archaeologica hispana, v. 6 of Publicaciones del Gabinete de Antigüedades. Strabo differentiated the Lusitanians from the Iberians, Iberian tribes and called them Celts who had been known as Oestri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kill Zone
In military tactics, the kill zone, also known as killing zone, is an area entirely covered by direct and effective fire, an element of ambush within which an approaching enemy force is trapped and destroyed. The objective of the ambush force is to quickly kill or capture all enemy soldiers inside the kill zone. The trapped soldiers may respond by counterattacking. The term is used in the analogous non-lethal sense in paintball and airsoft tactics. Practice Ambush The kill zone is an element of point ambush in which a military unit targets a single area with offensive fire such as mines, demolitions and section-level weapons. The kill zone may be bordered by obstacles, traps or indirect fire (artillery or mortars) to keep the enemy from escaping. In an area ambush, related multiple kill zones will be covered by multiple kill teams. The weapons of the kill team are not fired until the majority of the enemy unit is within the kill zone, ideally all of the targeted unit. Direct a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Cohesion
Unit cohesion is a military concept, defined by one former United States Chief of staff in the early 1980s as "the bonding together of soldiers in such a way as to sustain their will and commitment to each other, the unit, and mission accomplishment, despite combat or mission stress"."Morale and Cohesion in Military Psychiatry, Fred Manningp.4in ''Military Psychiatry: Preparing in Peace for War'', ; Manning cites Meyer, EC, "The unit", ''Defense'', 1982;82(February):1-9 This concept lacks a consensus definition among military analysts, sociologists and psychologists, however.Brian Palmer (2010)"Pentagon Sees Little Risk in Allowing Gay Men and Women to Serve Openly"Slate, Dec. 1, 2010 History Unit cohesion is a military concept dating back to at least Carl von Clausewitz, if not to antiquity. Several scholars have cited the influence of Sigmund Freud's thinking on theories of unit cohesion. A number of them noted that Freud wrote of cohesion breakdown among soldiers, asserting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_01.jpg)
