|
Amanita Spreta
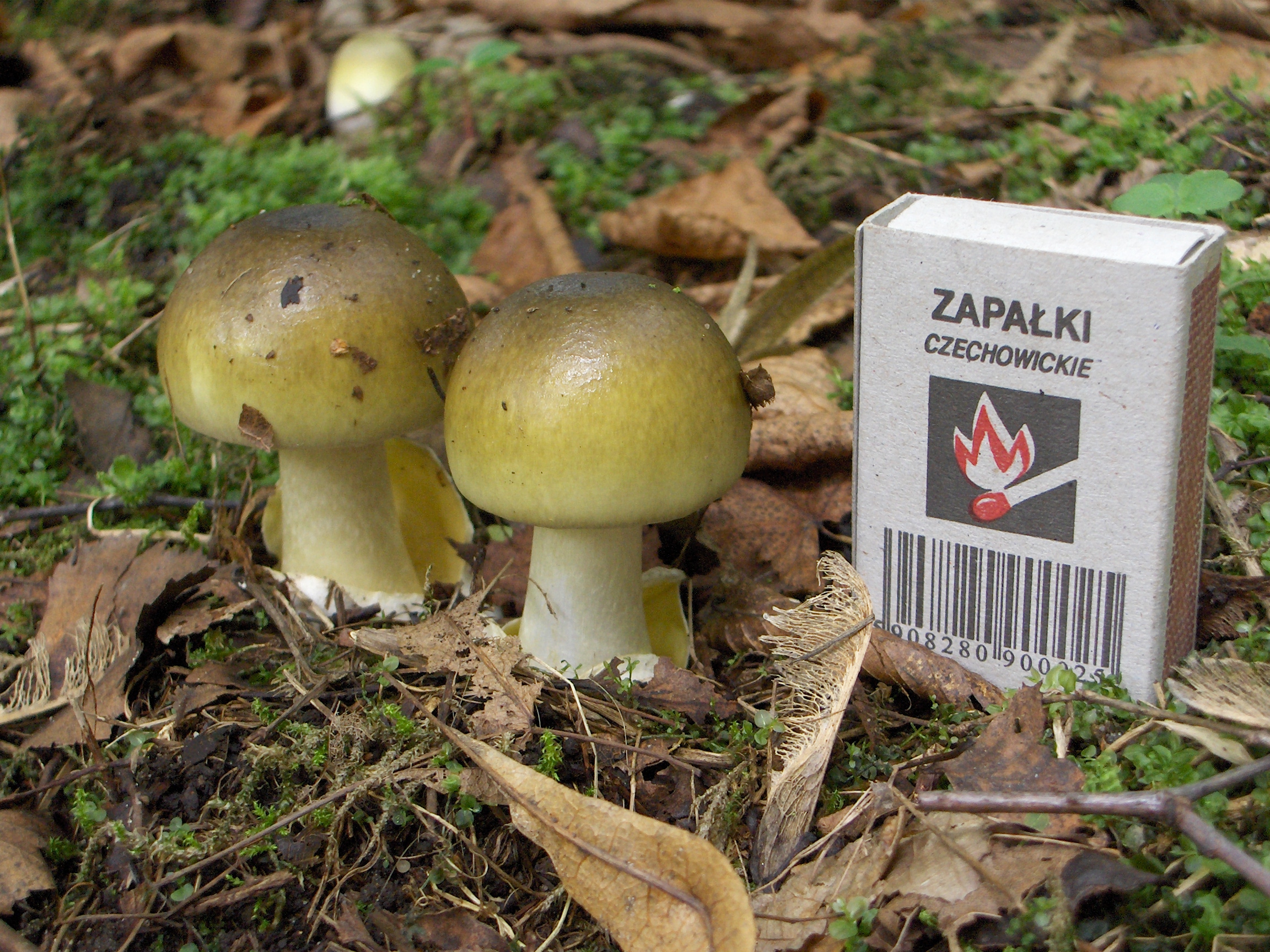
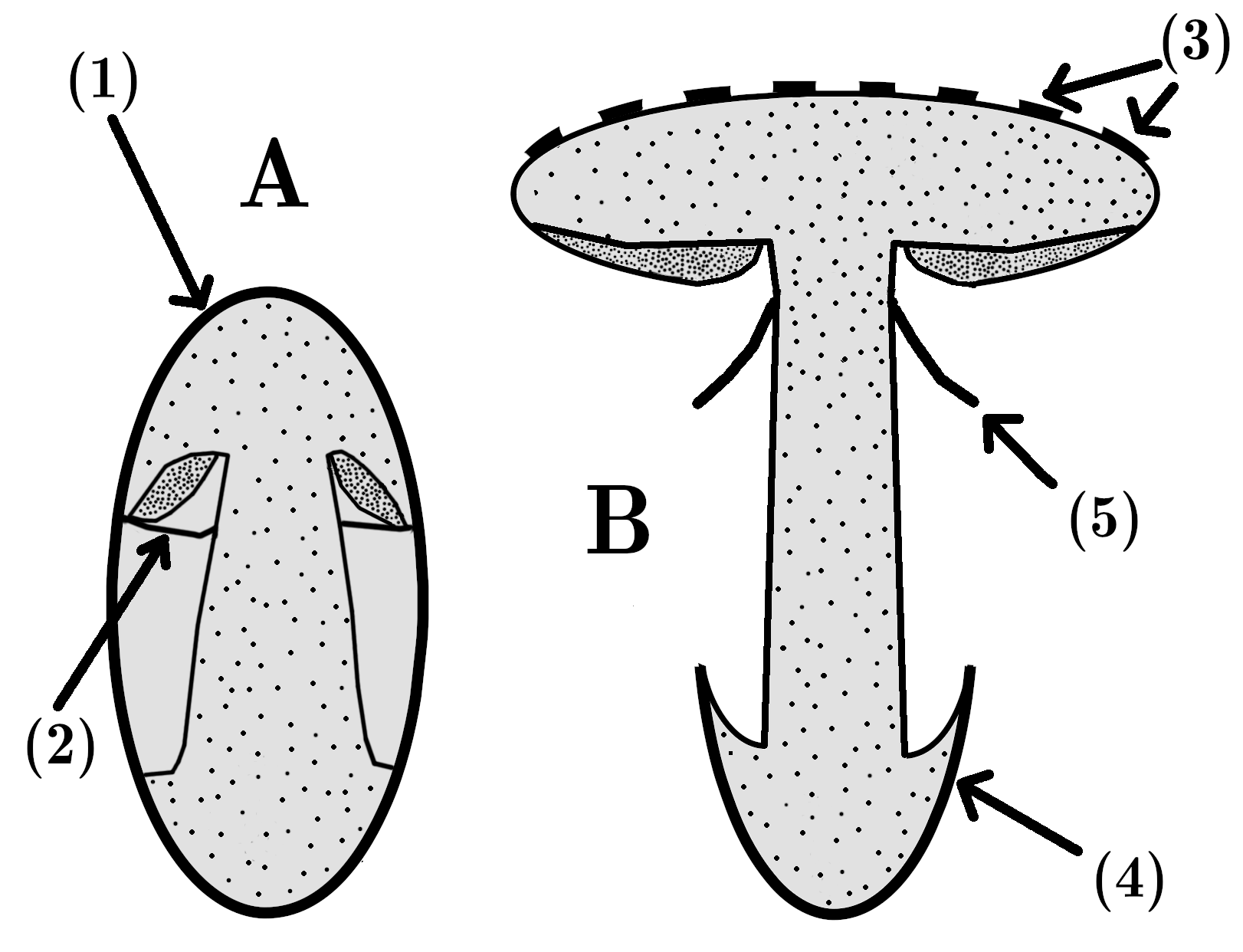
''Amanita spreta'' or the hated amanita is an inedible species of the genus ''Amanita The genus ''Amanita'' contains about 600 species of agarics, including some of the most toxic known mushrooms found worldwide, as well as some well-regarded edible species. This genus is responsible for approximately 95% of the fatalities result ...''. Description ''Amanita spreta'' is usually distinguished by its grayish brown cap with dark, radial streaks; its medium to large size, the presence of a ring on the upper stem, and its stem base, in which it features a white, sacklike volva and is not prominently swollen. Its ellipsoid, inamyloid spores also help to distinguish it. Cap The cap of ''A. spreta'' measures around 58 – 154 mm (5.8 - 15.4 cm) wide, with whitish or pallid tints of gray and/or brown at first, often darkening to gray-brown or brown-gray, often darkest in the center, often white or nearly white at the margin, having minute colorless spots and/or gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amanita
The genus ''Amanita'' contains about 600 species of agarics, including some of the most toxic known mushrooms found worldwide, as well as some well-regarded edible species. This genus is responsible for approximately 95% of the fatalities resulting from mushroom poisoning, with the death cap accounting for about 50% on its own. The most potent toxin present in these mushrooms is α-Amanitin. The genus also contains many edible mushrooms, but mycologists discourage mushroom hunters, other than experts, from selecting any of these for human consumption. Nonetheless, in some cultures, the larger local edible species of ''Amanita'' are mainstays of the markets in the local growing season. Samples of this are ''Amanita zambiana'' and other fleshy species in central Africa, ''Amanita basii, A. basii'' and similar species in Mexico, ''Amanita caesarea, A. caesarea'' and the "Blusher" ''Amanita rubescens'' in Europe, and ''Amanita chepangiana, A. chepangiana'' in South-East Asia. Other s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volva (mycology)
In mycology, a volva is a cup-like structure at the base of a mushroom that is a remnant of the universal veil, or the remains of the peridium that encloses the immature fruit bodies of gasteroid fungi. This macrofeature is important in wild mushroom identification because it is an easily observed, taxonomically significant feature that frequently signifies a member of Amanitaceae. This has particular importance due to the disproportionately high number of deadly poisonous species contained within that family. A mushroom's volva is often partially or completely buried in the ground, and therefore care must be taken to check for its presence when identifying mushrooms. Cutting or pulling mushrooms and attempting to identify them later without having noted this feature could be a fatal error. References {{Reflist, refs= {{cite book , vauthors=Kirk PM, Cannon PF, Minter DW, Stalpers JA , title=Dictionary of the Fungi , edition=10th , publisher=CAB International , location=Wallin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cap (mycology)
The pileus is the technical name for the cap, or cap-like part, of a basidiocarp or ascocarp (fungal fruiting body) that supports a spore-bearing surface, the hymenium.Moore-Landecker, E: "Fundamentals of the Fungi", page 560. Prentice Hall, 1972. The hymenium (hymenophore) may consist of lamellae, tubes, or teeth, on the underside of the pileus. A pileus is characteristic of agarics, boletes, some polypores, tooth fungi, and some ascomycetes. Classification Pilei can be formed in various shapes, and the shapes can change over the course of the developmental cycle of a fungus. The most familiar pileus shape is hemispherical or ''convex.'' Convex pilei often continue to expand as they mature until they become flat. Many well-known species have a convex pileus, including the button mushroom, various ''Amanita'' species and boletes. Some, such as the parasol mushroom, have distinct bosses or umbos and are described as ''umbonate''. An umbo is a knobby protrusion at the center of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbonate
'' Cantharellula umbonata'' has an umbo. The cap of '' Psilocybe makarorae'' is acutely papillate.">papillate.html" ;"title="Psilocybe makarorae'' is acutely papillate">Psilocybe makarorae'' is acutely papillate. An umbo is a raised area in the center of a mushroom cap. pileus (mycology), Caps that possess this feature are called ''umbonate''. Umbos that are sharply pointed are called ''acute'', while those that are more rounded are ''broadly umbonate''. If the umbo is elongated, it is ''cuspidate'', and if the umbo is sharply delineated but not elongated (somewhat resembling the shape of a human areola The human areola (''areola mammae'', or ) is the pigmented area on the breast around the nipple. Areola, more generally, is a small circular area on the body with a different histology from the surrounding tissue, or other small circular ar ...), it is called '' mammilate'' or ''papillate''. References {{reflist Fungal morphology and anatomy Mycology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Striate
In geology, a striation is a groove, created by a geological process, on the surface of a rock or a mineral. In structural geology, striations are linear furrows, or linear marks, generated from fault movement. The striation's direction reveals the movement direction in the fault plane. Similar striations, called glacial striations, can occur in areas subjected to glaciation. Striations can also be caused by underwater landslides. Striations can also be a growth pattern or mineral habit that looks like a set of hairline grooves, seen on crystal faces of certain minerals. Examples of minerals that can show growth striations include pyrite, feldspar, quartz, tourmaline, chalcocite and sphalerite. Glacial Striations The surface of rocks can have an altered appearance as a result of the movement of ice. They can show a polished looking surface scarred with glacial striations. Often these striations carved into the bedrock extend for long distances. The scars are a result of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volva (mycology)
In mycology, a volva is a cup-like structure at the base of a mushroom that is a remnant of the universal veil, or the remains of the peridium that encloses the immature fruit bodies of gasteroid fungi. This macrofeature is important in wild mushroom identification because it is an easily observed, taxonomically significant feature that frequently signifies a member of Amanitaceae. This has particular importance due to the disproportionately high number of deadly poisonous species contained within that family. A mushroom's volva is often partially or completely buried in the ground, and therefore care must be taken to check for its presence when identifying mushrooms. Cutting or pulling mushrooms and attempting to identify them later without having noted this feature could be a fatal error. References {{Reflist, refs= {{cite book , vauthors=Kirk PM, Cannon PF, Minter DW, Stalpers JA , title=Dictionary of the Fungi , edition=10th , publisher=CAB International , location=Wallin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |