|
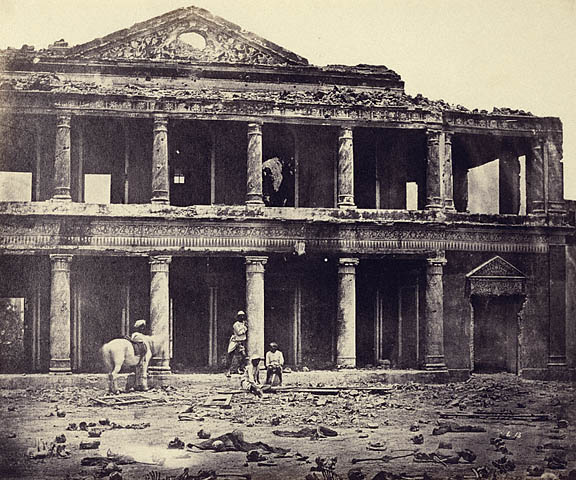
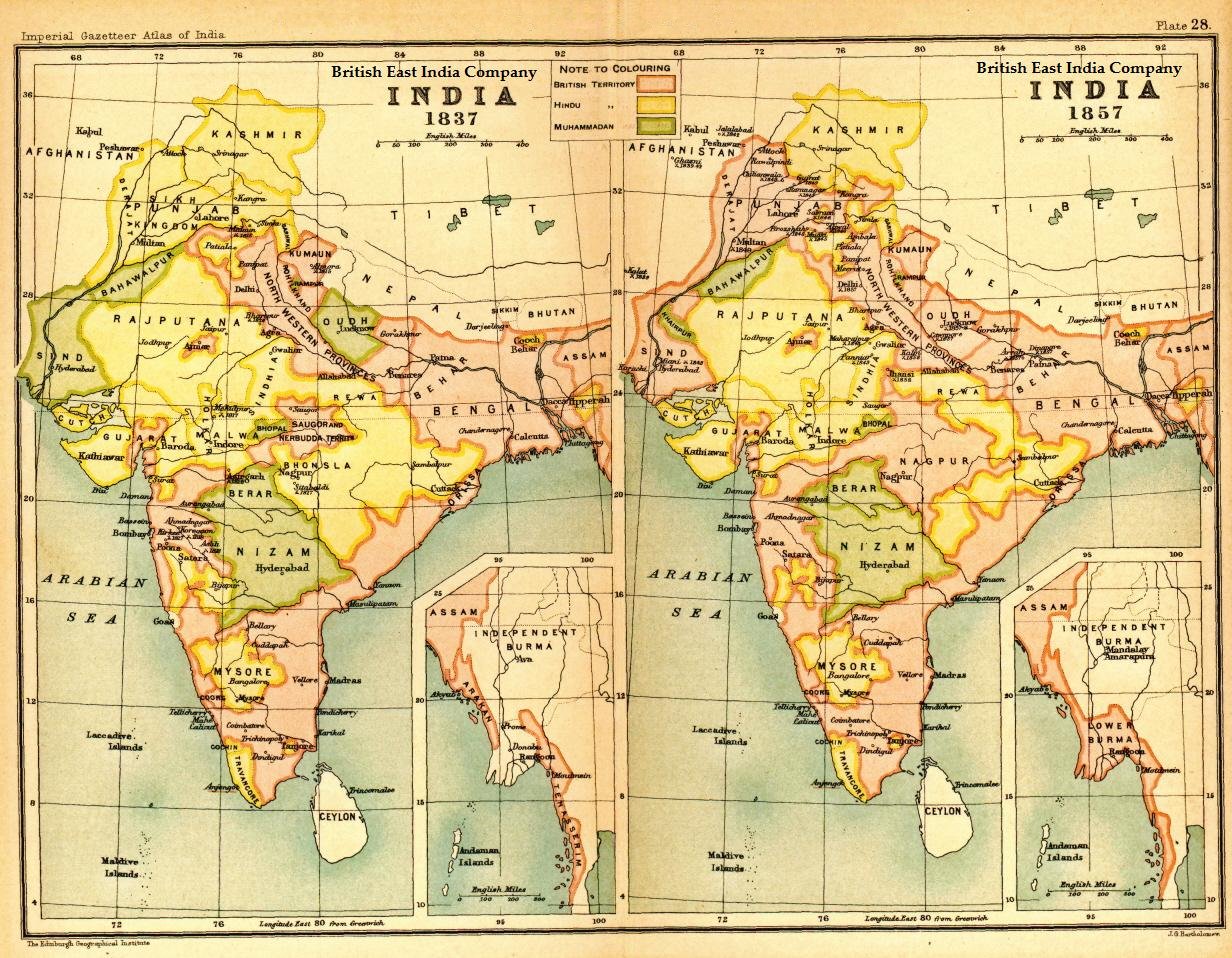
Alumbagh
Alambagh (Hindi: आलमबाग़, ) is a settlement located in Lucknow near Kanpur road in India. It is one of the most important residential and commercial areas of Lucknow and also one of the densely populated areas of the city. Alambagh falls in the Lucknow Cantonment constituency. History Earlier Alambagh contained a palace, a mosque and other buildings, as well as a beautiful garden. Alambagh was converted into a fort in November 1857 during the Indian mutiny of 1857."Alambagh" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes, 1961, Vol. 1, p. 212. The fort, under the command of General Outram was attacked repeatedly, but unsuccessfully until March 1858 when Sir Colin Campbell returned to attack Lucknow. After the British defeated the mutineers it served as the military command center for Lucknow and the nearby towns. Present Alambagh is towards the south end of Lucknow and serves as a common market place for surrounding villages. Farmers from nearby village ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Grant (soldier)
Robert Grant VC (1837 – 23 November 1874) was an English recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest and most prestigious award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth forces. Military service Grant was approximately 20 years old, and a corporal (subsequently promoted to sergeant) in the 1st Battalion, 5th Regiment of Foot (later The Northumberland Fusiliers), British Army during the Indian Mutiny when the following deed took place at Alumbagh for which he was awarded the VC. The citation was published in ''The London Gazette'' of 19 June 1860, and initially Grant was incorrectly named as Ewart, which was corrected in a subsequent ''Gazette'' of 12 October 1860. The citation read: Police service He later became a constable in the Metropolitan Police, and served in the Y Division Holloway area until his death of what was then commonly known as consumption in 1874. He was buried, at the expense of the parish, in a pauper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Newnes Ltd
George Newnes Ltd is a British publisher. The company was founded in 1891 by George Newnes (1851–1910), considered a founding father of popular journalism. Newnes published such magazines and periodicals as ''Tit-Bits'', ''The Wide World Magazine'', '' The Captain'', ''The Strand Magazine'', ''The Grand Magazine'', ''John O'London's Weekly'', '' Sunny Stories for Little Folk'', ''Woman's Own'', and the ''"Practical"'' line of magazines overseen by editor Frederick J. Camm. Long after the founder's death, Newnes was known for publishing ground-breaking consumer magazines such as ''Nova''. Newnes published books by such authors as Enid Blyton, Hall Caine, Richmal Crompton, Sir Arthur Conan Doyle, George Goodchild, W. E. Johns, P. G. Wodehouse, and John Wyndham. Initially an independent publisher, Newnes became an imprint of the International Publishing Company in 1961. Today, books under the Newnes imprint continue to be published by Elsevier. History Origins Founder George ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir James Outram
Lieutenant-General Sir James Outram, 1st Baronet (29 January 1803 – 11 March 1863) was a British general who fought in the Indian Rebellion of 1857. Early life James Outram was the son of Benjamin Outram of Butterley Hall, Butterley, Derbyshire, a civil engineer, and Margaret Anderson, a daughter of James Anderson of Hermiston a Scottish writer on agriculture. His father died in 1805, and his mother moved to Aberdeenshire in 1810. From Udny school the boy went in 1818 to the Marischal College, Aberdeen and in 1819 an Indian cadetship was given to him. Soon after his arrival at Bombay his remarkable energy attracted notice, and in July 1820 he became acting adjutant to the first battalion of the 12th regiment on its embodiment at Poona, an experience which he found to be of immense advantage to him later in his career. Khandesh - 1825 In 1825, he was sent to Khandesh, where he trained a light infantry corps, formed of the Bhils, a tribe native to the densely forested hills ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Lucknow
The siege of Lucknow was the prolonged defence of the British Residency within the city of Lucknow from rebel sepoys (Indian soldiers in the British East India Company's Army) during the Indian Rebellion of 1857. After two successive relief attempts had reached the city, the defenders and civilians were evacuated from the Residency, which was then abandoned. Background to the siege The state of Oudh/Awadh had been annexed by the British East India Company and the Nawab Wajid Ali Shah was exiled to Calcutta the year before the rebellion broke out. This high-handed action by the East India Company was greatly resented within the state and elsewhere in India. The first British Commissioner (in effect the governor) appointed to the newly acquired territory was Coverley Jackson. He behaved tactlessly, and Sir Henry Lawrence, a very experienced administrator, took up the appointment only six weeks before the rebellion broke out. The sepoys of the East India Company's Bengal Preside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Mutiny
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major uprising in India in 1857–58 against the rule of the British East India Company, which functioned as a sovereign power on behalf of the British Crown. The rebellion began on 10 May 1857 in the form of a mutiny of sepoys of the Company's army in the garrison town of Meerut, northeast of Delhi. It then erupted into other mutinies and civilian rebellions chiefly in the upper Gangetic plain and central India, though incidents of revolt also occurred farther north and east. The rebellion posed a considerable threat to British power in that region, and was contained only with the rebels' defeat in Gwalior on 20 June 1858., , and On 1 November 1858, the British granted amnesty to all rebels not involved in murder, though they did not declare the hostilities to have formally ended until 8 July 1859. Its name is contested, and it is variously described as the Sepoy Mutiny, the Indian Mutiny, the Great Rebellion, the Revolt of 1857, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colin Campbell, 1st Baron Clyde
Field Marshal Colin Campbell, 1st Baron Clyde, (20 October 1792– 14 August 1863), was a British Army officer. After serving in the Peninsular War and the War of 1812, he commanded the 98th Regiment of Foot during the First Opium War and then commanded a brigade during the Second Anglo-Sikh War. He went on to command the Highland Brigade at the Battle of Alma and with his " thin red line of Highlanders" he repulsed the Russian attack on Balaclava during the Crimean War. At an early stage of the Indian Mutiny, he became Commander-in-Chief, India and, in that role, he relieved and then evacuated Lucknow and, after attacking and decisively defeating Tatya Tope at the Second Battle of Cawnpore, captured Lucknow again. Whilst still commander-in-chief he dealt with the "White Mutiny" among East India Company troops, and organised the army sent east in the Second Opium War. Historian Adrian Greenwood argued in a 2015 biography of Campbell that he was a much more effective and si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir James Outram, 1st Baronet
Lieutenant-General Sir James Outram, 1st Baronet (29 January 1803 – 11 March 1863) was a British general who fought in the Indian Rebellion of 1857. Early life James Outram was the son of Benjamin Outram of Butterley Hall, Butterley, Derbyshire, a civil engineer, and Margaret Anderson, a daughter of James Anderson of Hermiston a Scottish writer on agriculture. His father died in 1805, and his mother moved to Aberdeenshire in 1810. From Udny school the boy went in 1818 to the Marischal College, Aberdeen and in 1819 an Indian cadetship was given to him. Soon after his arrival at Bombay his remarkable energy attracted notice, and in July 1820 he became acting adjutant to the first battalion of the 12th regiment on its embodiment at Poona, an experience which he found to be of immense advantage to him later in his career. Khandesh - 1825 In 1825, he was sent to Khandesh, where he trained a light infantry corps, formed of the Bhils, a tribe native to the densely forested hills of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chambers's Encyclopædia
''Chambers's Encyclopaedia'' was founded in 1859Chambers, W. & R"Concluding Notice"in ''Chambers's Encyclopaedia''. London: W. & R. Chambers, 1868, Vol. 10, pp. v–viii. by William Chambers (publisher), William and Robert Chambers (publisher, born 1802), Robert Chambers of Edinburgh and became one of the most important English language encyclopaedias of the 19th and 20th centuries, developing a reputation for accuracy and scholarliness that was reflected in other works produced by the Chambers Harrap, Chambers publishing company. The encyclopaedia is no longer produced. A selection of illustrations and woodblocks used to produce the first two editions of the encyclopaedia can be seen on digital resourcehosted on thNational Museums Scotland website ''Chambers's Information for the People'' Before publishing an encyclopedia, Chambers produced a smaller publication, ''Chambers's Information for the People''. This began as a serial publication in 1835. Like the ''Penny Cyclop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Rebellion Of 1857
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major uprising in India in 1857–58 against the rule of the British East India Company, which functioned as a sovereign power on behalf of the British Crown. The rebellion began on 10 May 1857 in the form of a mutiny of sepoys of the Company's army in the garrison town of Meerut, northeast of Delhi. It then erupted into other mutinies and civilian rebellions chiefly in the upper Gangetic plain and central India, though incidents of revolt also occurred farther north and east. The rebellion posed a considerable threat to British power in that region, and was contained only with the rebels' defeat in Gwalior on 20 June 1858., , and On 1 November 1858, the British granted amnesty to all rebels not involved in murder, though they did not declare the hostilities to have formally ended until 8 July 1859. Its name is contested, and it is variously described as the Sepoy Mutiny, the Indian Mutiny, the Great Rebellion, the Revolt of 1857, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garden
A garden is a planned space, usually outdoors, set aside for the cultivation, display, and enjoyment of plants and other forms of nature. The single feature identifying even the wildest wild garden is ''control''. The garden can incorporate both natural and artificial materials. Gardens often have design features including statuary, follies, pergolas, trellises, stumperies, dry creek beds, and water features such as fountains, ponds (with or without fish), waterfalls or creeks. Some gardens are for ornamental purposes only, while others also produce food crops, sometimes in separate areas, or sometimes intermixed with the ornamental plants. Food-producing gardens are distinguished from farms by their smaller scale, more labor-intensive methods, and their purpose (enjoyment of a hobby or self-sustenance rather than producing for sale, as in a market garden). Flower gardens combine plants of different heights, colors, textures, and fragrances to create interest and delight the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |