|
Altmetrics
In scholarly and scientific publishing, altmetrics are non-traditional bibliometrics proposed as an alternative or complement to more traditional citation impact metrics, such as impact factor and ''h''-index. The term altmetrics was proposed in 2010, as a generalization of article level metrics, and has its roots in the #altmetrics hashtag. Although altmetrics are often thought of as metrics about articles, they can be applied to people, journals, books, data sets, presentations, videos, source code repositories, web pages, etc. Altmetrics use public APIs across platforms to gather data with open scripts and algorithms. Altmetrics did not originally cover citation counts, but calculate scholar impact based on diverse online research output, such as social media, online news media, online reference managers and so on. It demonstrates both the impact and the detailed composition of the impact. Altmetrics could be applied to research filter, promotion and tenure dossiers, grant a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altmetrics
In scholarly and scientific publishing, altmetrics are non-traditional bibliometrics proposed as an alternative or complement to more traditional citation impact metrics, such as impact factor and ''h''-index. The term altmetrics was proposed in 2010, as a generalization of article level metrics, and has its roots in the #altmetrics hashtag. Although altmetrics are often thought of as metrics about articles, they can be applied to people, journals, books, data sets, presentations, videos, source code repositories, web pages, etc. Altmetrics use public APIs across platforms to gather data with open scripts and algorithms. Altmetrics did not originally cover citation counts, but calculate scholar impact based on diverse online research output, such as social media, online news media, online reference managers and so on. It demonstrates both the impact and the detailed composition of the impact. Altmetrics could be applied to research filter, promotion and tenure dossiers, grant a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bibliometrics
Bibliometrics is the use of statistical methods to analyse books, articles and other publications, especially in regard with scientific contents. Bibliometric methods are frequently used in the field of library and information science. Bibliometrics is closely associated with scientometrics, that is the analysis of scientific metrics and indicators, to the point that both fields largely overlap. Bibliometrics studies first appeared in the late 19th century. They have known a significative development after the Second World War in a context of "periodical crisis" and new technical opportunities offered by computing tools. In the early 1960s, the Science Citation Index of Eugene Garfield and the citation network analysis of Derek John de Solla Price laid the fundamental basis of a structured research program on bibliometrics. Citation analysis is a commonly used bibliometric method which is based on constructing the citation graph, a network or graph representation of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altmetric
Altmetric, or altmetric.com, is a data science company that tracks where published research is mentioned online, and provides tools and services to institutions, publishers, researchers, funders and other organisations to monitor this activity, commonly referred to as altmetrics. Altmetric was recognized by European Commissioner Máire Geoghegan-Quinn in 2014 as a company challenging the traditional reputation systems. Altmetric is a portfolio company of Digital Science, which is owned by Holtzbrinck Publishing Group. History Altmetric was founded by Euan Adie in 2011. Previously a researcher, Adie had already worked on Postgenomic.com, an open source scientific blog aggregator founded in 2006. In 2011, Adie entered an altmetrics app into Elsevier's Apps for Science competition and won. The prize money enabled Altmetric to develop a full version of the Altmetric Explorer, released in February 2012. In July 2012, Altmetric took on additional investment from Digital Science an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plum Analytics
Plum Analytics is a Philadelphia, Pennsylvania-based altmetrics company dedicated to measuring the influence of scientific research. History It was founded in 2011 by Andrea Michalek, who is its current president, and Mike Buschman. It was acquired by Elsevier in February 2017, which purchased it from EBSCO Information Services for an undisclosed amount. Its metrics were immediately incorporated into Elsevier's existing products, including Mendeley and Scopus. Product and services PlumX Plum Analytics is best known for PlumX, which was the company's first product. PlumX is an online tool that provides altmetrics for peer-reviewed journal articles and other scholarly works by aggregating information from different sources. In August 2015, Plum Analytics released the "PlumX Suite", which consists of five separate products: Metrics, Dashboards, +Grants, Benchmarks, and Funding Opportunities. See also * figshare * Altmetrics In scholarly and scientific publishing, altmetric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ImpactStory
OurResearch, formerly known as ImpactStory, is a nonprofit organization which creates and distributes tools and services for libraries, institutions and researchers. The organization follows open practices with their data (to the extent allowed by providers' terms of service), code, and governance. OurResearch is funded by the Alfred P. Sloan Foundation, the National Science Foundation, and Arcadia Fund. ImpactStory ImpactStory is the first open source, web-based tool released by ''OurResearch''. It provides altmetrics to help researchers measure the impacts of their research outputs including journal articles, blog posts, datasets, and software. This aims to change the focus of the scholarly reward system to value and encourage web-native scholarship. It provides context to its metrics so that they are meaningful without knowledge of the specific dataset: for example, instead of letting the reader guess whether having five forks on GitHub is common, ImpactStory would tell that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
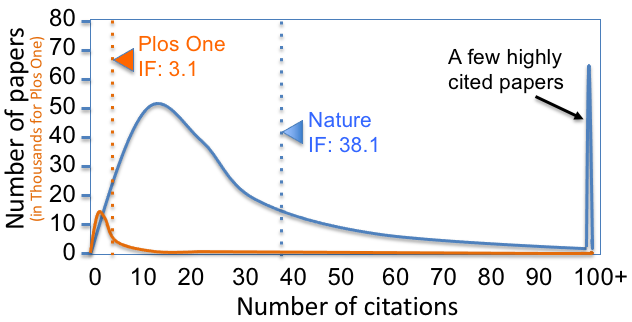
Impact Factor
The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as indexed by Clarivate's Web of Science. As a journal-level metric, it is frequently used as a proxy for the relative importance of a journal within its field; journals with higher impact factor values are given the status of being more important, or carry more prestige in their respective fields, than those with lower values. While frequently used by universities and funding bodies to decide on promotion and research proposals, it has come under attack for distorting good scientific practices. History The impact factor was devised by Eugene Garfield, the founder of the Institute for Scientific Information (ISI) in Philadelphia. Impact factors began to be calculated yearly starting from 1975 for journals listed in the ''Journal Citatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Article Level Metrics
Article-level metrics are citation metrics which measure the usage and impact of individual scholarly articles. Adoption Traditionally, bibliometrics have been used to evaluate the usage and impact of research, but have usually been focused on journal-level metrics such as the impact factor or researcher-level metrics such as the h-index. Article-level metrics, on the other hand, may demonstrate the impact of an individual article. This is related to, but distinct from, altmetrics. Starting in March 2009, the Public Library of Science introduced article-level metrics for all articles. The open access publisher PLOS provides article level metrics for all of its journals including downloads, citations, and altmetrics. In March 2014 it was announced that COUNTER statistics, which measure usage of online scholarly resources, are now available at the article level. See also *Bibliometrics *Scientometrics Scientometrics is the field of study which concerns itself with measuring and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citation
A citation is a reference to a source. More precisely, a citation is an abbreviated alphanumeric expression embedded in the body of an intellectual work that denotes an entry in the bibliographic references section of the work for the purpose of acknowledging the relevance of the works of others to the topic of discussion at the spot where the citation appears. Generally, the combination of both the in-body citation and the bibliographic entry constitutes what is commonly thought of as a citation (whereas bibliographic entries by themselves are not). Citations have several important purposes. While their uses for upholding intellectual honesty and bolstering claims are typically foregrounded in teaching materials and style guides (e.g.,), correct attribution of insights to previous sources is just one of these purposes. Linguistic analysis of citation-practices has indicated that they also serve critical roles in orchestrating the state of knowledge on a particular topic, identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Citation Impact
Citation impact is a measure of how many times an academic journal article or book or author is cited by other articles, books or authors. Citation counts are interpreted as measures of the impact or influence of academic work and have given rise to the field of bibliometrics or scientometrics, specializing in the study of patterns of academic impact through citation analysis. The journal impact factor, the two-year average ratio of citations to articles published, is a measure of the importance of journals. It is used by academic institutions in decisions about academic tenure, promotion and hiring, and hence also used by authors in deciding which journal to publish in. Citation-like measures are also used in other fields that do ranking, such as Google's PageRank algorithm, software metrics, college and university rankings, and business performance indicators. Article-level One of the most basic citation metrics is how often an article was cited in other articles, bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CiteULike
CiteULike was a web service which allowed users to save and share citations to academic papers. Based on the principle of social bookmarking, the site worked to promote and to develop the sharing of scientific references amongst researchers. In the same way that it is possible to catalog web pages (with Furl and delicious) or photographs (with Flickr), scientists could share citation information using CiteULike. Richard Cameron developed CiteULike in November 2004 and in 2006 Oversity Ltd. was established to develop and support CiteULike.CiteULike. "Frequently Asked Questions: Who is behind CiteULike?. In February 2019, CiteULike announced that it would be ceasing operations as of March 30, 2019. When browsing issues of research journals, small scripts stored in bookmarks ( bookmarklets) allowed one to import articles from repositories like PubMed, and CiteULike supported many more. Then the system attempted to determine the article metadata (title, authors, journal name, et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute For Health And Care Research
The National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) is the British government’s major funder of Clinical research, clinical, public health, Social care in England, social care and translational research. With a budget of over £1.2 billion in 2020–21, its mission is to "improve the health and wealth of the nation through research". The NIHR was established in 2006 under the government's Best Research for Best Health strategy, and is funded by the Department of Health and Social Care. As a Research funding in the United Kingdom, research funder and research partner of the National Health Service, NHS, public health and social care, the NIHR complements the work of the Medical Research Council (United Kingdom), Medical Research Council. NIHR focuses on translational research (translating discoveries from the laboratory to the clinic), clinical research and applied health and social care research. History The NIHR (originally named National Institute for Health Research) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mendeley
Mendeley is a reference manager software developed by Elsevier. It is used to manage and share research papers and generate bibliographies for scholarly articles. History The company Mendeley, named after the biologist Gregor Mendel and chemist Dmitri Mendeleev, was founded in London in November 2007 by three German PhD students. The first public beta version of the software was released in August 2008. The company's investors included some people previously involved with Last.fm, Skype, and Warner Music Group, as well as academicians from Cambridge and Johns Hopkins University. In 2009, Mendeley won several awards including Plugg.eu "European Start-up of the Year 2009", TechCrunch Europas "Best Social Innovation Which Benefits Society 2009", and The Guardian ranked it #6 in "Top 100 tech media companies". In 2012, Mendeley was one of the repositories for green Open Access recommended by Peter Suber. The recommendation was revoked after Elsevier bought Mendeley. Mendeley was pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)