|
Alternative Investment Market (AIM) Logo
AIM (formerly the Alternative Investment Market) is a sub-market of the London Stock Exchange that was launched on 19 June 1995 as a replacement to the previous Unlisted Securities Market (USM) that had been in operation since 1980. It allows companies that are smaller, less-developed, or want/need a more flexible approach to governance to float shares with a more flexible regulatory system than is applicable on the main market. At launch, AIM comprised only 10 companies valued collectively at £82.2 million. As at May 2021, 821 companies comprise the sub-market, with an average market cap of £80 million per listing. AIM has also started to become an international exchange, often due to its low regulatory burden, especially in relation to the US Sarbanes–Oxley Act (though only a quarter of AIM-listed companies would qualify to be listed on a US stock exchange even prior to passage of the Sarbanes–Oxley Act). By December 2005, over 270 foreign companies had been admitted t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternative Investment Market (AIM) Logo
AIM (formerly the Alternative Investment Market) is a sub-market of the London Stock Exchange that was launched on 19 June 1995 as a replacement to the previous Unlisted Securities Market (USM) that had been in operation since 1980. It allows companies that are smaller, less-developed, or want/need a more flexible approach to governance to float shares with a more flexible regulatory system than is applicable on the main market. At launch, AIM comprised only 10 companies valued collectively at £82.2 million. As at May 2021, 821 companies comprise the sub-market, with an average market cap of £80 million per listing. AIM has also started to become an international exchange, often due to its low regulatory burden, especially in relation to the US Sarbanes–Oxley Act (though only a quarter of AIM-listed companies would qualify to be listed on a US stock exchange even prior to passage of the Sarbanes–Oxley Act). By December 2005, over 270 foreign companies had been admitted t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FTSE AIM All-Share Index
The FTSE AIM All-Share Index was revised from the previous FTSE AIM Index on 16 May 2005, and is a stock market index consisting of all companies quoted on the Alternative Investment Market which meet the requirements for liquidity and free float In the context of stock markets, the public float or free float represents the portion of shares of a corporation that are in the hands of public investors as opposed to locked-in shares held by promoters, company officers, controlling-interest inv .... The index is reviewed quarterly, and the constituent companies may change based on market capitalisation data as at the end of February, May, August and November. The index is maintained by FTSE Russell, a subsidiary of the London Stock Exchange Group. External links AIM page on LSE siteFTSE Group websiteBloomberg page for AXX:IND Economy of the United Kingdom European stock market indices {{stockexchange-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fever-Tree
Fevertree Drinks plc, known as Fever-Tree, is a British producer of premium drink mixers, founded by Charles Rolls and Tim Warrillow in 2004. The company's name comes from its initial product, a tonic water. Their tonic was flavoured with quinine, a chemical extracted from the bark of the South American cinchona tree. When introduced to India as a pharmaceutical to aid in reducing the fever associated with malaria, quinine was blended with soda water and sugar to make it more palatable, producing the earliest tonic water. The cinchona tree was referred to in India as fever tree. Based in west London, Fever-Tree makes a variety of products, including tonic water, ginger beer and lemonade. As of March 2015, their products were exported to 50 countries. In March 2013, the founders sold 25% of the company to Lloyds Development Capital. In November 2014, the company floated on the London Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol LSE:FEVR; the IPO valued Fever-Tree at £154.4m. , its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abcam
Abcam is a producer, distributor and seller of protein research tools. History The company was founded in 1998 by Jonathan Milner with co-founders professor Tony Kouzarides and David Cleevely, with the idea of making it easier for research scientists to buy antibodies across the web. Milner was a postdoctoral researcher studying the newly discovered breast cancer protein BRCA2 in Kouzarides' Cambridge University laboratory. The project had slowed because of problems finding quality antibody reagents that had honest and up-to-date information about their uses and limitations. This scenario provided the motivation to form an on-line service that would help themselves and researchers across the globe. Since its inception in 1998, the company has diversified from carrying only antibodies. It supplies antibody related products such as immunoassays (e.g. SimpleStep ELISA Kits), peptides, proteins and protein detection products (e.g. immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining kits). Abcam also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boohoo
{{disambig ...
Boo hoo may refer to the sound of someone crying. Boo hoo may also refer to: * ''Boo Hoo'', a 2002 album by musician Voltaire * "Boo-Hoo", a 1937 hit song recorded by Guy Lombardo and His Royal Canadians * Boo Hoo the Bear, the mascot of Queen's University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada * Boohoo the Clown, a Machine Empire monster from the ''Power Rangers'' television series * Boohoo.com, a UK online fashion retailer See also * Boo (other) * Hoo (other) Hoo may refer to: People *Hoo (surname), including a list of people with the name *Thomas Hoo, Baron Hoo and Hastings (c. 1396 – 1455) Places *Hoo, Suffolk, England *Hoo Peninsula, in Kent, England **Hoo St Werburgh, or simply Hoo **Hoo Fort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ASOS '' anime television series.
{{disambiguation ...
ASOS or Asos may refer to: * Asos, a village in Greece * ASOS (retailer), a UK online fashion store * Association Sportive Oussou Saka, a Beninese football team * Automated Surface Observing System, a type of weather station * Air Support Operations Squadron, US Air Force, see List of United States Air Force air support operations squadrons * '' A Saucerful of Secrets'', the second album by Pink Floyd * ASOS Brigade, a live-action fictional group to support the English dub release of the ''Haruhi Suzumiya is a Japanese light novel series written by Nagaru Tanigawa and illustrated by Noizi Ito. It was first published in 2003 by Kadokawa Shoten in Japan with the novel ''The Melancholy of Haruhi Suzumiya'', and has since been followed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institutional Investor
An institutional investor is an entity which pools money to purchase securities, real property, and other investment assets or originate loans. Institutional investors include commercial banks, central banks, credit unions, government-linked companies, insurers, pension funds, sovereign wealth funds, charities, hedge funds, REITs, investment advisors, endowments, and mutual funds. Operating companies which invest excess capital in these types of assets may also be included in the term. Activist institutional investors may also influence corporate governance by exercising voting rights in their investments. In 2019, the world's top 500 asset managers collectively managed $104.4 trillion in Assets under Management (AuM). Although institutional investors appear to be more sophisticated than retail investors, it remains unclear if professional active investment managers can reliably enhance risk-adjusted returns by an amount that exceeds fees and expenses of investment managemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
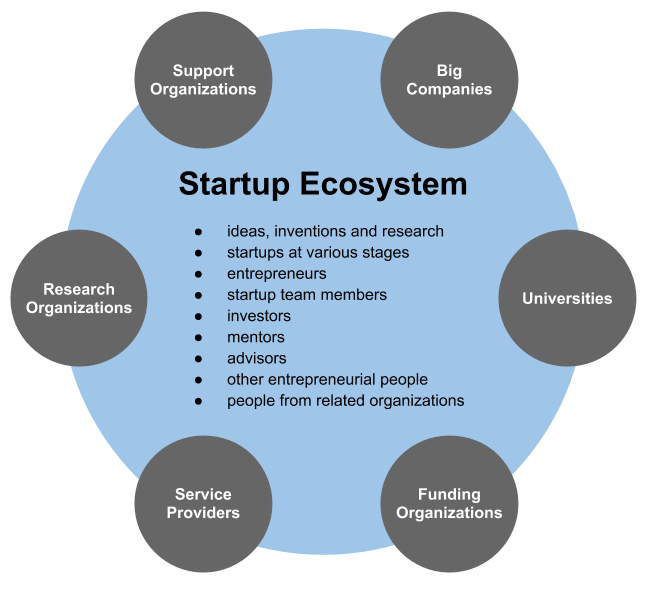
Startup Company
A startup or start-up is a company or project undertaken by an entrepreneur to seek, develop, and validate a scalable business model. While entrepreneurship refers to all new businesses, including self-employment and businesses that never intend to become registered, startups refer to new businesses that intend to grow large beyond the solo founder. At the beginning, startups face high uncertainty and have high rates of failure, but a minority of them do go on to be successful and influential.Erin Griffith (2014)Why startups fail, according to their founders Fortune.com, 25 September 2014; accessed 27 October 2017 Actions Startups typically begin by a founder (solo-founder) or co-founders who have a way to solve a problem. The founder of a startup will begin market validation by problem interview, solution interview, and building a minimum viable product (MVP), i.e. a prototype, to develop and validate their business models. The startup process can take a long period of time (by so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IFRS
International Financial Reporting Standards, commonly called IFRS, are accounting standards issued by the IFRS Foundation and the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB). They constitute a standardised way of describing the company's financial performance and position so that company financial statements are understandable and comparable across international boundaries. They are particularly relevant for companies with shares or securities listed on a public stock exchange. IFRS have replaced many different national accounting standards around the world but have not replaced the separate accounting standards in the United States where U.S. GAAP is applied. History The International Accounting Standards Committee (IASC) was established in June 1973 by accountancy bodies representing ten countries. It devised and published International Accounting Standards (IAS), interpretations and a conceptual framework. These were looked to by many national accounting standard-setter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been described as a '' sui generis'' political entity (without precedent or comparison) combining the characteristics of both a federation and a confederation. Containing 5.8per cent of the world population in 2020, the EU generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of around trillion in 2021, constituting approximately 18per cent of global nominal GDP. Additionally, all EU states but Bulgaria have a very high Human Development Index according to the United Nations Development Programme. Its cornerstone, the Customs Union, paved the way to establishing an internal single market based on standardised legal framework and legislation that applies in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where the states have agreed to act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Services Authority
The Financial Services Authority (FSA) was a quasi-judicial body accountable for the financial regulation, regulation of the financial services industry in the United Kingdom between 2001 and 2013. It was founded as the Securities and Investments Board (SIB) in 1985. Its board was appointed by the HM Treasury, Treasury, although it operated independently of government. It was structured as a company limited by guarantee and was funded entirely by fees charged to the financial services industry. Due to perceived regulatory failure of the banks during the financial crisis of 2007–2008, the Cameron–Clegg coalition, UK government decided to restructure financial regulation and abolish the FSA. On 19 December 2012, the ''Financial Services Act 2012'' received royal assent, abolishing the FSA with effect from 1 April 2013. Its responsibilities were then split between two new agencies: the Financial Conduct Authority and the Prudential Regulation Authority (United Kingdom), Prudent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nominated Adviser
A nominated adviser (NOMAD) is a firm or company which has been approved by the London Stock Exchange (LSE) as a nominated adviser for the Alternative Investment Market (AIM) and whose name has been placed on the register of nominated advisers published by the London Stock Exchange. The NOMAD project manages the admission of new issues to AIM and also acts as the effective Regulatory agency, regulator. Typically the NOMAD is a firm of investment bankers with experience of bringing companies to the market. The NOMAD performs this regulator role under licence from the LSE. This unique situation arises largely because the AIM is an exchange regulated market. External linksAIM rules for Nominated Advisers [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |