|
Alpha Persei Moving Cluster
The Alpha Persei Cluster, also known as Melotte 20 or Collinder 39, is an open cluster of stars in the northern constellation of Perseus (constellation), Perseus. To the naked eye, the cluster consists of several blue-hued spectral type B stars. The most luminous member is the ~2nd magnitude white-yellow supergiant star, supergiant Mirfak, also known as Alpha Persei. Bright members also include Delta Persei, Delta, Sigma Persei, Sigma, Psi Persei, Psi, 29, 30, 34, and 48 Persei. The Hipparcos satellite and infrared color-magnitude diagram fitting have been used to establish a distance to the cluster of ~. The distance established via the independent analyses agree, thereby making the cluster an important rung on the cosmic distance ladder. As seen from the Earth, the Extinction (astronomy), extinction of the cluster due to interstellar dust is around 0.30. The cluster is centered to the northeast of Alpha Persei. It has a core radius of , a half-mass radius of , and a tidal radius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
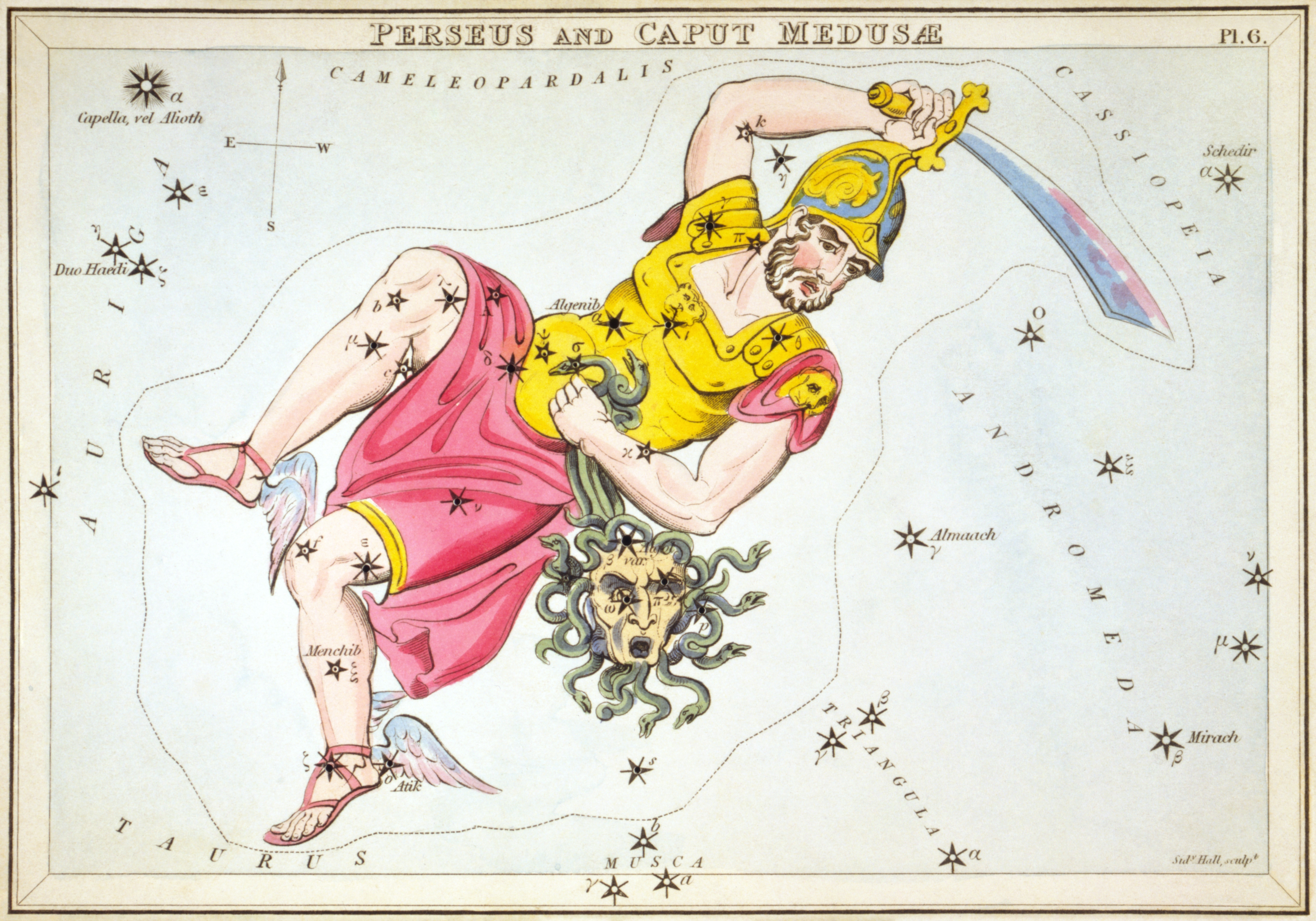
Perseus (constellation)
Perseus is a constellation in the northern sky, being named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus. It is one of the 48 ancient constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located near several other constellations named after ancient Greek legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west. Some star atlases during the early 19th century also depicted Perseus holding the disembodied head of Medusa, whose asterism was named together as ''Perseus et Caput Medusae''; however, this never came into popular usage. The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus, whose brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Core Radius
A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars. Globular clusters are bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards their centers. They can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of member stars. Their name is derived from Latin (small sphere). Globular clusters are occasionally known simply as "globulars". Although one globular cluster, Omega Centauri, was observed in antiquity and long thought to be a star, recognition of the clusters' true nature came with the advent of telescopes in the 17th century. In early telescopic observations globular clusters appeared as fuzzy blobs, leading French astronomer Charles Messier to include many of them in his catalog of astronomical objects that he thought could be mistaken for comets. Using larger telescopes, 18th-century astronomers recognized that globular clusters are groups of many individual stars. Early in the 20th century the distribution of globular clusters in the sky w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HD 21278
HD 21278 is a binary star system in the constellation Perseus, located within the million year old Alpha Persei Cluster. It has a blue-white hue and is visible to the naked eye with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.99. The system is located at a distance of approximately 580 light years from the Sun based on parallax, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +1.20 km/s. The binary nature of this star was announced in 1925 by Otto Struve. It is a double-lined spectroscopic binary with an orbital period of 21.7 days and an eccentricity of 0.12. The primary component is a B-type main-sequence star with a stellar classification of B5V, indicating it is generating energy through core hydrogen fusion. The star is spinning with a projected rotational velocity of 75 km/s. It has 4.6 times the mass of the Sun and about 3.9 times the Sun's radius. HD 21278 is radiating 940 times the luminosity of the Sun The solar lum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
45 Persei
Epsilon Persei, Latinized from ε Persei, is a multiple star system in the northern constellation of Perseus. It has a combined apparent visual magnitude of +2.88, which is bright enough to be viewed with the naked eye. Based upon parallax measurements, this system is located at a distance of roughly 640 light-years (196 parsecs) from Earth. This is a spectroscopic binary system, which means that the presence of an orbiting companion has been revealed by radial velocity variations in the spectrum of the primary. The two components are orbiting each other with a period of 14 days at a high orbital eccentricity of 0.55. The secondary component has about 6–13% of the primary's mass and may have a stellar classification in the range from A6 V to K1 V. There may be a third component to this system with an orbital period of roughly 9,428 days (25.8 years), although this has not been conclusively demonstrated. If this component exists, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epsilon Persei
Epsilon Persei, Latinized from ε Persei, is a multiple star system in the northern constellation of Perseus. It has a combined apparent visual magnitude of +2.88, which is bright enough to be viewed with the naked eye. Based upon parallax measurements, this system is located at a distance of roughly 640 light-years (196 parsecs) from Earth. This is a spectroscopic binary system, which means that the presence of an orbiting companion has been revealed by radial velocity variations in the spectrum of the primary. The two components are orbiting each other with a period of 14 days at a high orbital eccentricity of 0.55. The secondary component has about 6–13% of the primary's mass and may have a stellar classification in the range from A6 V to K1 V. There may be a third component to this system with an orbital period of roughly 9,428 days (25.8 years), although this has not been conclusively demonstrated. If this component exists, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
39 Persei
Delta Persei (Delta Per, δ Persei, δ Per) is a double star in the northern constellation of Perseus. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 3.01, making it readily visible with the naked eye. Parallax measurements give it a distance of about from the Earth. The spectrum of this star matches a stellar classification of B5 III, which indicates it is a giant star that has evolved away from the main sequence after exhausting the hydrogen at its core. It has about seven times the Sun's mass and has an estimated age of 6.8 million years. The effective temperature of the outer envelope is 14,890 K, with the energy being emitted at this temperature giving it the blue-white hue that is a characteristic of a B-type star. It is rotating rapidly with a projected rotational velocity of 190 km s−1, which gives a lower bound for the actual azimuthal velocity along the star's equator. This is most probably a binary star and may be a triple star ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
33 Persei
Alpha Persei ( Latinized from α Persei, abbreviated Alpha Per, α Per), formally named Mirfak (pronounced or ), is the brightest star in the northern constellation of Perseus, outshining the constellation's best-known star, Algol. Alpha Persei has an apparent visual magnitude of 1.8, and is a circumpolar star when viewed from mid-northern latitudes. Alpha Persei lies in the midst of a cluster of stars named as the eponymous Alpha Persei Cluster, or ''Melotte 20'', which is easily visible in binoculars and includes many of the fainter stars in the constellation. Determined distance using the trigonometric parallax, places the star from the Sun. Nomenclature ''α Persei'' is the star's Bayer designation. The star also bore the traditional names Mirfak and Algenib, which are Arabic in origin. The former, meaning 'Elbow' and also written Mirphak, Marfak or Mirzac, comes from the Arabic ''Mirfaq al-Thurayya'', while Algenib, also spelt Algeneb, Elg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's light caused by interstellar dust along the line of sight to the observer. The word ''magnitude'' in astronomy, unless stated otherwise, usually refers to a celestial object's apparent magnitude. The magnitude scale dates back to the ancient Roman astronomer Claudius Ptolemy, whose star catalog listed stars from 1st magnitude (brightest) to 6th magnitude (dimmest). The modern scale was mathematically defined in a way to closely match this historical system. The scale is reverse logarithmic: the brighter an object is, the lower its magnitude number. A difference of 1.0 in magnitude corresponds to a brightness ratio of \sqrt /math>, or about 2.512. For example, a star of magnitude 2.0 is 2.512 times as bright as a star of magnitude 3.0, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectral Type
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the rainbow of colors interspersed with spectral lines. Each line indicates a particular chemical element or molecule, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that element. The strengths of the different spectral lines vary mainly due to the temperature of the photosphere, although in some cases there are true abundance differences. The ''spectral class'' of a star is a short code primarily summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature. Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters ''O'', ''B'', ''A'', ''F'', ''G'', ''K'', and ''M'', a sequence from the hottest (''O'' type) to the coolest (''M'' type). Each letter class is then subdivide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Star Stream
This is a list of stellar streams. A stellar stream is an association of stars orbiting a galaxy that was once a globular cluster or dwarf galaxy that has now been torn apart and stretched out along its orbit by tidal forces. An exception in the list about Milky Way streams given below is the Magellanic Stream, composed of gas (mostly hydrogen). Local Group streams Milky Way streams Andromeda Galaxy streams Streams beyond the Local Group See also * Lists of astronomical objects * List of nearby stellar associations and moving groups * Field of Streams * Stellar kinematics * Galaxy merger * Local Bubble * Satellite galaxies of the Milky Way The Milky Way has several smaller galaxies gravitationally bound to it, as part of the Milky Way subgroup, which is part of the local galaxy cluster, the Local Group. There are 59 small galaxies confirmed to be within of the Milky Way, but not a ... References Further reading * External links * * * * * {{Portal bar, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
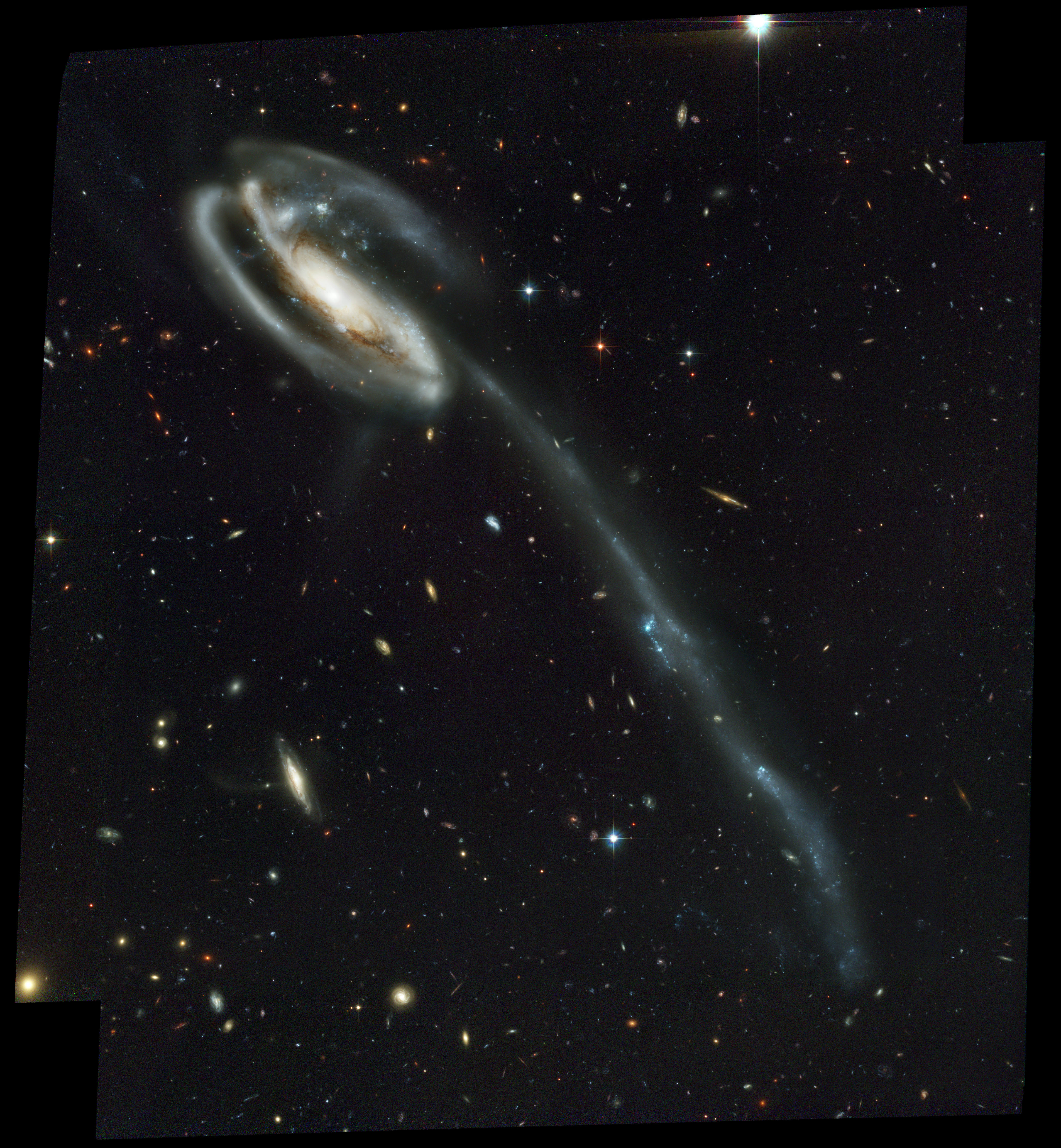
Tidal Tail
A tidal tail is a thin, elongated region of stars and interstellar gas that extends into space from a galaxy. Tidal tails occur as a result of galactic tide forces between interacting galaxies. Examples of galaxies with tidal tails include the Tadpole Galaxy and the Mice Galaxies. Tidal forces can eject a significant amount of a galaxy's gas into the tail; within the Antennae Galaxies, for example, nearly half of the observed gaseous matter is found within the tail structures. Within those galaxies which have tidal tails, approximately 10% of the galaxy's stellar formation takes place in the tail. Overall, roughly 1% of all stellar formation in the known universe occurs within tidal tails. Some interacting galaxy pairs have two distinct tails, as is the case for the Antennae Galaxies, while other systems have only one tail. Most tidal tails are slightly curved due to the rotation of the host galaxies. Those that are straight may actually be curved but still appear to be stra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Number
The atomic number or nuclear charge number (symbol ''Z'') of a chemical element is the charge number of an atomic nucleus. For ordinary nuclei, this is equal to the proton number (''n''p) or the number of protons found in the nucleus of every atom of that element. The atomic number can be used to uniquely identify ordinary chemical elements. In an ordinary uncharged atom, the atomic number is also equal to the number of electrons. For an ordinary atom, the sum of the atomic number ''Z'' and the neutron number ''N'' gives the atom's atomic mass number ''A''. Since protons and neutrons have approximately the same mass (and the mass of the electrons is negligible for many purposes) and the mass defect of the nucleon binding is always small compared to the nucleon mass, the atomic mass of any atom, when expressed in unified atomic mass units (making a quantity called the " relative isotopic mass"), is within 1% of the whole number ''A''. Atoms with the same atomic number b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |