|
Allorhizobium
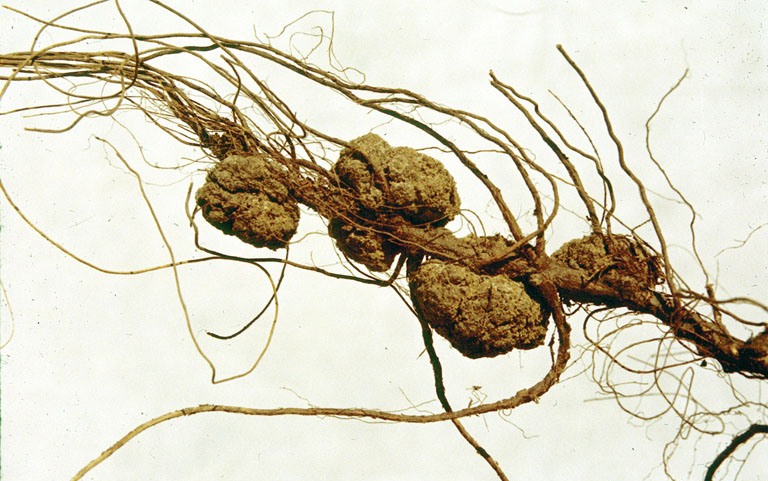
''Allorhizobium'' is a genus of Gram-negative soil bacteria. Some species of ''Allorhizobium'' form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with roots of legumes A legume () is a plant in the family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock fo ..., while others are known to cause crown gall. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Allorhizobium Rhizobiaceae Bacteria genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allorhizobium Undicola
''Allorhizobium'' is a genus of Gram-negative soil bacteria. Some species of ''Allorhizobium'' form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with roots of legumes A legume () is a plant in the family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock fo ..., while others are known to cause crown gall. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Allorhizobium Rhizobiaceae Bacteria genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allorhizobium Ampelinum
''Allorhizobium'' is a genus of Gram-negative soil bacteria. Some species of ''Allorhizobium'' form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with roots of legumes A legume () is a plant in the family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock fo ..., while others are known to cause crown gall. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Allorhizobium Rhizobiaceae Bacteria genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allorhizobium Borbori
''Allorhizobium'' is a genus of Gram-negative soil bacteria. Some species of ''Allorhizobium'' form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with roots of legumes A legume () is a plant in the family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock fo ..., while others are known to cause crown gall. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Allorhizobium Rhizobiaceae Bacteria genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allorhizobium Oryziradicis
''Allorhizobium'' is a genus of Gram-negative soil bacteria. Some species of ''Allorhizobium'' form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with roots of legumes A legume () is a plant in the family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock fo ..., while others are known to cause crown gall. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Allorhizobium Rhizobiaceae Bacteria genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allorhizobium Paknamense
''Allorhizobium'' is a genus of Gram-negative soil bacteria. Some species of ''Allorhizobium'' form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with roots of legumes A legume () is a plant in the family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock fo ..., while others are known to cause crown gall. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Allorhizobium Rhizobiaceae Bacteria genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allorhizobium Pseudoryzae
''Allorhizobium'' is a genus of Gram-negative soil bacteria. Some species of ''Allorhizobium'' form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with roots of legumes A legume () is a plant in the family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock fo ..., while others are known to cause crown gall. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Allorhizobium Rhizobiaceae Bacteria genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allorhizobium Taibaishanense
''Allorhizobium'' is a genus of Gram-negative soil bacteria. Some species of ''Allorhizobium'' form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with roots of legumes A legume () is a plant in the family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock fo ..., while others are known to cause crown gall. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Allorhizobium Rhizobiaceae Bacteria genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allorhizobium Terrae
''Allorhizobium'' is a genus of Gram-negative soil bacteria. Some species of ''Allorhizobium'' form an endosymbiotic nitrogen-fixing association with roots of legumes A legume () is a plant in the family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock fo ..., while others are known to cause crown gall. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Allorhizobium Rhizobiaceae Bacteria genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allorhizobium Vitis
''Allorhizobium vitis'' is a plant pathogen that infects grapevines. The species is best known for causing a tumor known as crown gall disease. One of the virulent strains, ''A. vitis'' S4, is responsible both for crown gall on grapevines and for inducing a hypersensitive response in other plant species. Grapevines that have been affected by crown gall disease produce fewer grapes than unaffected plants. Though not all strains of ''A. vitis'' are tumorigenic, most strains can damage plant hosts. ''A. vitis'' shares many genetic and morphological characteristics with several ''Agrobacterium'' species, including ''A. tumefaciens''. The two species have overlapping host ranges, and both ''A. vitis'' and ''A. tumefaciens'' may reduce the yield of infected crops. For this reason, research on ''A. vitis'' focuses on transmission and methods of control. Biology Identification ''A. vitis'' is a Gram-negative bacterium with a thin peptidoglycan layer in its cell wall. The species is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Gall
''Agrobacterium'' is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria established by H. J. Conn that uses horizontal gene transfer to cause tumors in plants. ''Agrobacterium tumefaciens'' is the most commonly studied species in this genus. ''Agrobacterium'' is well known for its ability to transfer DNA between itself and plants, and for this reason it has become an important tool for genetic engineering. Nomenclatural History Leading up to the 1990s, the genus ''Agrobacterium'' was used as a wastebasket taxon. With the advent of 16S sequencing, many ''Agrobacterium'' species (especially the marine species) were reassigned to genera such as ''Ahrensia'', ''Pseudorhodobacter'', ''Ruegeria'', and ''Stappia''. The remaining ''Agrobacterium'' species were assigned to three biovars: biovar 1 (''Agrobacterium tumefaciens''), biovar 2 (''Agrobacterium rhizogenes''), and biovar 3 (''Agrobacterium vitis''). In the early 2000s, ''Agrobacterium'' was synonymized with the genus ''Rhizobium''. This move pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizobiaceae
The Rhizobiaceae is a family of Pseudomonadota comprising multiple subgroups that enhance and hinder plant development. Some bacteria found in the family are used for plant nutrition and collectively make up the rhizobia. Other bacteria such as '' Agrobacterium tumefaciens'' and '' Rhizobium rhizogenes'' severely alter the development of plants in their ability to induce crown galls or hairy roots, respectively. The family has been of an interest to scientists for centuries in their ability to associate with plants and modify plant development. The Rhizobiaceae are, like all Pseudomonadota, Gram-negative. They are aerobic, and the cells are usually rod-shaped.Garrity, George M.; Brenner, Don J.; Krieg, Noel R.; Staley, James T. (eds.) (2005). Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Volume Two: The Proteobacteria, Part C: The Alpha-, Beta-, Delta-, and Epsilonproteobacteria. New York, New York: Springer. . Many species of the Rhizobiaceae are diazotrophs which are able to fix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gram-negative
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner cytoplasmic cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane. Gram-negative bacteria are found in virtually all environments on Earth that support life. The gram-negative bacteria include the model organism ''Escherichia coli'', as well as many pathogenic bacteria, such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'', ''Chlamydia trachomatis'', and ''Yersinia pestis''. They are a significant medical challenge as their outer membrane protects them from many antibiotics (including penicillin), detergents that would normally damage the inner cell membrane, and lysozyme, an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. Additionally, the outer leaflet of this membrane comprises a complex lipo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |