|
Allodiplogaster Sudhausi
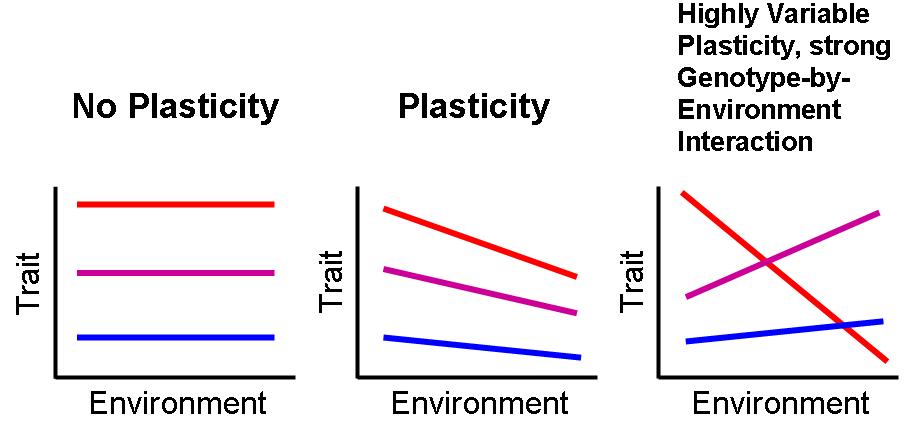
''Allodiplogaster sudhausi'' is a free-living nematode species in the Diplogastridae family. It was described in 2008 as ''Koerneria sudhausi'', before being moved to the genus ''Allodiplogaster'' in 2014. ''A. sudhausi'' is omnivorous. It predates on other nematodes, but can be cultured on '' Escherichia coli'' OP50 bacterium on agar. Mouth dimorphism Like many other Diplogastridae, such as ''Pristionchus pacificus'', ''A. sudhausi'' displays phenotypic plasticity, with a polyphenism A polyphenic trait is a trait for which multiple, discrete phenotypes can arise from a single genotype as a result of differing environmental conditions. It is therefore a special case of phenotypic plasticity. There are several types of polyphen ... in its adult mouth-form that leads to formation of one of two distinct stomas (mouth openings) of different dimensions. The two morphs that differ in stoma dimension are termed stenostomatous (narrow-mouthed) and eurystomatous (wide-mouthed). Canni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematode
The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-Parasitism, parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhabiting a broad range of environments. Less formally, they are categorized as Helminths, but are taxonomically classified along with Arthropod, arthropods, Tardigrade, tardigrades and other moulting animalia, animals in the clade Ecdysozoa, and unlike platyhelminthe, flatworms, have tubular digestion, digestive systems with openings at both ends. Like tardigrades, they have a reduced number of Hox genes, but their sister phylum Nematomorpha has kept the ancestral protostome Hox genotype, which shows that the reduction has occurred within the nematode phylum. Nematode species can be difficult to distinguish from one another. Consequently, estimates of the number of nematode species described to date vary by author and may change rapidly over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diplogastridae
Diplogastridae, formerly Diplogasteridae, are a family of nematodes (roundworms) known from a wide range of habitats, often in commensal or parasitic associations with insects. Description Diplogastrid nematodes are characterized by a distinct "two-lobed" pharynx (hence their name from the Greek διπλόος = "double" and γαστήρ = "stomach"), the second ( posterior) lobe being composed mostly of glandular tissue. Most known species also have at least one tooth, which has presumably allowed them to access many new food sources compared with the related nematodes of Rhabditidae (including '' Caenorhabditis elegans''), most species of which feed on bacteria. Several diplogastrid species also have a polyphenism in their mouthparts, allowing resource specialization within species. The wide array of feeding modes in the Diplogastridae is reflected by the relatively high diversity and complexity of their mouth structures, which show accelerated rates of evolution in comparis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematology
Nematology is the scientific discipline concerned with the study of nematodes, or roundworms. Although nematological investigation dates back to the days of Aristotle or even earlier, nematology as an independent discipline has its recognizable beginnings in the mid to late 19th century.Chen, Z. X., Chen, S. Y., and Dickson, D. W. (2004). "A Century of Plant Nematology", pp. 1–42 in ''Nematology Advances and Perspectives'', Vol 1. Tsinghua University Press, Beijing, China.Chitwood, B. G., and Chitwood, M. B. (1950). "An Introduction to Nematology", pp. 1–5 in ''Introduction to Nematology''. University Park Press, Baltimore. History: pre-1850 Nematology research, like most fields of science, has its foundations in observations and the recording of these observations. The earliest written account of a nematode "sighting," as it were, may be found in the Pentateuch of the Old Testament in the Bible, in the Fourth Book of Moses called Numbers: "And the Lord sent fiery serpen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allodiplogaster
''Allodiplogaster'' is a genus of nematodes (roundworms) in the family Diplogastridae that currently includes about 35 described species. List of species ''henrichae'' group *''Allodiplogaster henrichae'' *''Allodiplogaster colobocerca'' *''Allodiplogaster hirschmannae'' *''Allodiplogaster histophora'' *''Allodiplogaster hylobii'' *''Allodiplogaster incurva'' *''Allodiplogaster labiomorpha'' *''Allodiplogaster lepida'' *''Allodiplogaster lucani'' *''Allodiplogaster pierci'' *''Allodiplogaster pini'' *''Allodiplogaster robinicola'' *''Allodiplogaster sudhausi'' ''striata'' group *''Allodiplogaster angarensis'' *''Allodiplogaster aquatica'' *''Allodiplogaster baicalensis'' *''Allodiplogaster carinata'' *''Allodiplogaster didentata'' *''Allodiplogaster filicaudata'' *''Allodiplogaster ivanegae'' *''Allodiplogaster lupata'' *''Allodiplogaster mordax'' *''Allodiplogaster mulveyi'' *''Allodiplogaster pantolaba'' *''Allodiplogaster pararmata'' *''Allodiplogaster regia'' *''Allodiplogas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZooKeys
''ZooKeys'' is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal covering zoological taxonomy, phylogeny, and biogeography. It was established in 2008 and the editor-in-chief is Terry Erwin (Smithsonian Institution). It is published by Pensoft Publishers. ''ZooKeys'' provides all new taxa to the Encyclopedia of Life on the day of publication. See also * ''Zootaxa ''Zootaxa'' is a peer-reviewed scientific mega journal for animal taxonomists. It is published by Magnolia Press (Auckland, New Zealand). The journal was established by Zhi-Qiang Zhang in 2001 and new issues are published multiple times a week. ...'' References External links * * * Creative Commons Attribution-licensed journals English-language journals Open access journals Publications established in 2008 Zoology journals Pensoft Publishers academic journals Continuous journals {{zoo-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematologica
''Nematology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the study of nematode The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant-Parasitism, parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a diverse animal phylum inhab ...s. In 1978, French zoologist Michel Luc established the ''Revue de Nématologie'' (soon renamed ''Fundamental and Applied Nematology'') that fused with ''Nematologica'' in 1999 to become ''Nematology''. The editors-in-chief are David Hunt ( CABI Europe) and Roland Perry ( Rothamsted Research). References External links * {{wikispecies, ISSN 1388-5545 Nematology journals Brill Publishers academic journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are harmless, but some serotypes ( EPEC, ETEC etc.) can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains do not cause disease in humans and are part of the normal microbiota of the gut; such strains are harmless or even beneficial to humans (although these strains tend to be less studied than the pathogenic ones). For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pristionchus Pacificus
''Pristionchus pacificus'' is a species of free-living nematodes (roundworms) in the family Diplogastridae. The species has been established as a satellite model organism to '' Caenorhabditis elegans'', with which it shared a common ancestor 200–300 million years ago. The genome of ''P. pacificus'' has been fully sequenced, which in combination with other tools for genetic analysis make this species a tractable model in the laboratory, especially for studies of developmental biology. Mouth dimorphism Like other species of '' Pristionchus'' and many other free-living nematodes, ''P. pacificus'' exhibits a polyphenism in its mouthparts that allows individual nematodes to specialize on different food sources, which has made the species a case study in phenotypic plasticity. The polyphenism has two forms (morphs). The most common type, at least in wild-type lab strains, is the "eurystomatous" morph, which can feed on both bacteria and other nematode species. The "stenostomat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenotypic Plasticity
Phenotypic plasticity refers to some of the changes in an organism's behavior, morphology and physiology in response to a unique environment. Fundamental to the way in which organisms cope with environmental variation, phenotypic plasticity encompasses all types of environmentally induced changes (e.g. morphological, physiological, behavioural, phenological) that may or may not be permanent throughout an individual's lifespan. The term was originally used to describe developmental effects on morphological characters, but is now more broadly used to describe all phenotypic responses to environmental change, such as acclimation (acclimatization), as well as learning. The special case when differences in environment induce discrete phenotypes is termed polyphenism. Generally, phenotypic plasticity is more important for immobile organisms (e.g. plants) than mobile organisms (e.g. most animals), as mobile organisms can often move away from unfavourable environments. Nevertheless, mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyphenism
A polyphenic trait is a trait for which multiple, discrete phenotypes can arise from a single genotype as a result of differing environmental conditions. It is therefore a special case of phenotypic plasticity. There are several types of polyphenism in animals, from having sex determined by the environment to the castes of honey bees and other social insects. Some polyphenisms are seasonal, as in some butterflies which have different patterns during the year, and some Arctic animals like the snowshoe hare and Arctic fox, which are white in winter. Other animals have predator-induced or resource polyphenisms, allowing them to exploit variations in their environment. Some nematode worms can develop either into adults or into resting dauer larvae according to resource availability. Definition upright=1.2, Polyphenism in termites A : Primary king B : Primary queen C : Secondary queen D : Tertiary queen E : Soldiers F : Worker A polyphenism is the occurr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ELife
''eLife'' is a not-for-profit, peer-reviewed, open access, scientific journal for the biomedical and life sciences. It was established at the end of 2012 by the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Max Planck Society, and Wellcome Trust, following a workshop held in 2010 at the Janelia Farm Research Campus. Together, these organizations provided the initial funding to support the business and publishing operations. In 2016, the organizations committed US$26 million to continue publication of the journal. The current editor-in-chief is Michael Eisen (University of California, Berkeley). Editorial decisions are made largely by senior editors and members of the board of reviewing editors, all of whom are active scientists working in fields ranging from human genetics and neuroscience to biophysics, epidemiology, and ecology. Business model ''eLife'' is a non-profit organisation, but for long-term sustainability of the service, the journal asks for an article processing charge of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannibalistic
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s .... Human cannibalism is well documented, both in ancient and in recent times. The rate of cannibalism increases in nutritionally poor environments as individuals turn to members of their own species as an additional food source.Elgar, M.A. & Crespi, B.J. (1992) ''Cannibalism: ecology and evolution among diverse taxa'', Oxford University Press, Oxford [England]; New York. Cannibalism regulates population numbers, whereby resources such as food, shelter and territory become more readily available with the decrease of potential competi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |