|
Allied Bombing Of Yugoslavia In World War II
The Allied bombing of Yugoslavia in World War II involved air attacks on cities and towns in the Kingdom of Yugoslavia by the United States Army Air Force (USAAF) and Royal Air Force (RAF), including the Balkan Air Force (BAF), between 1941 and 1945, during which period the entire country was occupied by the Axis powers. Dozens of Yugoslav cities and towns were bombed, many repeatedly. These attacks included intensive air support for Yugoslav Partisan operations in May–June 1944, and a bombing campaign against transport infrastructure in September 1944 as the German ''Wehrmacht'' withdrew from Greece and Yugoslavia. This latter operation was known as Operation ''Ratweek''. Some of the attacks caused significant civilian casualties. First bombings The bombings of Serbia and Montenegro lasted from 20 October 1943 to 18 September 1944. Especially hit was the industrial town of Niš in south Serbia. The bombing began on 20 October 1943, instantly killing 250 people. German forces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II In Yugoslavia
World War II in the Kingdom of Yugoslavia began on 6 April 1941, when the country was swiftly conquered by Axis forces and partitioned between Germany, Italy, Hungary, Bulgaria and their client regimes. Shortly after Germany attacked the USSR on 22 June 1941, the communist-led republican Yugoslav Partisans, on orders from Moscow, launched a guerrilla liberation war fighting against the Axis forces and their locally established Puppet state, puppet regimes, including the Axis-allied Independent State of Croatia (NDH) and the Government of National Salvation in the Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia, German-occupied territory of Serbia. This was dubbed the National Liberation War and Socialist Revolution in post-war Yugoslav communist historiography. Simultaneously, a multi-side civil war was waged between the Yugoslav communist Partisans, the Serbian royalist Chetniks, the Axis-allied Croatian Ustaše and Croatian Home Guard (World War II), Home Guard, Serbian Volun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foggia
Foggia (, , ; nap, label= Foggiano, Fògge ) is a city and former ''comune'' of Apulia, in Southern Italy, capital of the province of Foggia. In 2013, its population was 153,143. Foggia is the main city of a plain called Tavoliere, also known as the "granary of Italy". History The name "''Foggia''" (originally ''Focis'') probably derives from Latin "''fovea''", meaning "''pit''", referring to the pits where wheat was stored. The name's etymology remains uncertain however, as it could as well stem from "''Phocaea''", or possibly probably from the Medieval Greek word for "''fire''", which is "''fotia''", as according to legend the original settlers of the 11th century AD were peasants, allegedly after having iraculouslydiscovered there a panel portraying the Madonna Nicopeia, on which three flames burnt. The area had been settled since Neolithic times, and later on a Daunian settlement known as Arpi (in Greek ''Argos Hippium'' or ''Ἀργόριππα'') existed nearby, clos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sajmište Concentration Camp
The Sajmište concentration camp () was a Nazi German concentration and extermination camp during World War II. It was located at the former Belgrade fairground site near the town of Zemun, in the Independent State of Croatia (NDH). The camp was organized and operated by SS ''Einsatzgruppen'' units stationed in occupied Serbia. It became operational in September 1941 and was officially opened on 28 October of that year. The Germans dubbed it the Jewish camp in Zemun (german: Judenlager Semlin). At the end of 1941 and the beginning of 1942, thousands of Jewish women, children and old men were brought to the camp, along with 500 Jewish men and 292 Romani women and children, most of whom were from Niš, Smederevo and Šabac. Women and children were placed in makeshift barracks and suffered during numerous influenza epidemics. Kept in squalid conditions, they were provided with inadequate amounts of food and many froze to death during the winter of 1941–42. Between March and May 1942 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
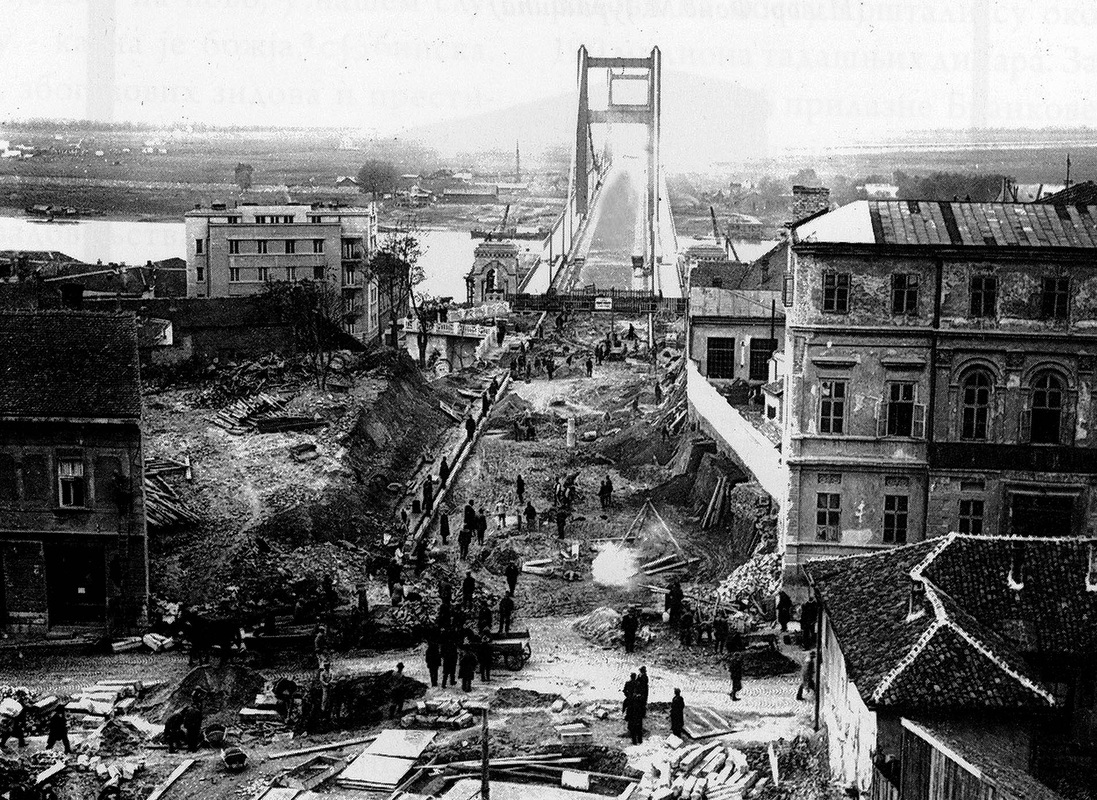
King Alexander Bridge
King Alexander Bridge ( sr, Мост краља Александра, ), in full The Bridge of King Alexander Karađorđević or The Bridge of the Knightly King Alexander, was a road and tram bridge over the Sava river, in Belgrade, capital of Yugoslavia. It was the first permanent road bridge across the Sava in Belgrade after almost 250 years and the Long Bridge from 1688. Finished in 1934, it was damaged and out of use since 1941, and fully demolished in 1944, during World War II. Its pylons were later used for the modern Branko's Bridge, built in 1956. The bridge was revered while existed being described as "gorgeous" and "one of the most important object ever built in Belgrade". Location On the right bank, the bridge was starting at the Sava Port, in the neighborhood of Savamala, a transportation and commercial hub and one of the busiest parts of Belgrade in that period. On the left bank, the bridge entered the still marshy and un-urbanized area where New Belgrade was built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dušanovac, Belgrade
Dušanovac ( sr-cyr, Душановац, ), is an urban neighbourhood of Belgrade, the capital of Serbia. It is located in the municipality of Voždovac. Location The Dušanovac is bounded by the other Belgrade neighbourhoods: Autokomanda to the west, Pašino Brdo to the north, Šumice, Konjarnik, Marinkova Bara, Medaković and Braće Jerković to the east, and Voždovac itself to the south. History As a pre-World War I suburb of Belgrade, in the area that was eastern border of the city at that time, Dušanovac was administratively part of the municipality of Kumodraž. After the liberation in World War I in 1918, the neighborhood came under Belgrade's administrative rule. A string of new or expanded and renovated neighborhoods encircled eastern outskirts of Belgrade after the war. The inspiration for the design of the neighborhoods came from the complex built in 1912 along the in Paris. It consisted of 40 one-floor houses with gardens, indented from the main street. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pašino Brdo
Pašino Brdo ( sr-cyr, Пашино Брдо) is an urban neighborhood of Belgrade, the capital of Serbia. It is located in Belgrade's municipality of Voždovac, while the northern section belongs to the municipality of Vračar. It is also known as Lekino Brdo ( sr-cyr, Лекино Брдо) after the top Communist official, Aleksandar Ranković (1909–80), whose nickname was Leka ("Leka's hill"). Location Pašino Brdo, as the name says it (Serbian for "Pasha's hill"), is located on the hill of the same name, in the extreme north of the municipality of Voždovac and extreme south of the municipality of Vračar. Geographically, the hill and its slopes cover much larger area than what is today considered the neighborhood of Pašino Brdo, which is generally bordered by the neighborhoods of Dušanovac on the south, Šumice on the east and extends into Crveni Krst on the north-east and Čubura on the north-west. Geography On the southern side, the hill originates from the B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vračar
Vračar ( sr-Cyrl, Врачар, ) is an affluent urban area and municipality of the city of Belgrade known as the location of many embassies and museums. According to the 2011 census results, the municipality has a population of 56,333 inhabitants. With an area of only 291 hectares, it is the smallest of all Belgrade's (and Serbian) municipalities, but also the most densely populated. Vračar is one of the three municipalities that constitute the very center area of Belgrade, together with Savski Venac and Stari Grad. It is an affluent municipality, having one of the most expensive real estate prices within Belgrade, and has the highest proportion of university educated inhabitants compared to all other Serbian municipalities. One of the most famous landmarks in Belgrade, the Saint Sava Temple is located in Vračar. Vračar borders five other Belgrade municipalities: Voždovac to the south, Zvezdara to the east, Palilula to the northeast, Stari Grad to the north and Savski Vena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorćol
Dorćol ( sr-cyr, Дорћол; ) is an affluent urban neighborhood of Belgrade, the capital of Serbia. It is located in Belgrade's municipality of Stari Grad. Located along the right bank of the Danube, Dorćol is oldest surviving neighborhood in Belgrade. It is known for its specific urban charm and the mentality of its residents. The neighborhood has experienced artistic revival since the 2000s concurrently with the Savamala neighborhood on the opposite, Sava, bank. After being featured in numerous reports, including by the BBC and ''The Guardian'', '' Time Out'' magazine placed Dorćol on their list of "50 coolest neighborhoods". It has been described as a Belgrade "phenomenon", an "exciting, creative and inventive spot", and the "authentic, organic soul of the city". A section of Upper Dorćol was declared a spatial cultural-historical unit in 1989, and placed under protection as the "Area surrounding Dositej's Lyceum". Location Dorćol begins already some 700 meters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krunski Venac
Krunski Venac ( sr, Крунски Венац) is an urban neighborhood of Belgrade, the capital of Serbia. It is located in Belgrade's municipality of Vračar. In May 2021, the neighborhood was protected as the spatial cultural-historical unit. Location Krunski Venac is located along the ''Krunska'' street after which the neighborhood got its name (Serbian for "coronation street"), in the northern part of Vračar, stretches to the neighborhood of Kalenić. History 19th century At the corner of modern Krunska and Kneza Miloša streets, Jevrem Obrenović, brother of the ruling prince Miloš Obrenović, built the large house in the first half of the 19th century, and the spacious flower garden. Kept by his wife Tomanija, it was considered the most beautiful private garden in Belgrade at the time. The plants were imported from Turkey, Wallachia, Austria and France. In time, the area became known among the Belgraders as the "Corner at Mrs. Tomanija". The residence itself be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgrade Main Railway Station
The Belgrade Main railway station ( sr, Железничка станица Београд Главна, Železnička stanica Beograd Glavna) is a former train station in Belgrade, the capital of Serbia. It was built between 1882 and 1885 according to the designs of the architect Dragutin Milutinović, and it has the status of a сultural monument of great importance. Until the opening of the new Belgrade Center station (Prokop) in 2016, it was the city's main station, and the busiest one in the country. In order to free up the space for the Belgrade Waterfront project, the station was closed on 1 July 2018, and repurposed to become a museum. Passenger trains have been gradually relocated to the new station during 2016 and 2017. Most national railway traffic was moved to the new station in December 2017, thus leaving only international trains and two trains to Novi Sad in the old station. The Main station operated until 30 June 2018, when the last train, international train 34 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
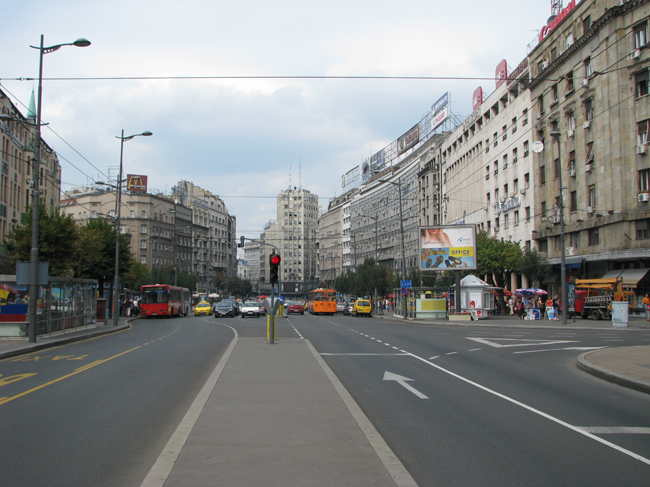
Terazije
Terazije ( sr-Cyrl, Теразијe) is the central town square and the surrounding neighborhood of Belgrade, Serbia. It is located in the municipality of Stari Grad. Today, Terazije has primarily function of the main transit square, surrounded by the important public buildings, cultural institutions, hotels, public monuments and parks. Though not classically shaped square, Terazije was historically important as the gathering spot and the former business and commercial center of Belgrade. With the Knez Mihailova Street, which extends to the northeast connecting directly Terazije and Belgrade Fortress, the square is one of the oldest and most recognizable ambience units of Belgrade. Due to its historical and cultural importance, Terazije was declared a protected spatial cultural-historical unit in January 2020. Location Despite the fact that many Belgraders consider the Republic Square or Kalemegdan to be the city's centerpiece areas, Terazije is Belgrade's designated center. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Theater In Belgrade
The National Theatre ( sr-cyr, Народно позориште, Narodno pozorište) is a theatre located in Belgrade, Serbia. Founded in the later half of the 19th century, it is located on the Republic Square, at the corner of Vasina and Francuska Street. With the raising of this building as well as with the implementation of the Regulations Plan of Town in Trench by Josimović from 1867, the conditions were made for the formation of today's main Republic Square in Belgrade. Built back in 1868, the National Theatre, following the fate of its own people and the country, went through different phases of the architectural and artistic development, surviving as a symbol of Serbian culture, tradition and spirituality. Today, under its roof, there are three artistic ensembles: opera, ballet, and drama. The National Theatre was declared a Monument of Culture of Great Importance in 1983, and it is protected by the Republic of Serbia. Origin In 1868, the Serbian National Theatre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |