|
Allergies In Children
Allergies in children, an incidence which has increased over the last fifty years, are overreactions of the immune system often caused by foreign substances or genetics that may present themselves in different ways. There are multiple forms of testing, prevention, management, and treatment available if an allergy is present in a child. In some cases, it is possible for children to outgrow their allergies. Morbidity Children affected by allergies in the developed world: * 1 in 13 have eczema * 1 in 8 have allergic rhinitis * 3-6% are affected by food allergy Children in the United States under 18 years of age: * Percent with any allergy: 27.2% * Percent with seasonal allergy: 18.9% * Percent with eczema: 10.8% * Percent with food allergy: 5.8% Children in the United Kingdom: * 1 in 6 with eczema * 1 in 5 with allergic rhinitis * 7.1% of breast-fed infants who develop food allergies Pathophysiology A child's allergy is an immune system reaction to a foreign substance, or allerge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hives
Hives, also known as urticaria, is a kind of skin rash with red, raised, itchy bumps. Hives may burn or sting. The patches of rash may appear on different body parts, with variable duration from minutes to days, and does not leave any long-lasting skin change. Fewer than 5% of cases last for more than six weeks. The condition frequently recurs. Hives frequently occur following an infection or as a result of an Allergy, allergic reaction such as to medication, insect bites, or food. Psychological stress, cold temperature, or vibration may also be a trigger. In half of cases the idiopathy, cause remains unknown. Risk factors include having conditions such as hay fever or asthma. Diagnosis is typically based on the appearance. Patch testing may be useful to determine the allergy. Prevention is by avoiding whatever it is that causes the condition. Treatment is typically with antihistamines such as diphenhydramine and cetirizine. In severe cases, corticosteroids or leukotriene inhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histamine Antagonist
Antihistamines are drugs which treat allergic rhinitis, common cold, influenza, and other allergies. Typically, people take antihistamines as an inexpensive, generic (not patented) drug that can be bought without a prescription and provides relief from nasal congestion, sneezing, or hives caused by pollen, dust mites, or animal allergy with few side effects. Antihistamines are usually for short-term treatment. Chronic allergies increase the risk of health problems which antihistamines might not treat, including asthma, sinusitis, and lower respiratory tract infection. Consultation of a medical professional is recommended for those who intend to take antihistamines for longer-term use. Although people typically use the word "antihistamine" to describe drugs for treating allergies, doctors and scientists use the term to describe a class of drug that opposes the activity of histamine receptors in the body. In this sense of the word, antihistamines are subclassified according to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
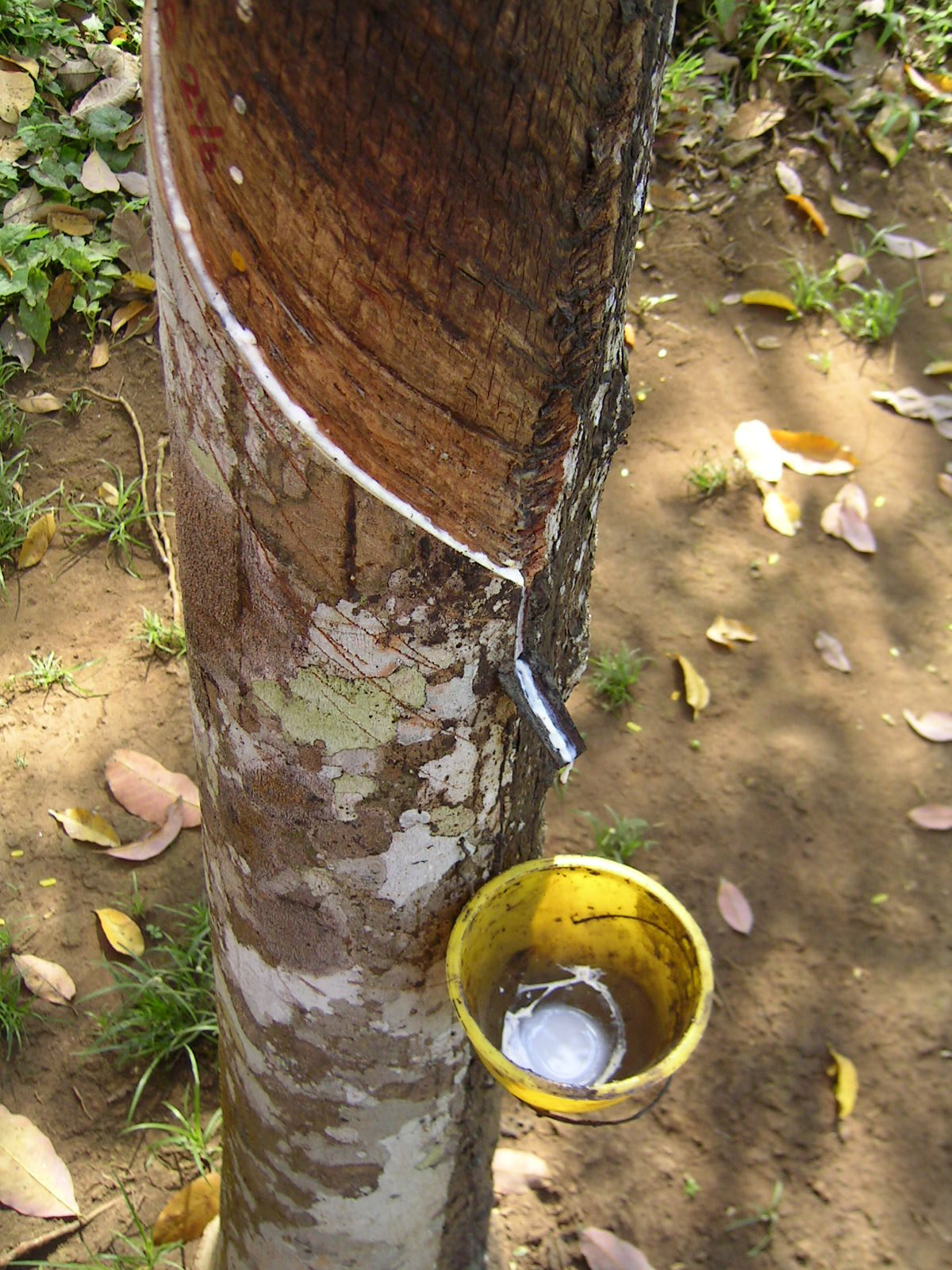
Latex
Latex is an emulsion (stable dispersion) of polymer microparticles in water. Latexes are found in nature, but synthetic latexes are common as well. In nature, latex is found as a milky fluid found in 10% of all flowering plants (angiosperms). It is a complex emulsion that coagulates on exposure to air, consisting of proteins, alkaloids, starches, sugars, oils, tannins, resins, and gums. It is usually exuded after tissue injury. In most plants, latex is white, but some have yellow, orange, or scarlet latex. Since the 17th century, latex has been used as a term for the fluid substance in plants, deriving from the Latin word for "liquid". It serves mainly as defense against herbivorous insects. Latex is not to be confused with plant sap; it is a distinct substance, separately produced, and with different functions. The word latex is also used to refer to natural latex rubber, particularly non-vulcanized rubber. Such is the case in products like latex gloves, latex condoms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soy Formula
Soy formula is a substitute for human breast milk. It is a commercial product based on the proteins found in soybeans. Soy infant formula uses processed soybeans as its source of protein, and comes in powdered or liquid form. Usually lactose-free, soy infant formula contains a different sugar. Infants who are intolerant of cows’ milk protein may also be intolerant of soy protein. It differs from human breast milk in a number of ways. Soy protein inhibits the absorption of iron. The soy-based formulas discussed by the World Health Organization reports that soy formula is fortified with iron to compensate for this effect. One naturally occurring plant-based compound found in soy-based infant formula is phytic acid. It is also a strong inhibitor of iron absorption, though it can be removed in processing. It is not known how many manufacturers of soy-based formula incorporate this practice. China and Vietnam have regulated soy-based infant formulas to include NaFeEDTA (sodium-feric ethy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
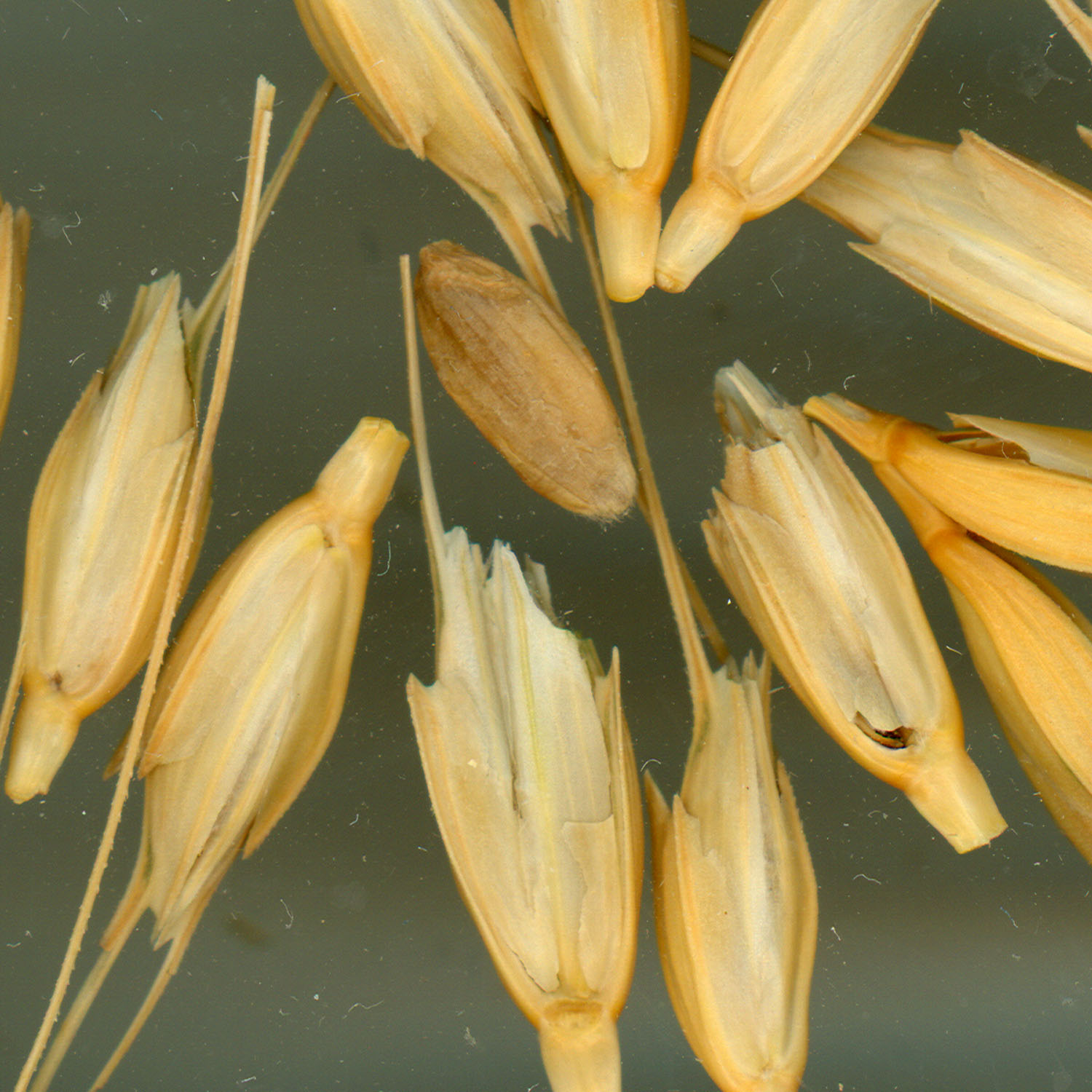
Wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeological record suggests that wheat was first cultivated in the regions of the Fertile Crescent around 9600 BCE. Botanically, the wheat kernel is a type of fruit called a caryopsis. Wheat is grown on more land area than any other food crop (, 2014). World trade in wheat is greater than for all other crops combined. In 2020, world production of wheat was , making it the second most-produced cereal after maize. Since 1960, world production of wheat and other grain crops has tripled and is expected to grow further through the middle of the 21st century. Global demand for wheat is increasing due to the unique viscoelastic and adhesive properties of gluten proteins, which facilitate the production of processed foods, whose consumption is inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cod Fish
Cod is the common name for the demersal fish genus ''Gadus'', belonging to the family Gadidae. Cod is also used as part of the common name for a number of other fish species, and one species that belongs to genus ''Gadus'' is commonly not called cod (Alaska pollock, ''Gadus chalcogrammus''). The two most common species of cod are the Atlantic cod (''Gadus morhua''), which lives in the colder waters and deeper sea regions throughout the North Atlantic, and the Pacific cod (''Gadus macrocephalus''), found in both eastern and western regions of the northern Pacific. ''Gadus morhua'' was named by Linnaeus in 1758. (However, ''G. morhua callarias'', a low-salinity, nonmigratory race restricted to parts of the Baltic, was originally described as ''Gadus callarias'' by Linnaeus.) Cod is popular as a food with a mild flavour and a dense, flaky, white flesh. Cod livers are processed to make cod liver oil, a common source of vitamin A, vitamin D, vitamin E, and omega-3 fatty acids (EPA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
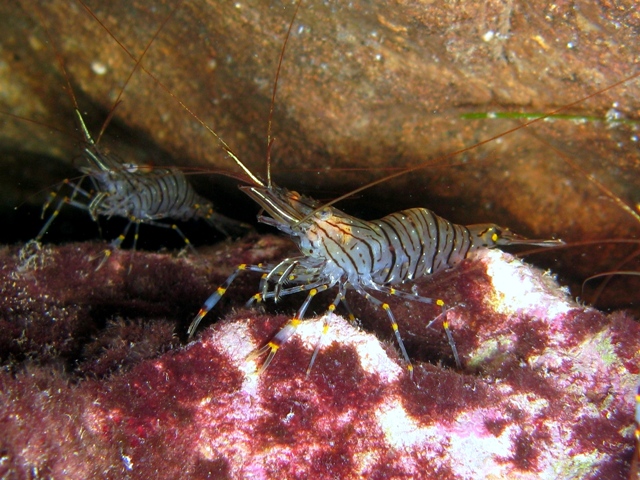
Shrimp
Shrimp are crustaceans (a form of shellfish) with elongated bodies and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – most commonly Caridea and Dendrobranchiata of the decapod order, although some crustaceans outside of this order are referred to as "shrimp". More narrow definitions may be restricted to Caridea, to smaller species of either group or to only the marine species. Under a broader definition, ''shrimp'' may be synonymous with prawn, covering stalk-eyed swimming crustaceans with long, narrow muscular tails (abdomens), long whiskers ( antennae), and slender legs. Any small crustacean which resembles a shrimp tends to be called one. They swim forward by paddling with swimmerets on the underside of their abdomens, although their escape response is typically repeated flicks with the tail driving them backwards very quickly. Crabs and lobsters have strong walking legs, whereas shrimp have thin, fragile legs which they use primarily for perching.Rudloe & Rudloe (2009 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walnut
A walnut is the edible seed of a drupe of any tree of the genus ''Juglans'' (family Juglandaceae), particularly the Persian or English walnut, '' Juglans regia''. Although culinarily considered a "nut" and used as such, it is not a true botanical nut. After full ripening, the shell is discarded and the kernel is eaten. Nuts of the eastern black walnut (''Juglans nigra'') and butternuts ('' Juglans cinerea'') are less commonly consumed. Characteristics Walnuts are rounded, single-seeded stone fruits of the walnut tree commonly used for food after fully ripening between September and November, in which the removal of the husk at this stage reveals a browning wrinkly walnut shell, which is usually commercially found in two segments (three or four-segment shells can also form). During the ripening process, the husk will become brittle and the shell hard. The shell encloses the kernel or meat, which is usually made up of two halves separated by a membranous partition. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible Seed, seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics, important to both small and large commercial producers. It is classified as both a grain legume and, due to its high oil content, an oil crop. World annual production of shelled peanuts was 44 million tonnes in 2016, led by China with 38% of the world total. Atypically among legume crop plants, peanut pods develop underground (geocarpy) rather than above ground. With this characteristic in mind, the botanist Carl Linnaeus gave peanuts the specific epithet ''hypogaea'', which means "under the earth." The peanut belongs to the botanical Family (biology), family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), commonly known as the legume, bean, or pea family. Like most other legumes, peanuts harbor symbiotic Nitrogen fixation, nitrogen-fixing bacteria in root nodules. The capacity to fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfed human infants) before they are able to digestion, digest solid food. Immune factors and immune-modulating components in milk contribute to milk immunity. Early-lactation milk, which is called colostrum, contains antibody, antibodies that strengthen the immune system, and thus reduces the risk of many diseases. Milk contains many nutrients, including protein and lactose. As an agricultural product, dairy milk is Milking, collected from farm animals. In 2011, Dairy farming, dairy farms produced around of milk from 260 million dairy cows. India is the world's largest producer of milk and the leading exporter of skimmed milk powder, but it exports few other milk products. Because there is an ever-increasing demand for dairy products within India, it could eventually become a net importer of dairy products. New Zealand, Germany and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egg White
Egg white is the clear liquid (also called the albumen or the glair/glaire) contained within an egg. In chickens it is formed from the layers of secretions of the anterior section of the hen's oviduct during the passage of the egg. It forms around fertilized or unfertilized egg yolks. The primary natural purpose of egg white is to protect the yolk and provide additional nutrition for the growth of the embryo (when fertilized). Egg white consists primarily of about 90% water into which about 10% proteins (including albumins, mucoproteins, and globulins) are dissolved. Unlike the yolk, which is high in lipids (fats), egg white contains almost no fat, and carbohydrate content is less than 1%. Egg whites contain about 56% of the protein in the egg. Egg white has many uses in food (e.g. meringue, mousse) as well as many other uses (e.g. in the preparation of vaccines such as those for influenza). Composition Egg white makes up around two-thirds of a chicken egg by weight. Water co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
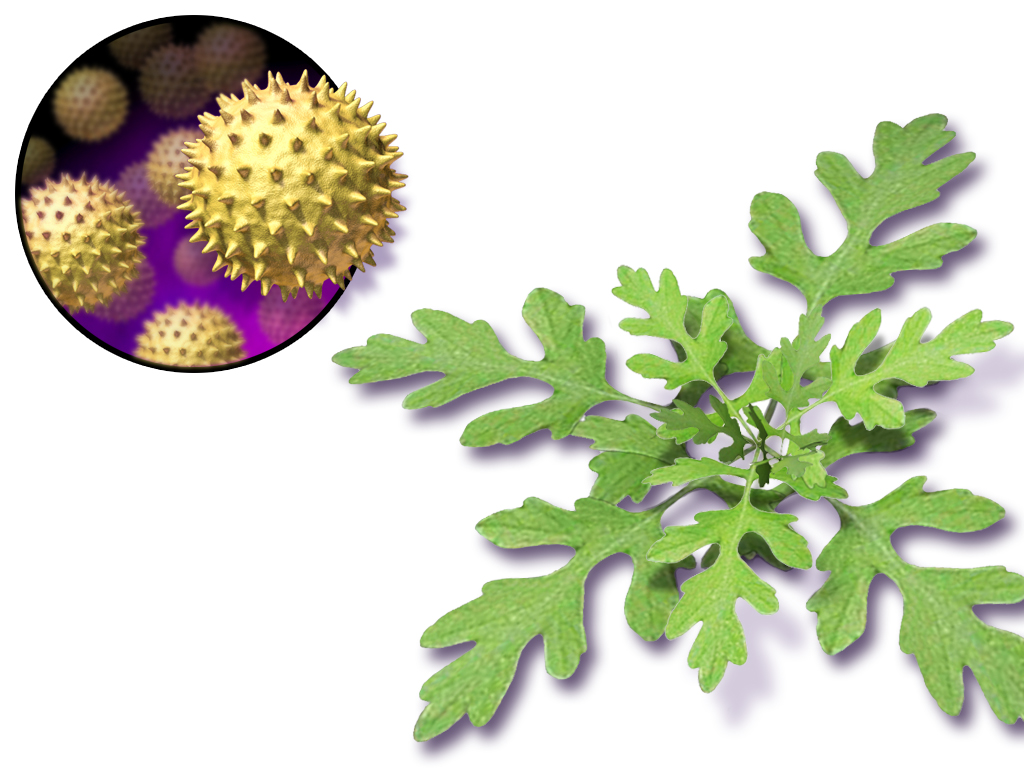
Ragweed
Ragweeds are flowering plants in the genus ''Ambrosia'' in the aster family, Asteraceae. They are distributed in the tropical and subtropical regions of the Americas, especially North America,''Ambrosia'' Flora of North America. where the origin and center of diversity of the genus are in the and northwestern . Several species have been [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

