|
Allalmeia
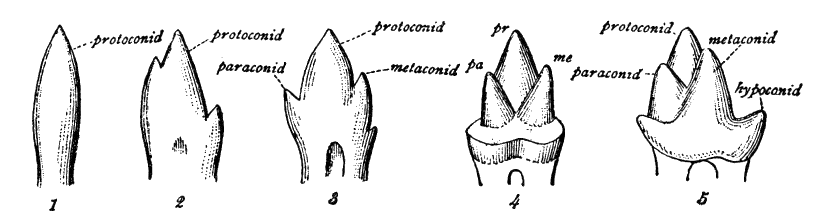
''Allalmeia'' was a small notoungulate mammal of around 3 kilograms. It lived in Mendoza Province, Argentina (Divisadero Largo Formation) during the Late Eocene. ''Allalmeia'' belonged to the Oldfieldthomasiidae family within the suborder Typotheria.''Allalmeia'' at .org Description It was a small mammal, with and lophobunodont teeth, teeth that have a combination of ridges ( |
Divisaderan
The Divisaderan age is a South American land mammal age, covering a period of geologic time (42.0–36.0 Ma) within the Middle and Late Eocene epochs of the Paleogene. It follows the Mustersan age and is followed by the Tinguirirican age.Divisaderan at .org Etymology The age is named after the Divisadero Largo Formation of Divisadero Largo, Mendoza, |
Oldfieldthomasiidae
Oldfieldthomasiidae is an extinct family of notoungulate mammals known from the Late Paleocene to Late Eocene of South America. The family was classified by George Gaylord Simpson in 1945 and a synonym is Acoelodidae, defined by Florentino Ameghino in 1901.Oldfieldthomasiidae at .org Etymology The family is named after British zoologistOldfield Thomas
Michael Rogers Oldfield Thomas (21 February 1858 – 16 June 1929) was a British zoologist.
Career
Thomas worked at the Natural Histor ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of Argentina
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleogene Argentina
The Paleogene ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene; informally Lower Tertiary or Early Tertiary) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period million years ago ( Mya) to the beginning of the Neogene Period Mya. It is the beginning of the Cenozoic Era of the present Phanerozoic Eon. The earlier term Tertiary Period was used to define the span of time now covered by the Paleogene Period and subsequent Neogene Period; despite no longer being recognised as a formal stratigraphic term, 'Tertiary' is still widely found in earth science literature and remains in informal use. Paleogene is often abbreviated "Pg" (but the United States Geological Survey uses the abbreviation PE for the Paleogene on the Survey's geologic maps). During the Paleogene, mammals diversified from relatively small, simple forms into a large group of diverse animals in the wake of the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event that ended the preceding Cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene Mammals Of South America
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and end of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typotheres
Typotheria is a suborder of the extinct mammalian order Notoungulata and includes five families: Archaeopithecidae, Campanorcidae, Interatheriidae, Mesotheriidae, and Oldfieldthomasiidae. CifelliCifelli, Richard L. 1993. The phylogeny of the native South American ungulates. pp. 195-216 ''in'' F. S. Szalay, M. J. Novacek and M. C. McKenna (''eds.'') ''Mammal Phylogeny, Volume 2, Placentals''. Springer-Verlag, New York. indicated that Typotheria would be paraphyletic if it excluded members of the suborder Hegetotheria and he advocated inclusion of the hegetothere families Archaeohyracidae and Hegetotheriidae Hegetotheriidae is an extinct family of notoungulate mammals known from the Oligocene through the Pliocene of South America South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a r ... in Typotheria. References Prehistoric animal suborders Mammal suborders {{paleo-mammal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
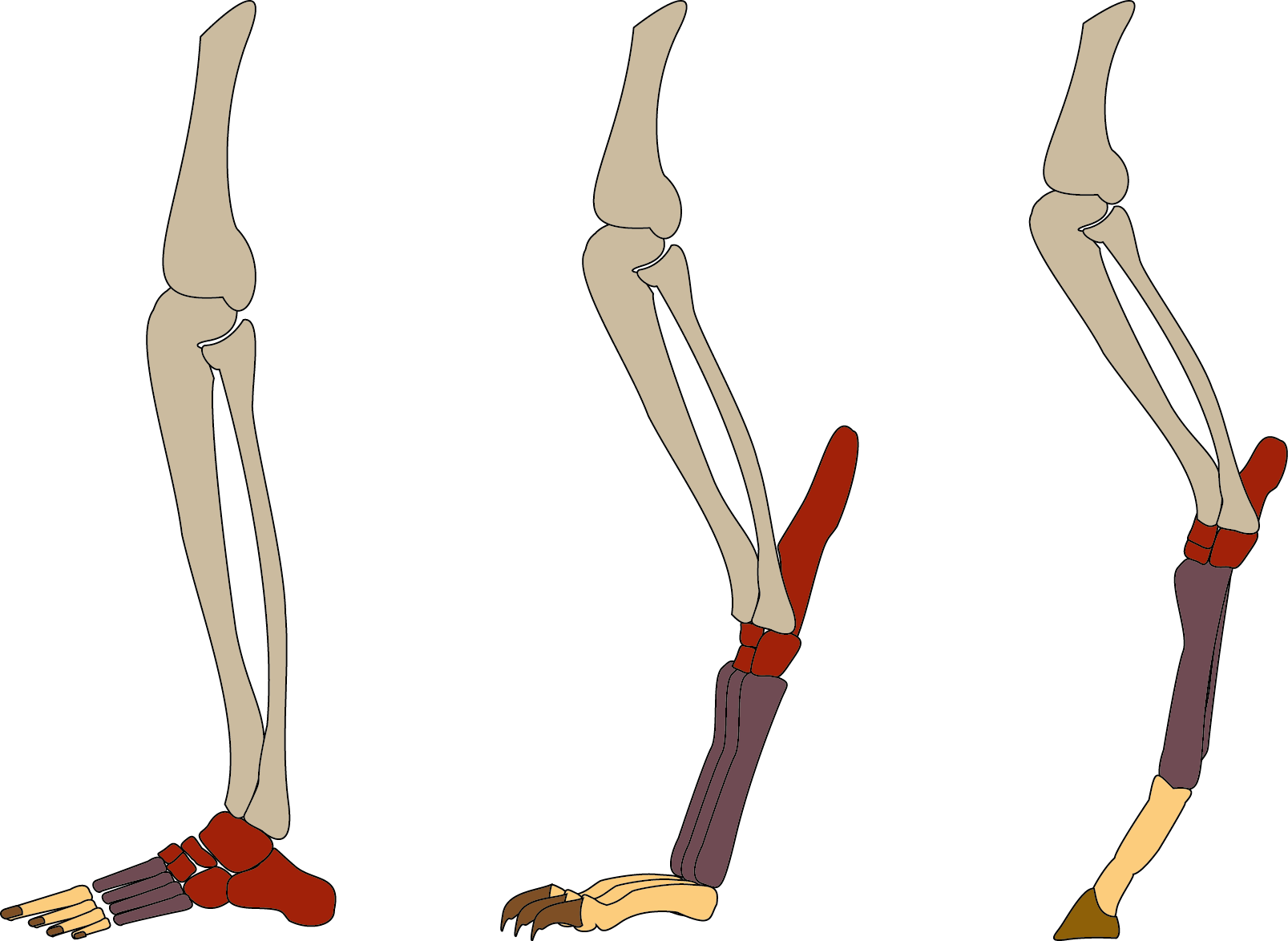
Ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, camels, sheep, deer, and hippopotamuses. Cetaceans such as whales, dolphins, and porpoises are also classified as even-toed ungulates, although they do not have hooves. Most terrestrial ungulates use the hoofed tips of their toes to support their body weight while standing or moving. The term means, roughly, "being hoofed" or "hoofed animal". As a descriptive term, "ungulate" normally excludes cetaceans as they do not possess most of the typical morphological characteristics of other ungulates, but recent discoveries indicate that they were also descended from early artiodactyls. Ungulates are typically herbivorous and many employ specialized gut bacteria to allow them to digest cellulose. Some modern species, such as pigs, are omnivorous, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunodont
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies from individual to individual. Race can also affect the age at which this occurs, with statistical variations between groups. In some cases, it may not even erupt at all. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lophodont
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies from individual to individual. Race can also affect the age at which this occurs, with statistical variations between groups. In some cases, it may not even erupt at all. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachyodont
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies from individual to individual. Race can also affect the age at which this occurs, with statistical variations between groups. In some cases, it may not even erupt at all. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digitigrade
In terrestrial vertebrates, digitigrade () locomotion is walking or running on the toes (from the Latin ''digitus'', 'finger', and ''gradior'', 'walk'). A digitigrade animal is one that stands or walks with its toes (metatarsals) touching the ground, and the rest of its foot lifted. Digitigrades include walking birds (what many assume to be bird knees are actually ankles), cats, dogs, and many other mammals, but not plantigrades or unguligrades. Digitigrades generally move more quickly and quietly than other animals. There are anatomical differences between the limbs of plantigrades, like humans, and both unguligrade and digitigrade limbs. Digitigrade and unguligrade animals have relatively long carpals and tarsals, and the bones which would correspond to the human ankle are thus set much higher in the limb than in a human. In a digitigrade animal, this effectively lengthens the foot, so much so that what are often thought of as a digitigrade animal's "hands" and "feet" correspon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope Carbon-13, 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope Carbon-12, 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Popigai impact structure, Siberia and in what is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |