|
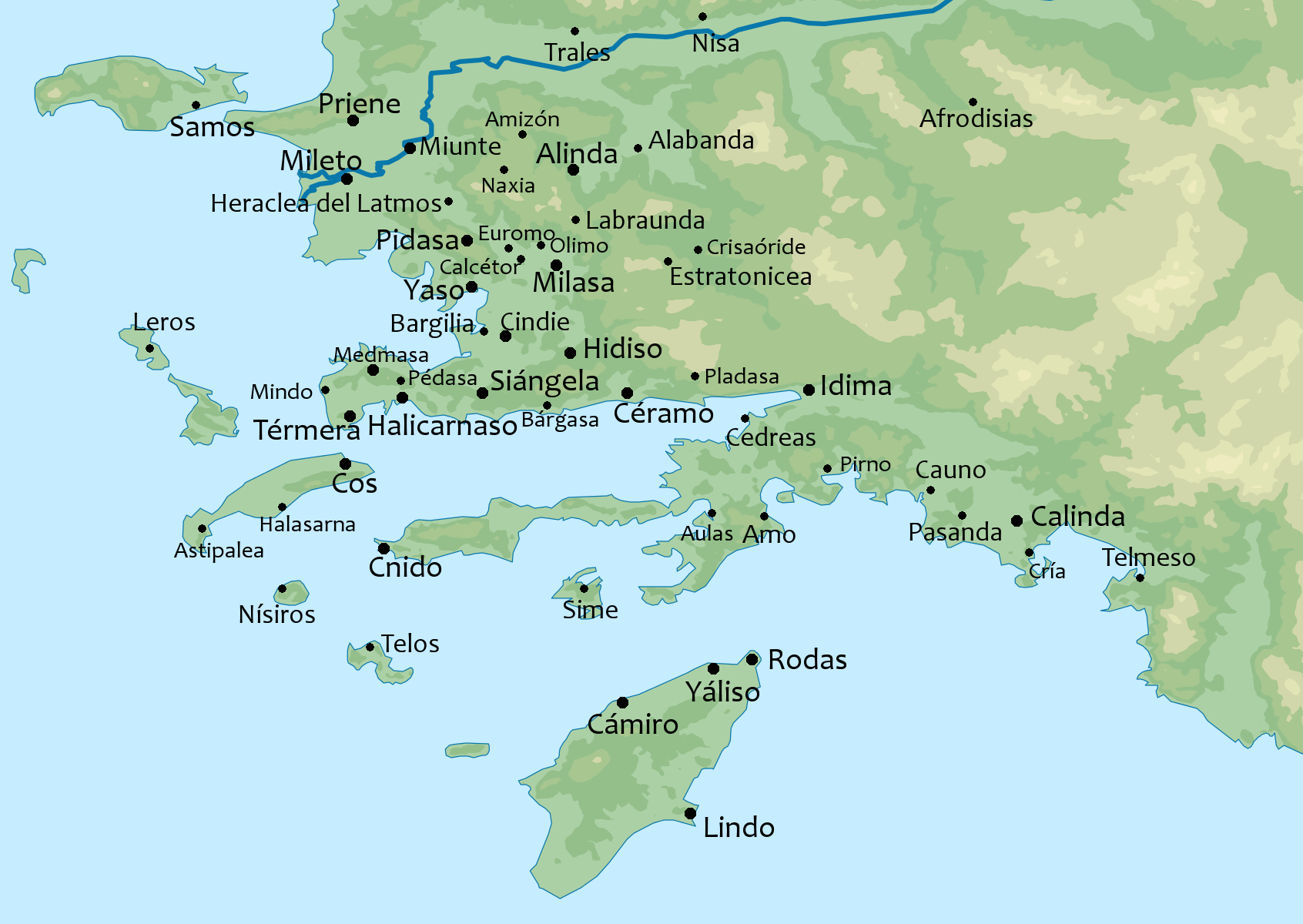
Alinda
Alinda ( grc, Ἄλινδα) was an inland city and bishopric in ancient Caria, in Asia Minor (Anatolia). Modern scholars identify Alinda with the Hellenistic foundation of Alexandria ad Latmum (Ἀλεξάνδρεια πρὸς τῷ Λάτμῳ) noted by Stephanus of Byzantium. Location and remains It is situated near Demircideresi, on a hilltop which commands the modern-day town of Karpuzlu, Aydın Province, in western Turkey, and overlooks a fertile plain. The non-restored but very well preserved ruins are much visited, especially within the circuit of organized tours (''locally called "safaris"'') with departure from either the international tourism center of Bodrum or from Milas and reaching Karpuzlu through a mountain road from the south. In 2018, four kilometers of the ancient stone road, which connects the ancient cities of Alinda and Latmus, were destroyed by villagers to make way for their olive groves. History Alinda has perhaps been an important city since ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ada Of Caria
Ada of Caria ( grc, Ἄδα) (fl. 377 – 326 BC)377 BC is the date of her father's death: was a member of the House of Hecatomnus (the Hecatomnids) and ruler of Caria during the mid-4th century BC, first as Persian Satrap and later as Queen under the auspices of Alexander III (the Great) of Macedon. History Ada was the daughter of Hecatomnus, satrap of Caria, sister of Mausolus, Pixodarus, Artemisia, and Idrieus.Sears, Matthew A. (2014). p.213 Four of the siblings intermarried: Mausolus wed Artemisia, while Ada was married to her brother Idrieus. Pixodarus married outside of the family. Every child of Hecatomnus would govern over Caria at some point. Mausolus and Artemisia first ruled together, and after Mausolus' death, Artemisia ruled alone until she died in 344 BC. Idrieus and Ada ruled together for four years, until his death. During their rule, they kept close ties to the Hellenic world.Sears, Matthew A. (2014). p.217 The joint regents were mentioned as donors t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karpuzlu
Karpuzlu is a town and district of Aydın Province, in the Aegean region of Turkey, from the city of Aydın. It became a district centre after separation from Çine in 1990. Karpuzlu is reached by turning off the road from Aydın to Çine. There is infrequent public transport (by minibus) from both towns to Karpuzlu, which can also be reached by the mountain road from Bodrum or Milas. This latter route is popular with tourists on "jeep safaris" coming to see the ruins of Alinda. The town is partially situated on the slopes of a hill on the top of which can be seen the well-preserved ruins of the ancient acropolis of Alinda. The modern district of Karpuzlu covers part of the Çine plain that is part of the southern reaches of the fertile Menderes River (Meander) valley. The main crops are cotton, corn and many other grains and vegetables. Karpuzlu (former Demircidere) itself is a very small town of 2,300 people. See also * Alinda *Gülkız Ürbül Gülkız Ürbül (1901–1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aydın Province
Aydın Province ( tr, ) is a province of southwestern Turkey, located in the Aegean Region. The provincial capital is the city of Aydın which has a population of almost 200,000 (2012). Other towns in the province include the summer seaside resorts of Didim and Kuşadası. Geography Neighboring provinces are Manisa to the north east, İzmir to the north, Denizli to the east, Muğla to the south. The central and western parts of the province are fertile plains watered by the largest river in the Aegean region the Büyük Menderes River, with the Aydın Mountains to the north and the Menteşe Mountains to the south. The western end of the province is the Aegean coast with Lake Bafa a major feature of the Menderes delta area. The climate is typical of the Aegean region, very hot in summer. The Germencik region contains a number of hot springs. Districts Aydın province is divided into 17 districts: Flora Much of the countryside is a mix of fig, olive and citrus trees, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joined the Carian population in forming Greek-dominated states there. Carians were described by Herodotus as being of Minoan descent,''The Histories'', Book I Section 171. while he reports that the Carians themselves maintained that they were Anatolian mainlanders intensely engaged in seafaring and were akin to the Mysians and the Lydians. The Carians spoke Carian, a native Anatolian language closely related to Luwian. Also closely associated with the Carians were the Leleges, which could be an earlier name for Carians. Municipalities of Caria Cramer's detailed catalog of Carian towns in classical Greece is based entirely on ancient sources. The multiple names of towns and geomorphic features, such as bays and headlands, reveal an ethnic layer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia ( Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionian and Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joined the Carian population in forming Greek-dominated states there. Carians were described by Herodotus as being of Minoan descent,''The Histories'', Book I Section 171. while he reports that the Carians themselves maintained that they were Anatolian mainlanders intensely engaged in seafaring and were akin to the Mysians and the Lydians. The Carians spoke Carian, a native Anatolian language closely related to Luwian. Also closely associated with the Carians were the Leleges, which could be an earlier name for Carians. Municipalities of Caria Cramer's detailed catalog of Carian towns in classical Greece is based entirely on ancient sources. The multiple names of towns and geomorphic features, such as bays and headlands, reveal an ethni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographia (Ptolemy)
The ''Geography'' ( grc-gre, Γεωγραφικὴ Ὑφήγησις, ''Geōgraphikḕ Hyphḗgēsis'', "Geographical Guidance"), also known by its Latin names as the ' and the ', is a gazetteer, an atlas, and a treatise on cartography, compiling the geographical knowledge of the 2nd-century Roman Empire. Originally written by Claudius Ptolemy in Greek at Alexandria around AD 150, the work was a revision of a now-lost atlas by Marinus of Tyre using additional Roman and Persian gazetteers and new principles. Its translation into Arabic in the 9th century and Latin in 1406 was highly influential on the geographical knowledge and cartographic traditions of the medieval Caliphate and Renaissance Europe. Manuscripts Versions of Ptolemy's work in antiquity were probably proper atlases with attached maps, although some scholars believe that the references to maps in the text were later additions. No Greek manuscript of the ''Geography'' survives from earlier than the 13th c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stauropolis (diocese)
The Stauropolis ( gr, Σταυρόπολις) is the former metropolitan see of Caria in Asia Minor within the Patriarchate of Constantinople. It remains a titular see of the Roman Catholic Church. History The bishopric was centered on the ancient town of Stauropolis (Aphrodisias), on the site of modern Geyre, Turkey. It was the metropolitan seat of the Roman province of Caria in the civil Diocese of Asia and the Patriarchate of Constantinople. In the Hellenistic-Roman era, the city was called Aphrodisia. In the Christian era, it was renamed Stauropolis ( grc-gre, Σταυρούπολις) 'city of the cross'. In later Byzantine times, it assumed the name of Caria, a name preserved by the village of Geyre. Stauropolis was home to an ancient Christian community. The Roman Martyrology of May 3 remember the martyrs Diodorus and Rodopiano, who were condemned to be stoned to Aphrodisias during the Diocletianic Persecution.The Roman Martyrology'' Transl. by the Archbishop of Baltimor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffragan
A suffragan bishop is a type of bishop in some Christian denominations. In the Anglican Communion, a suffragan bishop is a bishop who is subordinate to a metropolitan bishop or diocesan bishop (bishop ordinary) and so is not normally jurisdictional in their role. Suffragan bishops may be charged by a metropolitan to oversee a suffragan diocese and may be assigned to areas which do not have a cathedral of their own. In the Catholic Church, a suffragan bishop instead leads a diocese within an ecclesiastical province other than the principal diocese, the metropolitan archdiocese; the diocese led by the suffragan is called a suffragan diocese. Anglican Communion In the Anglican churches, the term applies to a bishop who is assigned responsibilities to support a diocesan bishop. For example, the Bishop of Jarrow is a suffragan to the diocesan Bishop of Durham. Suffragan bishops in the Anglican Communion are nearly identical in their role to auxiliary bishops in the Roman Catholic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcophagus
A sarcophagus (plural sarcophagi or sarcophaguses) is a box-like funeral receptacle for a corpse, most commonly carved in stone, and usually displayed above ground, though it may also be buried. The word ''sarcophagus'' comes from the Greek σάρξ ' meaning "flesh", and φαγεῖν ' meaning "to eat"; hence ''sarcophagus'' means "flesh-eating", from the phrase ''lithos sarkophagos'' ( λίθος σαρκοφάγος), "flesh-eating stone". The word also came to refer to a particular kind of limestone that was thought to rapidly facilitate the decomposition of the flesh of corpses contained within it due to the chemical properties of the limestone itself. History of the sarcophagus Sarcophagi were most often designed to remain above ground. The earliest stone sarcophagi were used by Egyptian pharaohs of the 3rd dynasty, which reigned from about 2686 to 2613 B.C. The Hagia Triada sarcophagus is a stone sarcophagus elaborately painted in fresco; one style of late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphitheater
An amphitheatre (British English) or amphitheater (American English; both ) is an open-air venue used for entertainment, performances, and sports. The term derives from the ancient Greek ('), from ('), meaning "on both sides" or "around" and ('), meaning "place for viewing". Ancient Roman amphitheatres were oval or circular in plan, with seating tiers that surrounded the central performance area, like a modern open-air stadium. In contrast, both ancient Greek and ancient Roman theatres were built in a semicircle, with tiered seating rising on one side of the performance area. Modern parlance uses "amphitheatre" for any structure with sloping seating, including theatre-style stages with spectator seating on only one side, theatres in the round, and stadia. They can be indoor or outdoor. Natural formations of similar shape are sometimes known as natural amphitheatres. Roman amphitheatres About 230 Roman amphitheatres have been found across the area of the Roman Empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Aqueduct
The Romans constructed aqueducts throughout their Republic and later Empire, to bring water from outside sources into cities and towns. Aqueduct water supplied public baths, latrines, fountains, and private households; it also supported mining operations, milling, farms, and gardens. Aqueducts moved water through gravity alone, along a slight overall downward gradient within conduits of stone, brick, concrete or lead; the steeper the gradient, the faster the flow. Most conduits were buried beneath the ground and followed the contours of the terrain; obstructing peaks were circumvented or, less often, tunneled through. Where valleys or lowlands intervened, the conduit was carried on bridgework, or its contents fed into high-pressure lead, ceramic, or stone pipes and siphoned across. Most aqueduct systems included sedimentation tanks, which helped to reduce any water-borne debris. Sluices, ''castella aquae'' (distribution tanks) and stopcocks regulated the supply to individ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |