|
Aliciella Micromeria
''Aliciella micromeria'' (formerly ''Gilia micromeria'') is a species of flowering plant in the phlox family known by the common name dainty gilia. It is native to the western United States, especially the Great Basin. It is a small herb producing a thin, branching stem up to about 14 centimeters tall. It is coated thinly in soft hairs. Several deeply lobed leaves 1 to 6 centimeters long are located in a basal rosette at ground level around the stem. There are smaller, unlobed leaves along the stem. The inflorescence produces white or lavender flowers each about 3 millimeters wide. External links Jepson Manual Treatment micromeria
''Micromeria'' is a ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asa Gray
Asa Gray (November 18, 1810 – January 30, 1888) is considered the most important American botanist of the 19th century. His ''Darwiniana'' was considered an important explanation of how religion and science were not necessarily mutually exclusive. Gray was adamant that a genetic connection must exist between all members of a species. He was also strongly opposed to the ideas of hybridization within one generation and special creation in the sense of its not allowing for evolution. He was a strong supporter of Darwin, although Gray's theistic evolution was guided by a Creator. As a professor of botany at Harvard University for several decades, Gray regularly visited, and corresponded with, many of the leading natural scientists of the era, including Charles Darwin, who held great regard for him. Gray made several trips to Europe to collaborate with leading European scientists of the era, as well as trips to the southern and western United States. He also built an extensive ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polemoniaceae
The Polemoniaceae (Jacob's-ladder or phlox family) are a family of flowering plants consisting of about 25 genera with 270–400 species of annuals and perennials native to the Northern Hemisphere and South America, with the center of diversity in western North America. Only one genus (''Polemonium'') is found in Europe, and two (''Phlox'' and ''Polemonium'') in Asia, where they are confined to cool temperate to arctic regions; both genera also occur more widely in North America, suggesting relatively recent colonization of the Old World from North America. The family can be distinguished from most other eudicot families by the ovary made up of three fused carpels (usually with three chambers, but with one chamber in some species). The members of the family have five sepals, five petals fused, and five stamens that alternate with the lobes of the corolla. For decades, most sources used a classification of the family published by Grant in 1959, but new evidence, including mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
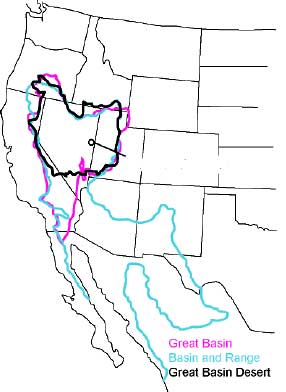
Great Basin
The Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic basin, endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja California. It is noted for both its arid climate and the basin and range topography that varies from the North American low point at Badwater Basin in Death Valley to the highest point of the contiguous United States, less than away at the summit of Mount Whitney. The region spans several physical geography, physiographic divisions, biomes, ecoregions, and deserts. Definition The term "Great Basin" is applied to hydrography, hydrographic, ecology, biological, floristic province, floristic, physiographic, topography, topographic, and Ethnography, ethnographic geographic areas. The name was originally coined by John C. Frémont, who, based on information gleaned from Joseph R. Walker as well as his own travels, recognized the hydrographic nature o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflorescence
An inflorescence is a group or cluster of flowers arranged on a stem that is composed of a main branch or a complicated arrangement of branches. Morphologically, it is the modified part of the shoot of seed plants where flowers are formed on the axis of a plant. The modifications can involve the length and the nature of the internodes and the phyllotaxis, as well as variations in the proportions, compressions, swellings, adnations, connations and reduction of main and secondary axes. One can also define an inflorescence as the reproductive portion of a plant that bears a cluster of flowers in a specific pattern. The stem holding the whole inflorescence is called a peduncle. The major axis (incorrectly referred to as the main stem) above the peduncle bearing the flowers or secondary branches is called the rachis. The stalk of each flower in the inflorescence is called a pedicel. A flower that is not part of an inflorescence is called a solitary flower and its stalk is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aliciella
''Aliciella'' is a genus of plants in the phlox family. These plants have been treated as members of genus ''Gilia'' until recently, when it was proposed they be moved back to ''Aliciella''. This genus was created in 1905 to include certain gilias that seemed distinct from most of the others, but it was abandoned soon after.The Story of ''Gilia'' and ''Aliciella''. Southwest Colorado Wildflowers. Recent genetic analyses suggest it should be revived.Porter, J. M. (1998). ''Aliciella'', a recircumscribed genus of Polemoniaceae. ''Aliso'' 17:1 23-46. Selected current species: *'' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)