|
Alianza Anticomunista Argentina
The Argentine Anticommunist Alliance ( es, Alianza Anticomunista Argentina, links=no, usually known as Triple A or AAA) was an Argentine Peronist political action group operated by a sector of the Federal Police and the Argentine Armed Forces, linked with the anticommunist lodge Propaganda Due, that killed artists, priests, intellectuals, leftist politicians, students, historians and union members, as well as issuing threats, carrying out extrajudicial killings and forced disappearances during the presidencies of Juan Perón and Isabel Perón between 1973 and 1976. The group was responsible for the disappearance and death of between 700 and 1100 people. The Triple A was secretly led by José López Rega, Minister of Social Welfare and personal secretary of Juan Perón. Rodolfo Almirón, arrested in Spain in 2006, was alleged to be his chief operating officer of the group, and was officially head of López Rega's and Isabel Perón's personal security. He was extradited from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José López Rega
José López Rega (17 November 1916 – 9 June 1989) was an Argentine politician who served as Minister of Social Welfare from 1973 to 1975, first under Juan Perón and continuing under Isabel Perón, Juan Perón's third wife and presidential successor. Lopez Rega exercised Rasputin-like authority over Isabel Perón during her presidency, and used his influence and unique access to become the ''de facto'' ruler of Argentina. His far-right politics and interest in the occult earned him the nickname ''El Brujo'' ("the Warlock"). Rega had one daughter, Norma Beatriz, who went on to become the spouse of President Raúl Lastiri. Biography Early life López Rega's mother died giving birth to him in Buenos Aires. According to his biography by Marcelo Larraquy (2002), he was a respectful, introverted boy, who had a library covering an entire wall and a special interest in spiritual topics (which would later turn into a passion for esoterism and occultism). He married at the age of 27. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
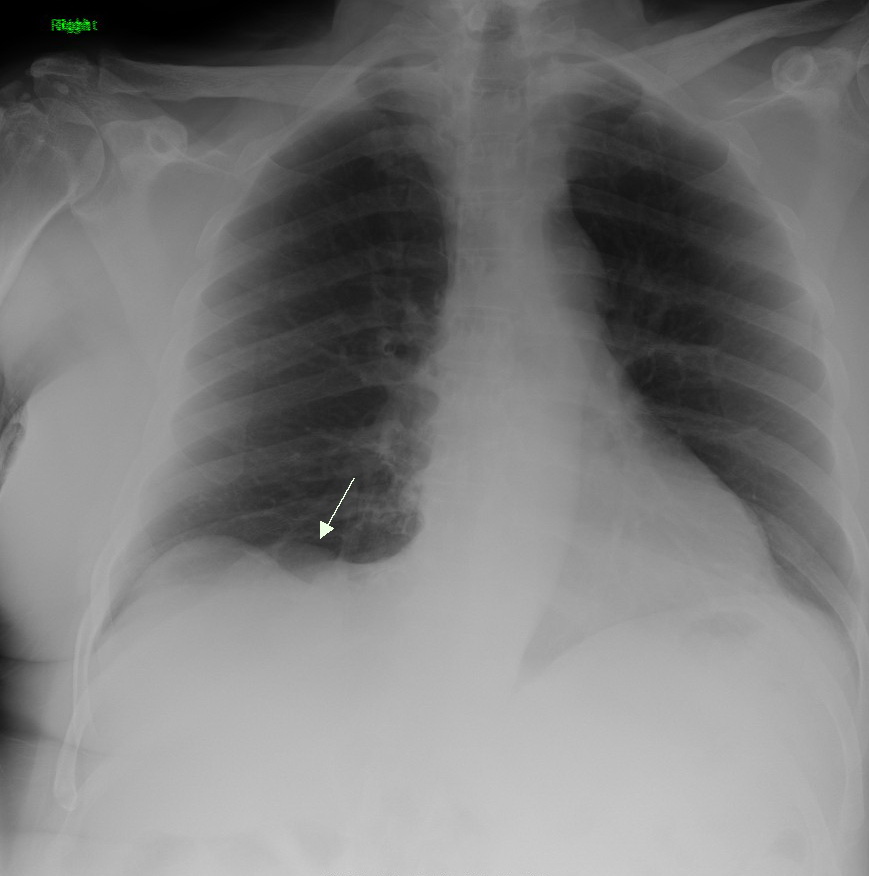
Lung Cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissue (biology), tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malignant cells that originate as epithelial cells, or from tissues composed of epithelial cells. Other lung cancers, such as the rare sarcomas of the lung, are generated by the malignant transformation of connective tissues (i.e. nerve, fat, muscle, bone), which arise from mesenchymal cells. Lymphomas and melanomas (from lymphoid and melanocyte cell lineages) can also rarely result in lung cancer. In time, this uncontrolled neoplasm, growth can metastasis, metastasize (spreading beyond the lung) either by direct extension, by entering the lymphatic circulation, or via hematogenous, bloodborne spread – into nearby tissue or other, more distant parts of the body. Most cancers that originate from within the lungs, known as primary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divination
Divination (from Latin ''divinare'', 'to foresee, to foretell, to predict, to prophesy') is the attempt to gain insight into a question or situation by way of an occultic, standardized process or ritual. Used in various forms throughout history, diviners ascertain their interpretations of how a querent should proceed by reading signs, events, or omens, or through alleged contact or interaction with a supernatural agency. Divination can be seen as a systematic method with which to organize what appears to be disjointed, random facets of existence such that they provide insight into a problem at hand. If a distinction is to be made between divination and fortune-telling, divination has a more formal or ritualistic element and often contains a more social character, usually in a religious context, as seen in traditional African medicine. Fortune-telling, on the other hand, is a more everyday practice for personal purposes. Particular divination methods vary by culture and reli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occultism
The occult, in the broadest sense, is a category of esoteric supernatural beliefs and practices which generally fall outside the scope of religion and science, encompassing phenomena involving otherworldly agency, such as magic and mysticism and their varied spells. It can also refer to supernatural ideas like extra-sensory perception and parapsychology. The term ''occult sciences'' was used in 16th-century Europe to refer to astrology, alchemy, and natural magic. The term ''occultism'' emerged in 19th-century France, amongst figures such as Antoine Court de Gébelin. It came to be associated with various French esoteric groups connected to Éliphas Lévi and Papus, and in 1875 was introduced into the English language by the esotericist Helena Blavatsky. Throughout the 20th century, the term was used idiosyncratically by a range of different authors, but by the 21st century was commonly employed – including by academic scholars of esotericism – to refer to a range of es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigre, Buenos Aires
Tigre (, ''Tiger'') is a city in the Buenos Aires Province, Argentina, situated in the north of Greater Buenos Aires, north of Buenos Aires city. Tigre lies on the Paraná Delta and is a tourist and weekend destination, reachable by bus and train services, including the scenic Tren de la Costa. It is the main city and administrative centre of the Tigre Partido. History The area's name derives from the "tigers" or jaguars that were hunted there, on occasions, in its early years. The area was first settled by Europeans who came to farm the land. The city sits on an island created by several small streams and rivers and was founded in 1820, after floods had destroyed other settlements in the area, then known as the ''Partido de las Conchas''. The port developed to serve the delta and to bring fruit and wood from the delta and ports upstream on the Paraná river. Tigre is still an important timber processing port. Transportation Road Tigre is connected to the capital by a spur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabin Cruiser
A cabin cruiser is a type of power boat that provides accommodation for its crew and passengers inside the structure of the craft. A cabin cruiser usually ranges in size from in length, with larger pleasure craft usually considered yachts. Many cabin cruisers can be recovered and towed with a trailer and thus easily stored on land, which reduces maintenance and expense. These craft are generally equipped with a head (toilet), a galley, and at least one berth. Most cabin cruisers usually have a small dining area and some have an aft cabin (a cabin to the rear of the cockpit, with a double bed). Some cabin cruisers are equipped with heating, air conditioning, and power generators. Most also have water heaters and shore power electric systems. The cabin cruiser provides many of the amenities of larger yachts, while costing much less and normally being fully operable by the owner, whereas larger yachts often require a professional crew. Most newer cabin cruisers are faster than ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José Humberto Martiarena
José is a predominantly Spanish and Portuguese form of the given name Joseph. While spelled alike, this name is pronounced differently in each language: Spanish ; Portuguese (or ). In French, the name ''José'', pronounced , is an old vernacular form of Joseph, which is also in current usage as a given name. José is also commonly used as part of masculine name composites, such as José Manuel, José Maria or Antonio José, and also in female name composites like Maria José or Marie-José. The feminine written form is ''Josée'' as in French. In Netherlandic Dutch, however, ''José'' is a feminine given name and is pronounced ; it may occur as part of name composites like Marie-José or as a feminine first name in its own right; it can also be short for the name ''Josina'' and even a Dutch hypocorism of the name ''Johanna''. In England, Jose is originally a Romano-Celtic surname, and people with this family name can usually be found in, or traced to, the English county of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benito Llambí
Benito may refer to: Places * Benito, Kentucky, United States * Benito, Manitoba, Canada * Benito River, a river in Equatorial Guinea Other uses * Benito (name) * ''Benito'' (1993), an Italian film See also * ''Benito Cereno'', a novella by Herman Melville * Benito Juárez (other) * Bonito, fish in the family Scombridae * Don Benito, a town and municipality in Badajoz, Extremadura, Spain * Olabiran Muyiwa Olabiran Blessing Muyiwa (born 7 September 1998), known as Benito, is a Nigerian professional footballer who plays for Dynamo Kyiv. Club career Benito was released by Russian Premier League The Russian Premier League (RPL; russian: Рос� ... (born 1998), Nigerian footballer known as Benito * San Benito (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peronist
Peronism, also called justicialism,. The Justicialist Party is the main Peronist party in Argentina, it derives its name from the concept of social justice., name=, group= is an Argentine political movement based on the ideas and legacy of Argentine ruler Juan Perón (1895–1974). It has been an influential movement in 20th and 21st century Argentine politics. Since 1946, Peronists have won 10 out of the 13 presidential elections in which they have been allowed to run. The main Peronist party is the Justicialist Party. The policies of Peronist presidents have differed greatly, but the general ideology has been described as "a vague blend of nationalism and labourism" or populism. Perón became Argentina's labour secretary after participating in the 1943 military coup and was elected president of Argentina in 1946. He introduced social programs that benefited the working class, supported labor unions and called for additional involvement of the state in the economy. In addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raúl Lastiri
Raúl Alberto Lastiri (11 September 1915 – 11 December 1978) was an Argentine politician who was interim president of Argentina from July 13, 1973 until October 12, 1973. Lastiri, who presided over the Argentine Chamber of Deputies, was promoted to the presidency of the country after Héctor Cámpora and Vicente Solano Lima resigned, he organized new elections and delivered the country's government to Juan Perón, who won with over 60% of the votes. Biography Rise to power His brief tenure marked a turn towards right-wing policies and factions within the Peronist Party. His father-in-law, José López Rega, a P2 member and the creator of the paramilitary organization ''Triple A'', was confirmed as Minister of Social Welfare. Alberto Juan Vignes replaced Puig in the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Benito Llambí took over from Esteban Righi as Minister of Interior. In spite of this, Argentine foreign policy kept a Third World orientation; for example, in August 1973, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentine Federal Police
The Argentine Federal Police ( es, Policía Federal Argentina or PFA) is the national civil police force of the Argentine federal government. The PFA has detachments throughout the country. Until January 1, 2017, it also acted as the local law enforcement agency in the capital, Buenos Aires. History The history of this police force can be traced to 1580, when the founder of Buenos Aires, Captain Juan de Garay, established a local militia for defense against potential Native American raids. The ''Policía de Buenos Aires'' (Buenos Aires Police) operated for the first three hundred years up to 1880, when the Federalization of Buenos Aires resulted in the creation of the ''Policía de la Capital'' (Police of the Capital). Incidents of social unrest in subsequent years helped prompt the Fraga Law in 1904, which provided for the inclusion of neighborhood representatives as commissioners in their respective precincts. The failed Argentine Revolution of 1905, Revolution of 1905, by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |