|
Ali Sabri
Ali Sabri ( ar, على صبرى, ) (30 August 1920 – 3 August 1991) was an Egyptian politician of Turkish origin. Family background His parents, Dewlet Shamsi (mother) and Abbas-Baligh Sabri (father) were of Turkish- Circassian descent and belonged to the privileged class. Ali Sabri was a grandson of nationalist Amin Shamsi Pasha (1833-1913) a member of the General Assembly and Provincial Council who in 1881-82 was a principal financial backer of Ahmed Urabi Pasha. Following the failure of what historian term the " Urabi Rebellion" of 1882, Khedive Tewfik imprisoned Shamsi Pasha later releasing him on a hefty bail. He resumed his seat at the General Assembly until his death. Sabri was also a nephew of Ali Shamsi Pasha (1885-1962) co-founder of the Wafd Party and a several-time minister during the reign of Fuad I of Egypt later to become the first Egyptian to head of the National Bank of Egypt which acted as the country's Central Bank. One of Ali Sabri's paternal grand- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vice President Of Egypt
The vice-president of the Arab Republic of Egypt is a senior official within the Egyptian government. History of the office Before 1971 In 1962, President Gamal Abdel Nasser instituted collective leadership in Egypt, separating the post of Prime Minister from that of President and establishing a presidential council to deal with all issues formerly considered presidential prerogatives. Five of the council's 11 members were Vice-Presidents of Egypt. Under the 1971 Constitution According to article 139 of the 1971 Constitution, the President "may appoint one or more Vice-Presidents define their jurisdiction and relieve them of their posts. The rules relating to the calling to account of the President of the Republic shall be applicable to the Vice-Presidents." The Constitution gave broad authority to the President to determine the number of Vice-Presidents, as well as their appointment, dismissal and duties of office. After the 2011 amendments, the president should appointed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turks In Egypt
The Turks in Egypt, also referred to as Egyptian Turks, Turkish-Egyptians and Turco-Egyptians ( ar, أتراك مصر tr, ) are Egyptian citizens of partial or full Turkish ancestry, who are the descendants of settlers that arrived in the region during the rule of several Turkic dynasties, including: the Tulunid (868–905), Ikhshidid (935–969), Mamluk (1250–1517), and Ottoman ( 1517–1867 and 1867–1914) eras. Today their descendants continue to live in Egypt and still identify as Egyptians of Turkish or mixed origin, though they are also fully integrated in Egyptian society. History Mamluk era Ottoman era During the four centuries of Ottoman rule, Turkish settlers arrived predominately from Anatolia; however, many also arrived from the Ottoman Isles (such as the Aegean islands, Crete, and Cyprus), as well as from prominent Ottoman cities (such as Istanbul, Algiers, and Tunis). In 1833 one estimate claimed that the Turkish population in Egypt was 30,000; howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
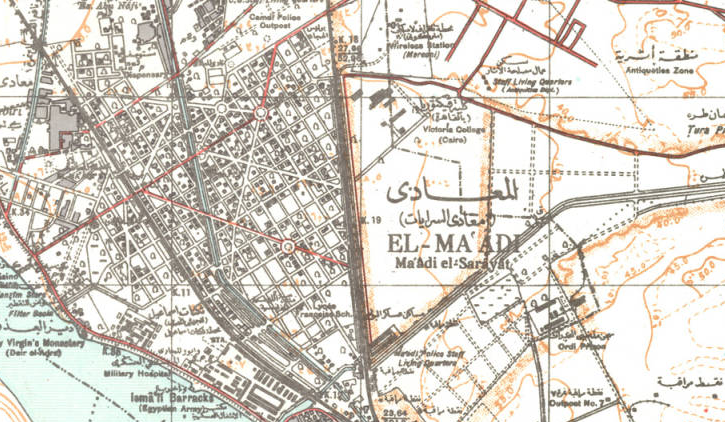
Maadi
Maadi ( ar, المعادي / transliterated: ) is a leafy suburban district south of Cairo, Egypt, on the east bank of the Nile about upriver from downtown Cairo. The Nile at Maadi is parallelled by the Corniche, a waterfront promenade and the main road north into Cairo. There is no bridge across the Nile at Maadi; the nearest one is located at El Mounib along the Ring Road (Tarik El-Da'eri, en, The Round Road) on the way north to the downtown. Maadi's population was estimated to be 97,000 in 2016. The district is popular with international expatriates as well as Egyptians and is home to many embassies, as well as major international schools, sporting clubs, and cultural institutions such as the Supreme Constitutional Court of Egypt and the national Egyptian Geological Museum. Name Ma'ǎdi معادي is the plural form of the word ma'diyya, arz, معدية, which means "ferry"; hence, El-Ma'adi literally means "The ferries". There was a story that the name comes from a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbas Hilmi II
Abbas II Helmy Bey (also known as ''ʿAbbās Ḥilmī Pāshā'', ar, عباس حلمي باشا) (14 July 1874 – 19 December 1944) was the last Khedive ( Ottoman viceroy) of Egypt and Sudan, ruling from 8January 1892 to 19 December 1914. In 1914, after the Ottoman Empire joined the Central Powers in World War I, the nationalist Khedive was removed by the British, then ruling Egypt, in favour of his more pro-British uncle, Hussein Kamel, marking the ''de jure'' end of Egypt's four-century era as a province of the Ottoman Empire, which had begun in 1517. Early life Abbas II (full name: Abbas Hilmy), the great-great-grandson of Muhammad Ali, was born in Alexandria, Egypt on 14 July 1874. In 1887 he was ceremonially circumcised together with his younger brother Mohammed Ali Tewfik. The festivities lasted for three weeks and were carried out with great pomp. As a boy he visited the United Kingdom, and he had a number of British tutors in Cairo including a governess who ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khedive
Khedive (, ota, خدیو, hıdiv; ar, خديوي, khudaywī) was an honorific title of Persian origin used for the sultans and grand viziers of the Ottoman Empire, but most famously for the viceroy of Egypt from 1805 to 1914.Adam Mestyan"Khedive" ''Encyclopaedia of Islam, Three'' (Leiden: Brill, 2020), 2:70–71. It is attested in Persian poetry from the 10th century and was used as an Ottoman honorific from the 16th. It was borrowed into Turkish directly from Persian. It was first used in Egypt, without official recognition, by Muhammad Ali Pasha, the ethnically Albanian governor of Egypt and Sudan from 1805 to 1848. The initially self-declared title was officially recognized by the Ottoman government in 1867, and used subsequently by Ismail Pasha, and his dynastic successors until 1914. The term entered Arabic in Egypt in the 1850s. Etymology This title is recorded in English since 1867, borrowed from French , in turn from Ottoman Turkish , from Classical Persian (" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuad I Of Egypt
Fuad I ( ar, فؤاد الأول ''Fu’ād al-Awwal''; tr, I. Fuad or ; 26 March 1868 – 28 April 1936) was the Sultan and later King of Egypt and the Sudan. The ninth ruler of Egypt and Sudan from the Muhammad Ali dynasty, he became Sultan in 1917, succeeding his elder brother Hussein Kamel. He replaced the title of Sultan with King when the United Kingdom unilaterally declared Egyptian independence in 1922. Early life Fuad was born in Giza Palace in Cairo, the fifth issue of Isma'il Pasha. He spent his childhood with his exiled father in Naples. He got his education from the military academy in Turin, Italy. His mother was Ferial Qadin. Prior to becoming sultan, Fuad had played a major role in the establishment of Egyptian University. He became the university's first rector in 1908, and remained in the post until his resignation in 1913. He was succeeded as rector by then-minister of Justice Hussein Rushdi Pasha. In 1913, Fuad made unsuccessful attempts to secure the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wafd Party
The Wafd Party (; ar, حزب الوفد, ''Ḥizb al-Wafd'') was a nationalist liberal political party in Egypt. It was said to be Egypt's most popular and influential political party for a period from the end of World War I through the 1930s. During this time, it was instrumental in the development of the 1923 constitution, and supported moving Egypt from dynastic rule to a constitutional monarchy, where power would be wielded by a nationally-elected parliament. The party was dissolved in 1952, after the 1952 Egyptian Revolution. History Rise The Wafd party was an Egyptian nationalist movement that came into existence in the aftermath of World War I. Although it was not the first nationalist group in Egypt, it had the longest lasting impact. It was preceded and influenced by smaller and less significant movements which evolved over time into the more modern and stronger nationalist Wafd Party. One of these earlier movements was the Urabi Revolt led by Ahmed Urabi in the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ali Shamsi Pasha
Ali Shamsi Pasha (also spelled Shamsy, Shemsi, or Chamsi) was an Egyptian statesman. Life He was born in Egypt in 1885 the scion of senior members of the Tufenkjians, an Ottoman mounted military corps dating back to the 17th century when Egypt was ruled by ''walis'' or governors appointed by the sultan in Istanbul. Family Among Ali's ancestors we find the five Tufenkjian brothers who were exiled to the Hedjaz in 1768 for their attempt at toppling the incumbent governor. Wrapping up four generations of righteous Tufenkjian officers, Ali Shamsi's ancestor, ''Serwan-Pasha'' Mohammed Tufkenjian-Shamsi, was aide-de-camp to Mohammed Ali Pasha. Having recently restored the Timraz al-Ahmadi Mosque in Cairo's Darb al-Shamsi (Sayeda Zeinab district), Mohammed was buried therein circa 1817. The mosque had already been renovated the previous century by Mohammed's uncle ''al-Sharif'' Hassan Tufenkjian-Shamsi, a devout member of the Sufi al-Qadiriyah Order founded by his maternal ancestor Ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khedive Tewfik
Mohamed Tewfik Pasha ( ar, محمد توفيق باشا ''Muḥammad Tawfīq Bāshā''; April 30 or 15 November 1852 – 7 January 1892), also known as Tawfiq of Egypt, was khedive of Egypt and the Sudan between 1879 and 1892 and the sixth ruler from the Muhammad Ali Dynasty. Early life He was the eldest son of Khedive Ismail, and was born on April 30 or November 15, 1852. His mother was Princess Shafiq-Nur. He was not sent to Europe to be educated like his younger brothers, but grew up in Egypt. He spoke French and English fluently. In 1866 Ismail succeeded in his endeavour to alter the order of succession to the Khedivate of Egypt. The title, instead of passing to the eldest living male descendant of Muhammad Ali, was now to descend from father to son. Ismail sought this alteration mainly because he disliked his uncle, Halim Pasha, who was his heir-presumptive, and he had imagined that he would be able to select whichever of his sons he pleased for his successor. But he fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |