|
Ali Coulibaly
Ali Coulibaly (r. 1757 – c. 1759) was a king of the Bambara Empire of Ségou. Son of empire founder Bitòn Coulibaly and brother to the previous king, Dinkoro Coulibaly, Ali took the throne following his brother's assassination. A devout Muslim, he attempted to convert his largely animist Bambara subjects. Ali became widely unpopular for his interference with local religious practices and his ban on millet beer, and was overthrown. His death triggered a decade of instability in the Bambara Empire until the 1766 ascension of Ngolo Diarra Ngolo Diarra was the king of the Bambara Empire from 1766 to 1795. Following the 1755 death of empire founder Bitòn Coulibaly, his descendants (the Bitonsi) proved unable to maintain control, the kingdom fell briefly into chaos. Ngolo Diarra, a fr ... to the throne. References Malian Muslims Bamana Empire 18th-century monarchs in Africa Year of death unknown Year of birth unknown {{Mali-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bambara Empire
The Bamana Empire (also Bambara Empire or Ségou Empire, bm, italics=no, ߓߊ߲ߓߊߙߊ߲߫ ߝߊ߯ߡߟߊ, Banbaran Fāmala) was a large West African state based at Ségou, now in Mali. This state was established after the fall of the Mali Empire and the Keita dynasty, as a smaller Bambara Empire founded by other Bambara families related to the Keita clan. It was ruled by the Kulubali or Coulibaly dynasty established c. 1640 by Kaladian Coulibaly also known as Fa Sine or Biton-si-u. The empire existed as a centralized state from 1712 until the 1861 invasion of Toucouleur conqueror, El Hadj Umar Tall. History Coulibaly dynasty In around 1640, Fa Sine became the third Faama ( Mande word for King) of a small kingdom of Bambara people in the city of Ségou in Mali. Though he made many successful conquests of neighboring tribes and kingdoms, he failed to set up a significant administrative framework, and the new empire disintegrated following his death (c. 1660). In the early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ségou
Ségou (; bm, ߛߋߓߎ, italic=no, ) is a town and an urban commune in south-central Mali that lies northeast of Bamako on the right bank of the River Niger. The town is the capital of the Ségou Cercle and the Ségou Region. With 130,690 inhabitants in 2009, it is the fifth-largest town in Mali. The village of Ségou-Koro, upstream of the present town, was established in the 17th century and became the capital of the Bambara Empire. History In the middle of the 19th century there were four villages with the name of Ségou spread out over a distance of around along the right bank of the river. They were, starting from the most upstream, Ségou-Koro (Old Ségou), Ségou-Bougou, Ségou-Koura (New Ségou) and Ségou-Sikoro. The present town is on the site of Ségou-Sikoro. The village of Ségou-Koro prospered after Biton Mamary Coulibaly became king in 1712 and founded the Ségou (or Bamana) Empire. Mungo Park became the first European known to have visited the village ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bitòn Coulibaly
Bitòn Coulibaly (1689?–1755), also known as Mamary Coulibaly, founded the Bambara Empire in what is now Mali's Ségou Region and Mopti Region. Biography Great-grandson of former Ségou king Kaladian Coulibaly, Mamary Coulibaly settled in Ségou in his youth and soon became head of the Tòn, a voluntary organization for young men, taking the title of "Bitòn." Under Coulibaly's leadership, the Tòn transformed from an egalitarian society into an army of "Tondions." Prompted by popular uprising against the king of Ségou, the populace suggested he take over the leadership of the Bambara kingdom. Coulibaly quickly subdued rival chiefs of Ségou through a vote a cloture of the chiefs, and used the city as a capital for his new Bambara Empire. Fortifying himself with defensive techniques from the Songhai tradition, Coulibaly created a thousand-man army and a navy of war canoes to patrol the Niger River, staffing both with men already captured in his conquests. Coulibal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinkoro Coulibaly
Dinkoro Coulibaly was the ruler of the Bambara Empire from 1755 to 1757. Successor and relative of empire founder Bitòn Coulibaly, Dinkoro soon lost control of the empire in a succession of military coups. Dinkoro was assassinated in 1757, and succeeded by his brother, Ali Coulibaly. The empire fell briefly into civil war before Ngolo Diarra Ngolo Diarra was the king of the Bambara Empire from 1766 to 1795. Following the 1755 death of empire founder Bitòn Coulibaly, his descendants (the Bitonsi) proved unable to maintain control, the kingdom fell briefly into chaos. Ngolo Diarra, a fr ... seized control in 1766 and reasserted stability. External linksPre-colonial Malian History (French language) 18th-century monarchs in Africa Bamana Empire 1757 deaths Year of birth unknown {{Mali-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the Muhammad in Islam, main and final Islamic prophet.Peters, F. E. 2009. "Allāh." In , edited by J. L. Esposito. Oxford: Oxford University Press. . (See alsoquick reference) "[T]he Muslims' understanding of Allāh is based...on the Qurʿān's public witness. Allāh is Unique, the Creator, Sovereign, and Judge of mankind. It is Allāh who directs the universe through his direct action on nature and who has guided human history through his prophets, Abraham, with whom he made his covenant, Moses/Moosa, Jesus/Eesa, and Muḥammad, through all of whom he founded his chosen communities, the 'Peoples of the Book.'" It is the Major religious groups, world's second-largest religion behind Christianity, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animism
Animism (from Latin: ' meaning 'breath, Soul, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct Spirituality, spiritual essence. Potentially, animism perceives all things—Animal, animals, Plant, plants, Rock (geology), rocks, River, rivers, Weather, weather systems, human handiwork, and perhaps even Word, words—as animated and alive. Animism is used in the anthropology of religion, as a term for the Belief, belief system of many Indigenous peoples, especially in contrast to the relatively more recent development of organized religions. Animism focuses on the Metaphysics, metaphysical universe, with a specific focus on the concept of the immaterial soul. Although each culture has its own mythologies and rituals, animism is said to describe the most common, foundational thread of indigenous peoples' "spiritual" or "supernatural" perspectives. The animistic perspective is so widely held and inherent to most indigenous peoples, that they ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bambara People
The Bambara ( bm, ߓߡߊߣߊ߲, italics=no, ''Bamana'' or ''Banmana'') are a Mandé ethnic group native to much of West Africa, primarily southern Mali, Guinea, Burkina Faso and Senegal. They have been associated with the historic Bambara Empire. Today they make up the largest Mandé ethnic group in Mali, with 80% of the population speaking the Bambara language, regardless of ethnicity. Ethnonym According to the ''Encyclopedia of Africa'', "Bambara" means "believer" or "infidel"; the group acquired the name because it resisted Islam after the religion was introduced in 1854 by Tukulor conqueror El Hadj Umar Tall." History The Bamana originated as a royal section of the Mandinka people. They are founders of the Mali Empire in the 13th Century. Both Manding and Bambara are part of the Mandé ethno-linguistic group, whose divergence is dated to at least about 7,000 years ago, and branches of which are associated with sites near Tichitt (now subsumed by the Sahara in sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millet Beer
Millet beer, also known as Bantu beer, malwa, pombe "Tchouk" or opaque beer, is an alcoholic beverage made from malted millet that is common throughout Africa. Its production process varies across regions and in the southern parts of Africa is more commonly known as umqombothi. Millet beer varies in taste and alcoholic content between ethnic groups. It is served in calabash gourds. Production This type of beer is common throughout Africa. Related African drinks include maize beer and sorghum beer. In the Balkans and Turkey a form of millet beer named boza is produced. In the U.S., Sprecher Brewery produces a type of beer that contains a mix of millet and sorghum known as Shakparo. A form of millet beer is also produced by the Ainu. Production process Millet kernels are soaked in warm water until they sprout, with the goal to increase the content of maltose in the grain. The millet is then dried out to arrest the germination process. The malted grain is then pulverized and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngolo Diarra
Ngolo Diarra was the king of the Bambara Empire from 1766 to 1795. Following the 1755 death of empire founder Bitòn Coulibaly, his descendants (the Bitonsi) proved unable to maintain control, the kingdom fell briefly into chaos. Ngolo Diarra, a freed slave, seized the throne in 1766 and soon restored order. Mungo Park, passing through the Bambara capital of Ségou two years after Diarra's 1795 death, recorded a testament to the Empire's prosperity under his reign: :"The view of this extensive city, the numerous canoes on the river, the crowded population, and the cultivated state of the surrounding countryside, formed altogether a prospect of civilization and magnificence that I little expected to find in the bosom of Africa." 1 Ngolo Diarra died in a campaign against the Mossi and was succeeded by his son Mansong Diarra. His descendants, the Ngolosi, continued to rule the Empire until its fall to Toucouleur conqueror El Hadj Umar Tall in 1861. French football player N'Golo Ka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malian Muslims
Malian may refer to: * Malian, Iran (other), places in Iran with the name * Something of, from, or related to Mali, a country in West Africa * Something of, from, or related to the Malians (Greek tribe) in Ancient Greece * Something of, from, or related to the Mali Empire The Mali Empire ( Manding: ''Mandé''Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: ''UNESCO General History of Africa, Vol. IV, Abridged Edition: Africa from the Twelfth to the Sixteenth Century'', p. 57. University of California Press, 1997. or Manden; ar, مالي, Māl ..., a medieval West African civilization from c. 1247 to c. 1600 See also * List of all pages beginning with "Malian" {{disambig Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bamana Empire
The Bamana Empire (also Bambara Empire or Ségou Empire, bm, italics=no, ߓߊ߲ߓߊߙߊ߲߫ ߝߊ߯ߡߟߊ, Banbaran Fāmala) was a large West African state based at Ségou, now in Mali. This state was established after the fall of the Mali Empire and the Keita dynasty, as a smaller Bambara Empire founded by other Bambara families related to the Keita clan. It was ruled by the Kulubali or Coulibaly dynasty established c. 1640 by Kaladian Coulibaly also known as Fa Sine or Biton-si-u. The empire existed as a centralized state from 1712 until the 1861 invasion of Toucouleur conqueror, El Hadj Umar Tall. History Coulibaly dynasty In around 1640, Fa Sine became the third Faama ( Mande word for King) of a small kingdom of Bambara people in the city of Ségou in Mali. Though he made many successful conquests of neighboring tribes and kingdoms, he failed to set up a significant administrative framework, and the new empire disintegrated following his death (c. 1660). In the early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century Monarchs In Africa
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic, while declining in Russia, China, and Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolution, with an emphasis on directly interconnected events. To historians who expand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

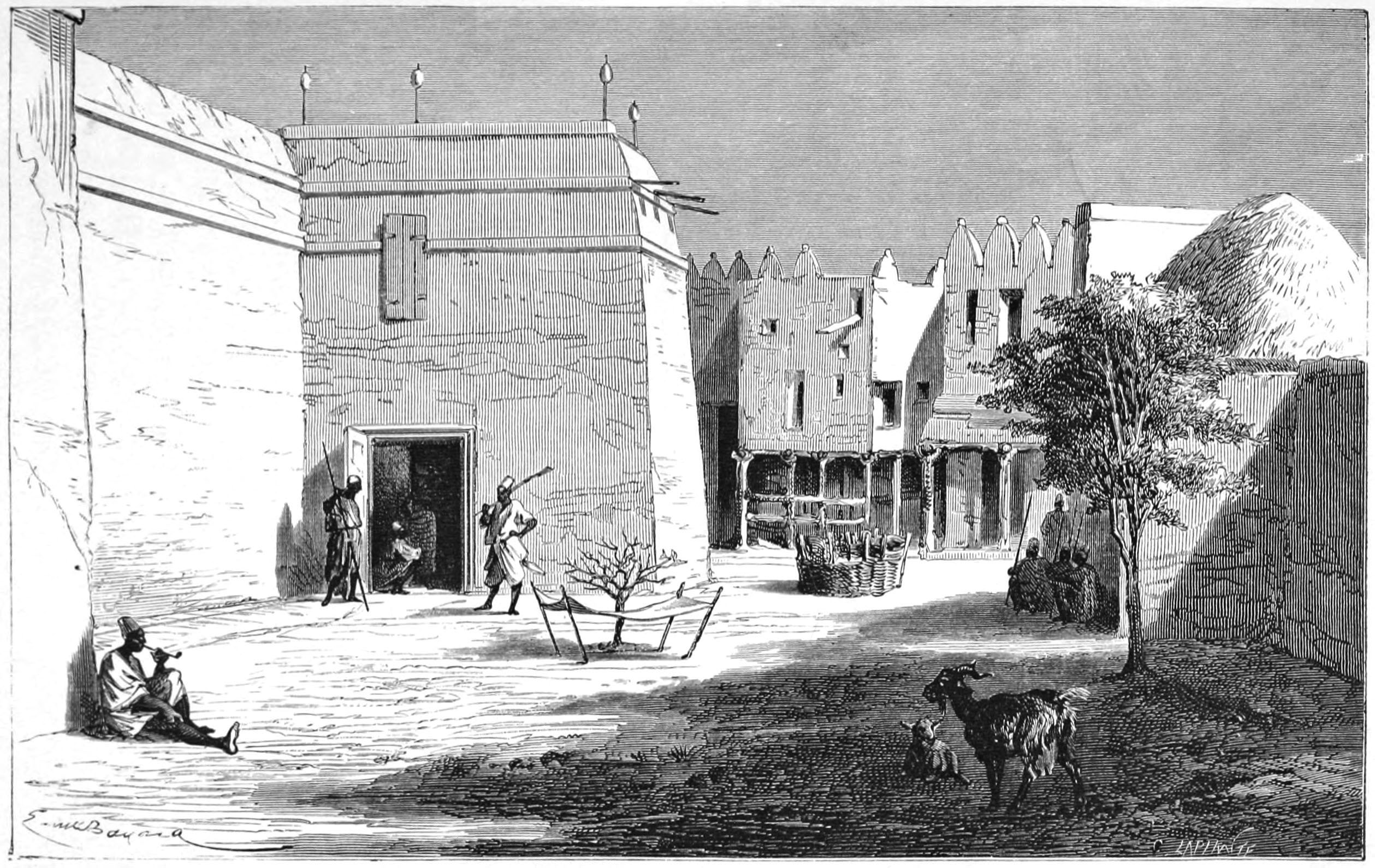
.jpg)


_op_het_bordes_van_Dr._Thoden_van_Velzen_terwijl_kinderen_toekijken_TMnr_20014576.jpg)