|
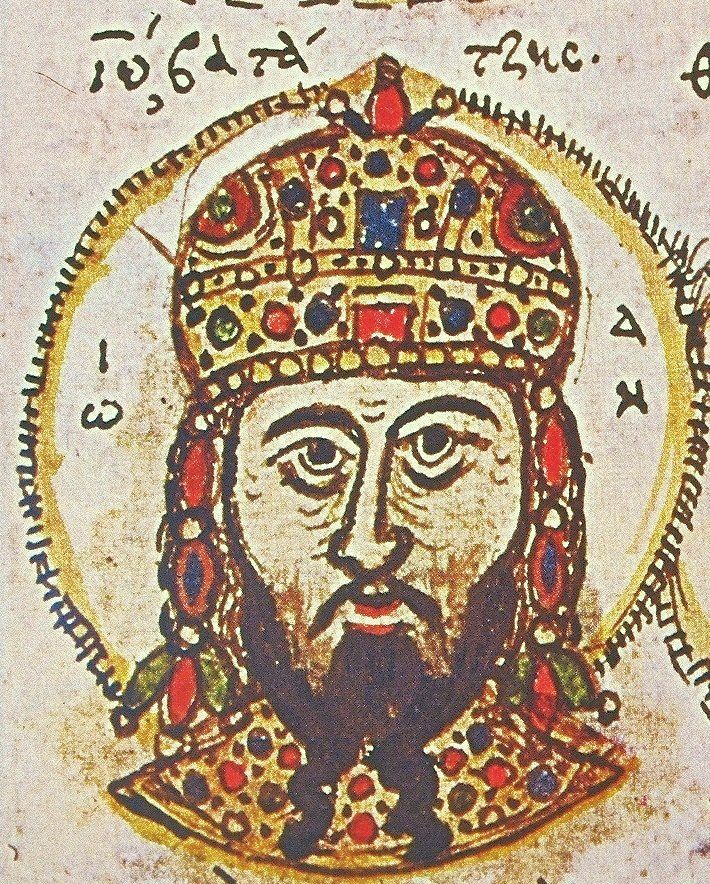
Alexios Strategopoulos
Alexios Komnenos Strategopoulos ( gr, Ἀλέξιος Κομνηνὸς Στρατηγόπουλος) was a Byzantine aristocrat and general who rose to the rank of '' megas domestikos'' and ''Caesar''. Distantly related to the Komnenian dynasty, he appears in the sources already at an advanced age in the early 1250s, leading armies for the Empire of Nicaea against Epirus. After falling out of favour and being imprisoned by Theodore II Laskaris, Strategopoulos sided with the aristocrats around Michael VIII Palaiologos, and supported him in his rise to the throne after Theodore II's death in 1258. He participated in the Pelagonia campaign in 1259, going on to capture Epirus, but his successes were undone in the next year and he was captured by the Epirotes. Released after a few months, he led the unexpected reconquest of Constantinople from the Latin Empire in July 1261, restoring the Byzantine Empire. He was captured again by the Epirotes in the next year and spent several years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empire Of Nicaea
The Empire of Nicaea or the Nicene Empire is the conventional historiographic name for the largest of the three Byzantine Greek''A Short history of Greece from early times to 1964'' by W. A. Heurtley, H. C. Darby, C. W. Crawley, C. M. Woodhouse (1967), p. 55: "There in the prosperous city of Nicaea, Theodoros Laskaris, the son in law of a former Byzantine Emperor, establish a court that soon become the Small but reviving Greek empire." rump states founded by the aristocracy of the Byzantine/Roman Empire that fled after Constantinople was occupied by Western European and Venetian armed forces during the Fourth Crusade, a military event known as the Sack of Constantinople. Like other Byzantine rump states that formed after the 1204 fracturing of the empire, such as the Empire of Trebizond and the Empire of Thessalonica, it was a continuation of the eastern half of the Roman Empire that survived well into the medieval period. A fourth state, known in historiography as the Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised sovereign authority are included, to the exclusion of junior co-emperors (''symbasileis'') who never attained the status of sole or senior ruler, as well as of the various usurpers or rebels who claimed the imperial title. The following list starts with Constantine the Great, the first Christian emperor, who rebuilt the city of Byzantium as an imperial capital, Constantinople, and who was regarded by the later emperors as the model ruler. It was under Constantine that the major characteristics of what is considered the Byzantine state emerged: a Roman polity centered at Constantinople and culturally dominated by the Greek East, with Christianity as the state religion A state religion (also called relig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
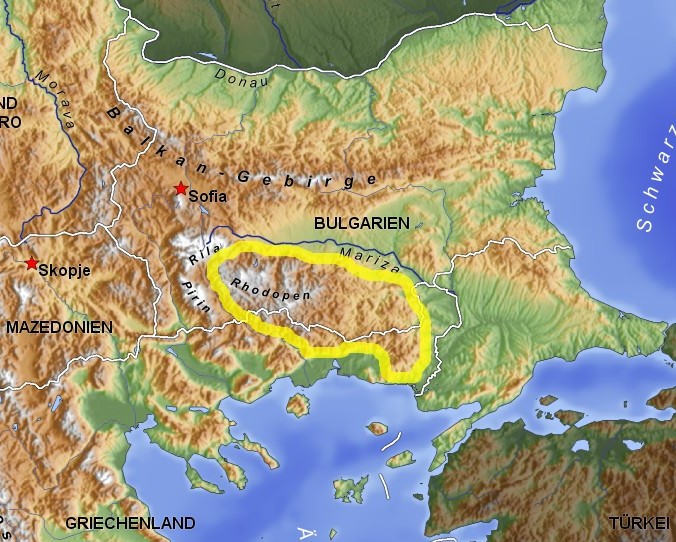
Rhodope Mountains
The Rhodopes (; bg, Родопи, ; el, Ροδόπη, ''Rodopi''; tr, Rodoplar) are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, and the largest by area in Bulgaria, with over 83% of its area in the southern part of the country and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak at . The mountain range gives its name to the terrestrial ecoregion Rodope montane mixed forests that belongs in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome and the Palearctic realm. The region is particularly notable for its karst areas with their deep river gorges, large caves and specific sculptured forms, such as the Trigrad Gorge. A significant part of Bulgaria's hydropower resources are located in the western areas of the range. There are a number of hydro-cascades and dams used for electricity production, irrigation, and as tourist destinations. In Greece, there are also the hydroelectric power plants of Thisavros and Platanovrysi. The Rhodopes have a rich cultural heritage includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine Tornikes (sebastokrator)
Constantine Tornikes or Tornikios ( gr, Κωνσταντῖνος Τορνίκης/Τορνίκιος) was one of the most senior officials during the reign of the Byzantine emperor Alexios III Angelos (r. 1195–1203). He was a descendant of the prominent Tornikios clan, of Armenian or Georgian origin.. His father, Demetrios Tornikios, was a prominent official who rose to become ''logothetes tou dromou'' (Postal Logothete, in effect foreign minister), a post he continuously occupied from circa 1191 until his death. Constantine is first mentioned as being involved in the riots that broke out in the imperial capital, Constantinople, in late 1198 or 1199. Originally, the mob protested against the crimes of the head of the capital's prison (the ''praetorium''), John Lagos, but soon it turned into a full-scale rebellion against Alexios III, which had to be bloodily suppressed. At the time, Constantine was Eparch (governor) of the capital. In 1200 or 1201, after his father's death, Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megas Primmikerios
The Latin term ''primicerius'', hellenized as ''primikērios'' ( el, πριμικήριος), was a title applied in the later Roman Empire and the Byzantine Empire to the heads of administrative departments, and also used by the Church to denote the heads of various colleges. Etymologically the term derives from ''primus in cera'', which is to say ''in tabula cerata'', the first name in a list of a class of officials, which was usually inscribed on a waxed tablet. Civil and military From their origin in the court of the Dominate, there were several ''primicerii'' (''primikērioi'' in Greek, from the 12th century usually spelled ''primmikērioi''). In the court, there was the ''primicerius sacri cubiculi'' (in Byzantine times the ''primikērios'' of the ''kouboukleion''), in charge of the emperor's bedchamber, almost always a eunuch. The title was also given to court officials in combination with other offices connected to the imperial person, such as the special treasury (''eidi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macedonia (region)
Macedonia () is a geographical and historical region of the Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. Its boundaries have changed considerably over time; however, it came to be defined as the modern geographical region by the mid 19th century. Today the region is considered to include parts of six Balkan countries: larger parts in Greece, North Macedonia, and Bulgaria, and smaller parts in Albania, Serbia, and Kosovo. It covers approximately and has a population of 4.76 million. Its oldest known settlements date back approximately to 7,000 BC. From the middle of the 4th century BC, the Kingdom of Macedon became the dominant power on the Balkan Peninsula; since then Macedonia has had a diverse history. Etymology Both proper nouns ''Makedṓn'' and ''Makednós'' are morphologically derived from the Ancient Greek adjective ''makednós'' meaning "tall, slim", and are related to the term Macedonia. Boundaries and definitions Ancient times The definition of Macedonia has chang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serres
Sérres ( el, Σέρρες ) is a city in Macedonia, Greece, capital of the Serres regional unit and second largest city in the region of Central Macedonia, after Thessaloniki. Serres is one of the administrative and economic centers of Northern Greece. The city is situated in a fertile plain at an elevation of about , some northeast of the Strymon river and north-east of Thessaloniki, respectively. Serres' official municipal population was 76,817 in 2011 with the total number of people living in the city and its immediate surroundings estimated at around 100,000. The city is home to the Department of Physical Education and Sport Science of the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki ( el, Τ.Ε.Φ.Α.Α. Σερρών) and the Serres Campus of the International Hellenic University (former " Technological Educational Institute of Central Macedonia"), composed of the Faculty of Engineering, the Faculty of Economics and Management, and the Department of Interior Architecture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Ostrovo
Lake Vegoritida ( el, Λίμνη Βεγορίτιδα, ''Limni Vegoritida''), also known in the past as Lake Ostrovo ( el, Λίμνη Οστρόβου, ''Limni Ostrovou''), is a large natural lake in western Macedonia, northern Greece. It is situated 6 km northeast of Amyntaio and 18 km west of Edessa Edessa (; grc, Ἔδεσσα, Édessa) was an ancient city (''polis'') in Upper Mesopotamia, founded during the Hellenistic period by King Seleucus I Nicator (), founder of the Seleucid Empire. It later became capital of the Kingdom of Osroene ..., at 540 m elevation. The Voras Mountains lie to the north. It belongs partly to the Florina regional unit and partly to the Pella regional unit. See also * List of lakes in Greece * Ostrovo Unit of the Scottish Women's Hospitals during the First World War Sources * K. Fytianos, V. Samanidou, T. Agelidis. Comparative Study of Heavy Metals Pollution in Various Rivers and Lakes of Northern Greece. Chemosphere, Vol.16, No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexios Strategopoulos
Alexios Komnenos Strategopoulos ( gr, Ἀλέξιος Κομνηνὸς Στρατηγόπουλος) was a Byzantine aristocrat and general who rose to the rank of '' megas domestikos'' and ''Caesar''. Distantly related to the Komnenian dynasty, he appears in the sources already at an advanced age in the early 1250s, leading armies for the Empire of Nicaea against Epirus. After falling out of favour and being imprisoned by Theodore II Laskaris, Strategopoulos sided with the aristocrats around Michael VIII Palaiologos, and supported him in his rise to the throne after Theodore II's death in 1258. He participated in the Pelagonia campaign in 1259, going on to capture Epirus, but his successes were undone in the next year and he was captured by the Epirotes. Released after a few months, he led the unexpected reconquest of Constantinople from the Latin Empire in July 1261, restoring the Byzantine Empire. He was captured again by the Epirotes in the next year and spent several years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Doukas Vatatzes
Isaac Doukas Vatatzes ( gr, Ἰσαάκιος Δούκας Βατάτζης, Isaakios Doukas Vatatzēs c. 1188-1261) was the brother of the Nicaean emperor John III Doukas Vatatzes (). Life His exact origin is obscure: probably born , he was the oldest of three brothers, alongside John III (the youngest) and an anonymous middle brother. Their parents are unknown, but are considered by modern scholars likely to have been the general Basil Vatatzes and his unknown wife, who was a cousin to the Byzantine emperors Isaac II Angelos and Alexios III Angelos. Like his brother John III, Isaac appears to have dropped the surname "Vatatzes" and was known only as "Isaac Doukas". Very little is known about his life. He held the rank of ''sebastokrator'' in 1253, and in 1261, he was present at the signing of the Treaty of Nymphaeum with the Republic of Genoa, holding the rank of ''pansebastos sebastos'' and the position of ''parakoimomenos'' of the great seal (''sphendone''). He was then sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebastokrator
''Sebastokrator'' ( grc-byz, Σεβαστοκράτωρ, Sevastokrátor, August Ruler, ; bg, севастократор, sevastokrator; sh, sebastokrator), was a senior court title in the late Byzantine Empire. It was also used by other rulers whose states bordered the Empire or were within its sphere of influence ( Bulgarian Empire, Serbian Empire). The word is a compound of '' sebastós'' (, the Greek equivalent of the Latin ''Augustus'') and ''krátōr'' ('ruler', the same element as is found in '' autokrator'', 'emperor'). The wife of a ''Sebastokrator'' was named ''sebastokratorissa'' (, ''sevastokratórissa'') in Greek, ''sevastokratitsa'' () in Bulgarian and ''sebastokratorica'' in Serbian. Eastern Roman Empire The title was created by Emperor Alexios I Komnenos () to honour his elder brother Isaac Komnenos.. According to Anna Komnene, Alexios did this to raise Isaac above the rank of ''Caesar'', which he had already promised to his brother-in-law, Nikephoros Melisse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |