|
Alexander Monro (secundus)
Alexander Monro of Craiglockhart and Cockburn (22 May 1733 – 2 October 1817) was a Scottish anatomist, physician and medical educator. He is typically known as or Junior to distinguish him as the second of three generations of physicians of the same name. His students included the naval physician and abolitionist Thomas Trotter. Munro was from the distinguished Monro of Auchenbowie family. His major achievements included, describing the lymphatic system, providing the most detailed elucidation of the musculo-skeletal system to date and introducing clinical medicine into the curriculum. He is known for the Monro–Kellie doctrine on intracranial pressure, a hypothesis developed by Monro and his former pupil George Kellie, who worked as a surgeon in the port of Leith. Life Alexander Monro, the third and youngest son of Isabella Macdonald of Sleat, and Alexander Monro Primus was born at Edinburgh on 20 May 1733. He was sent with his brothers to Mr Mundell's school, where h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Munro Secundus
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history. Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Aleksander and Aleksandr. Related names and diminutives include Iskandar, Alec, Alek, Alex, Alexandre, Aleks, Aleksa and Sander; feminine forms include Alexandra, Alexandria, and Sasha. Etymology The name ''Alexander'' originates from the (; 'defending men' or 'protector of men'). It is a compound of the verb (; 'to ward off, avert, defend') and the noun (, genitive: , ; meaning 'man'). It is an example of the widespread motif of Greek names expressing "battle-prowess", in this case the ability to withstand or push back an enemy battle line. The earliest attested form of the name, is the Mycenaean Greek feminine anthroponym , , (/ Alexandra/), written in the Linear B syllabic script. Alaksandu, alternatively called ''Alakasandu' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Pringle (physician)
Sir John Pringle, 1st Baronet (10 April 1707 – 18 January 1782) was a Scottish physician who has been called the "father of military medicine" (although Ambroise Paré and Jonathan Letterman have also been accorded this sobriquet). Biography Youth and early career John Pringle was the youngest son of Sir John Pringle, 2nd Baronet, of Stichill, Roxburghshire (1662–1721), by his spouse Magdalen (d. December 1739), daughter of Sir Gilbert Eliott, 3rd Baronet, of Stobs. He was educated at St Andrews, at Edinburgh, and at Leiden. In 1730 he graduated with a degree of Doctor of Physic at the last-named university, where he was an intimate friend of Gerard van Swieten and Albrecht von Haller. He settled in Edinburgh at first as a physician, but between 1733 and 1744 was also Professor of Moral Philosophy at Edinburgh University. In 1742 he became physician to the Earl of Stair, then commanding the British army in Flanders. About the time of the battle of Dettingen in Bavari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Hoffmann
Friedrich Hoffmann or Hofmann (19 February 1660 – 12 November 1742) was a German physician and chemist. He is also sometimes known in English as Frederick Hoffmann. Life His family had been connected with medicine for 200 years before him. Born in Halle, he attended the local gymnasium where he acquired that taste for and skill in mathematics to which he attributed much of his later success. Beginning at age 18, he studied medicine at the University of Jena. From there, in 1680, he went to Erfurt, to attend Kasper Cramer's lectures on chemistry. Next year, returning to Jena, he received his doctor's diploma, and, after publishing a thesis, was permitted to teach. Constant study then began to tell on his health, and in 1682, leaving his already numerous pupils, he opened a practice in Minden at the request of a relative who held a high position in that town. After practising at Minden for two years, Hoffmann made a journey to Holland and England, where he formed the acquaintan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Glisson
Francis Glisson (1597 – 14 October 1677Guido Giglioni'Glisson, Francis (1599?–1677)' ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'', Oxford University Press, Sept 2004; online edn, May 2006, accessed 31 December 2008) was a British physician, anatomist, and writer on medical subjects. He did important work on the anatomy of the liver, and he wrote an early pediatric text on rickets. An experiment he performed helped debunk the balloonist theory of muscle contraction by showing that when a muscle contracted under water, the water level did not rise, and thus no air or fluid could be entering the muscle. Glisson was born in Bristol and was educated in Rampisham, Dorset, and at Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge. Glisson is a well-known medical eponym; he was for forty years Regius Professor of Physic at Cambridge. He died in London. The Glisson family can be traced to present-day Somerset ( en, All The People of Somerset) , locator_map = , coordinates = , regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greyfriars Kirkyard
Greyfriars Kirkyard is the graveyard surrounding Greyfriars Kirk in Edinburgh, Scotland. It is located at the southern edge of the Old Town, adjacent to George Heriot's School. Burials have been taking place since the late 16th century, and a number of notable Edinburgh residents are interred at Greyfriars. The Kirkyard is operated by City of Edinburgh Council in liaison with a charitable trust, which is linked to but separate from the church. The Kirkyard and its monuments are protected as a category A listed building. History Greyfriars takes its name from the Franciscan friary on the site (the friars of which wear grey habits), which was dissolved in 1560. The churchyard was founded in August 1562 after Royal sanction was granted to replace the churchyard at St Giles' Cathedral in Edinburgh. The latter burial ground was not used after around 1600. The Kirkyard was involved in the history of the Covenanters. The Covenanting movement began with signing of the National Cov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
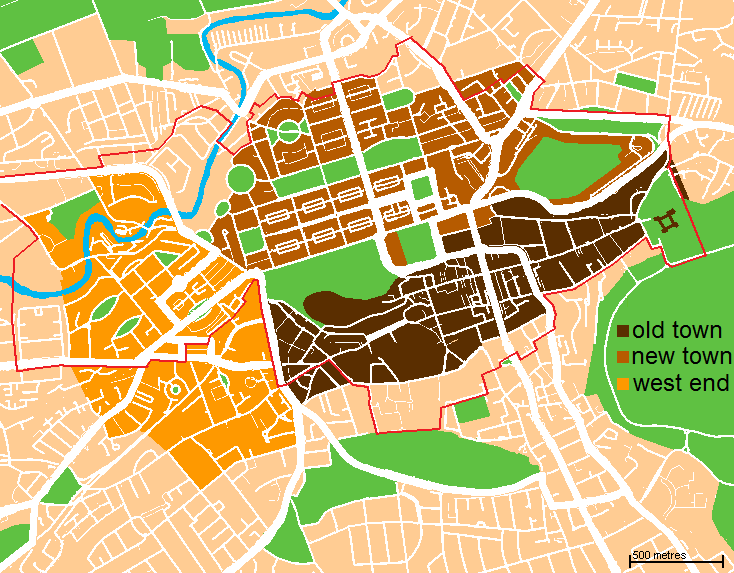
New Town, Edinburgh
The New Town is a central area of Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. It was built in stages between 1767 and around 1850, and retains much of its original neo-classical and Georgian period architecture. Its best known street is Princes Street, facing Edinburgh Castle and the Old Town across the geological depression of the former Nor Loch. Together with the West End, the New Town was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site alongside the Old Town in 1995. The area is also famed for the New Town Gardens, a heritage designation since March 2001. Proposal and planning The idea of a New Town was first suggested in the late 17th century when the Duke of Albany and York (later King James VII and II), when resident Royal Commissioner at Holyrood Palace, encouraged the idea of having an extended regality to the north of the city and a North Bridge. He gave the city a grant:That, when they should have occasion to enlarge their city by purchasing ground without the town, or to build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Monro (tertius)
Alexander Monro III of Craiglockhart, FRSE FRCPE FSA (Scot) MWS (5 November 1773 – 10 March 1859), was a Scottish anatomist and medical educator at the University of Edinburgh Medical School. According to his detractors, Monro was an uninspired anatomist who did not compare with his brilliant father or grandfather as a teacher or scientist. His students included Charles Darwin who asserted that Monro "made his lectures on human anatomy as dull as he was himself." Life Born at Nicolson Street in Edinburgh on 5 November 1773, he was the son of Alexander Monro (distinguished as "Secundus") and grandson of Alexander Monro (distinguished as "Primus") who had both preceded him in the Chair of Anatomy at the University of Edinburgh. He was educated at the Royal High School of Edinburgh, close to his home, then studied medicine at the University of Edinburgh receiving his doctorate (MD) in September 1797. On 5 November that year he became a Licentiate of the Royal College of P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal College Of Physicians Of Edinburgh
The Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh (RCPE) is a medical royal college in Scotland. It is one of three organisations that sets the specialty training standards for physicians in the United Kingdom. It was established by Royal charter in 1681. The college claims to have 12,000 fellows and members worldwide. History The RCPE was formed by a royal charter, granted in 1681, with Sir Robert Sibbald recognised as playing a key part in the negotiations. Three applications preceded this and had been unsuccessful. There were 21 original Fellows, eleven of whom were graduates or students of the University of Leiden. The Universities (Scotland) Act 1858 resulted in several items from the College's Charter becoming obsolete, and they obtained a further charter on 31 October 1861. In 1920 the College enacted changes that allowed women to be admitted on the same terms as men. The charter was amended on 7 May 2005. Edinburgh Pharmacopoeia In 1699 The College first published a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Friedrich Meckel, The Elder
Johann Friedrich Meckel the Elder (31 July 1724 – 18 September 1774) was a German anatomist born in Wetzlar. He often has "the Elder" appended to his name to avoid confusion with his famous grandson Johann Friedrich Meckel (1781–1833), who was also an anatomist and often has "the Younger" included with his name. The elder Meckel's son, Philipp Friedrich Theodor Meckel (1755–1803) and another grandson, August Albrecht Meckel (1790–1829) were also anatomists. Meckel earned his medical doctorate from the University of Göttingen in 1748, and in his thesis, "''Tractatus anatomico physiologicus de quinto pare nervorum cerebri''", he documented his discovery of the submandibular ganglion. Subsequently, he moved to Berlin, where he worked as a prosector and taught classes on midwifery. In 1751 he became a professor of anatomy, botany and obstetrics. In 1773, Meckel was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. Eponyms Meckel has a number of anatomical ep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrus Camper
Petrus Camper FRS (11 May 1722 – 7 April 1789), was a Dutch physician, anatomist, physiologist, midwife, zoologist, anthropologist, palaeontologist and a naturalist in the Age of Enlightenment. He was one of the first to take an interest in comparative anatomy, palaeontology, and the facial angle. He was among the first to mark out an "anthropology," which he distinguished from natural history. He studied the orangutan, the Javan rhinoceros, and the skull of a mosasaur, which he believed was a whale. Camper was a celebrity in Europe and became a member of the Royal Society (1750), the Göttingen (1779), and Russian Academy of Sciences (1778), the Royal Society of Edinburgh (1783), the French (1786) and the Prussian Academy of Sciences (1788). He designed and constructed tools for his patients, and for surgeries. He was an amateur drawer, a sculptor, a patron of art and a conservative, royalist politician. Camper published some lectures containing an account of his craniome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernhard Siegfried Albinus
Bernhard Siegfried Albinus (originally Weiss; 24 February 16979 September 1770) was a German-born Dutch anatomist. He served a professor of medicine at the University of Leiden like his father Bernhard Albinus (1653–1721). He also published a large-format artistic atlas of human anatomy, with engravings made by Jan Wandelaar. Biography Bernhard Siegfried Albinus was born at Frankfurt on the Oder where his father, Bernhard Albinus (1653–1721), was professor of the practice of medicine. In 1702 the latter was transferred to the chair of medicine at Leiden University, and it was there that Bernhard Siegfried began his studies in 1709, at the age of 12, having for his teachers such men as Boerhaave and Govert Bidloo. Having finished his studies at Leiden, he went to Paris in 1718, where, under the instruction of Sébastien Vaillant (1669–1722), Jacob Winslow (1669–1760) and Frederik Ruysch, he devoted himself especially to anatomy and botany. After a year's absence he wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leyden University
Leiden University (abbreviated as ''LEI''; nl, Universiteit Leiden) is a Public university, public research university in Leiden, Netherlands. The university was founded as a Protestant university in 1575 by William the Silent, William, Prince of Orange, as a reward to the city of Leiden for its Siege of Leiden, defence against Spanish attacks during the Eighty Years' War. As the oldest institution of higher education in the Netherlands, it enjoys a reputation across Europe and the world. Known for its historic foundations and emphasis on the social sciences, the university came into particular prominence during the Dutch Golden Age, when scholars from around Europe were attracted to the Dutch Republic due to its climate of intellectual tolerance and Leiden's international reputation. During this time, Leiden became the home to individuals such as René Descartes, Rembrandt, Christiaan Huygens, Hugo Grotius, Baruch Spinoza and Baron d'Holbach. The university has seven academic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |