|
Alejandro Aballay
Alejandro Aballay is an American biologist, currently Dean of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center UTHealth Houston Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences. Aballay was Professor and Chair of the Department of Molecular Microbiology & Immunology at Oregon Health & Science University until 2024. Before that, Aballay was Professor and the Director of the Center for Host-Microbial Interactions at Duke University School of Medicine until 2017. In 2013, he was elected to the American Association for the Advancement of Science. Education Alejandro Aballay earned his bachelor's degree in pharmacy from Juan Agustín Maza University, in Mendoza, Argentina, in 1994. During this time, he worked as an undergraduate student at the National University of Cuyo, in Mendoza, Argentina, where he studied soil bioremediation. He finished his M.S. equivalent studies in 1995 and started exploring the machinery that governs early steps in endocytosis Endocytosis is a cellular process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocytosis
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material. Endocytosis includes pinocytosis (cell drinking) and phagocytosis (cell eating). It is a form of active transport. History The term was proposed by De Duve in 1963. Phagocytosis was discovered by Élie Metchnikoff in 1882. Pathways Endocytosis pathways can be subdivided into four categories: namely, receptor-mediated endocytosis (also known as clathrin-mediated endocytosis), caveolae, pinocytosis, and phagocytosis Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is .... *Clathrin-mediated endocytosis is mediated by the production of smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentine Emigrants To The United States
Argentines (mistakenly translated Argentineans in the past; in Spanish (masculine) or (feminine)) are people identified with the country of Argentina. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Argentines, several (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of their being ''Argentine''. Argentina is a multiethnic and multilingual society, home to people of various ethnic, religious, and national origins, with the majority of the population made up of Old World immigrants and their descendants. As a result, Argentines do not equate their nationality with ethnicity, but with citizenship and allegiance to Argentina. Aside from the indigenous population, nearly all Argentines or their ancestors immigrated within the past five centuries. Among countries in the world that have received the most immigrants in modern history, Argentina, with 6.6 million, ranks second to the United States (27 million), and ahead of other immigr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
21st-century American Biologists
The 1st century was the century spanning AD 1 ( I) through AD 100 ( C) according to the Julian calendar. It is often written as the or to distinguish it from the 1st century BC (or BCE) which preceded it. The 1st century is considered part of the Classical era, epoch, or historical period. The 1st century also saw the appearance of Christianity. During this period, Europe, North Africa and the Near East fell under increasing domination by the Roman Empire, which continued expanding, most notably conquering Britain under the emperor Claudius ( AD 43). The reforms introduced by Augustus during his long reign stabilized the empire after the turmoil of the previous century's civil wars. Later in the century the Julio-Claudian dynasty, which had been founded by Augustus, came to an end with the suicide of Nero in AD 68. There followed the famous Year of Four Emperors, a brief period of civil war and instability, which was finally brought to an end by Vespasian, ninth Roman em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke University Faculty
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are ranked below princess nobility and grand dukes. The title comes from French ''duc'', itself from the Latin ''dux'', 'leader', a term used in republican Rome to refer to a military commander without an official rank (particularly one of Germanic or Celtic origin), and later coming to mean the leading military commander of a province. In most countries, the word ''duchess'' is the female equivalent. Following the reforms of the emperor Diocletian (which separated the civilian and military administrations of the Roman provinces), a ''dux'' became the military commander in each province. The title ''dux'', Hellenised to ''doux'', survived in the Eastern Roman Empire where it continued in several contexts, signifying a rank equivalent to a captain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellows Of The American Association For The Advancement Of Science
Fellowship of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (FAAAS) is an honor accorded by the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) to distinguished persons who are members of the Association. Fellows are elected annually by the AAAS Council for "efforts on behalf of the advancement of science or its applications hichare scientifically or socially distinguished". Examples of areas in which nominees may have made significant contributions are research; teaching; technology; services to professional societies; administration in academe, industry, and government; and communicating and interpreting science to the public. The association has awarded fellowships since 1874. AAAS publishes annual update of active Fellows list, which also provides email address to verify status of non-active Fellows. See also :Fellows of the American Association for the Advancement of Science for more examples. AAAS Fellows AAAS Fellows include Nobel Prize winners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Related categories * :Year of birth missing (living people) / :Year of birth unknown * :Date of birth missing (living people) / :Date of birth unknown * :Place of birth missing (living people) / :Place of birth unknown * :Year of death missing / :Year of death unknown * :Date of death missing / :Date of death unknown * :Place of death missing / :Place of death unknown * :Missing middle or first names See also * :Dead people * :Template:L, which generates this category or death years, and birth year and sort keys. : {{DEFAULTSORT:Living people 21st-century people People by status ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Of Birth Missing (living People)
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
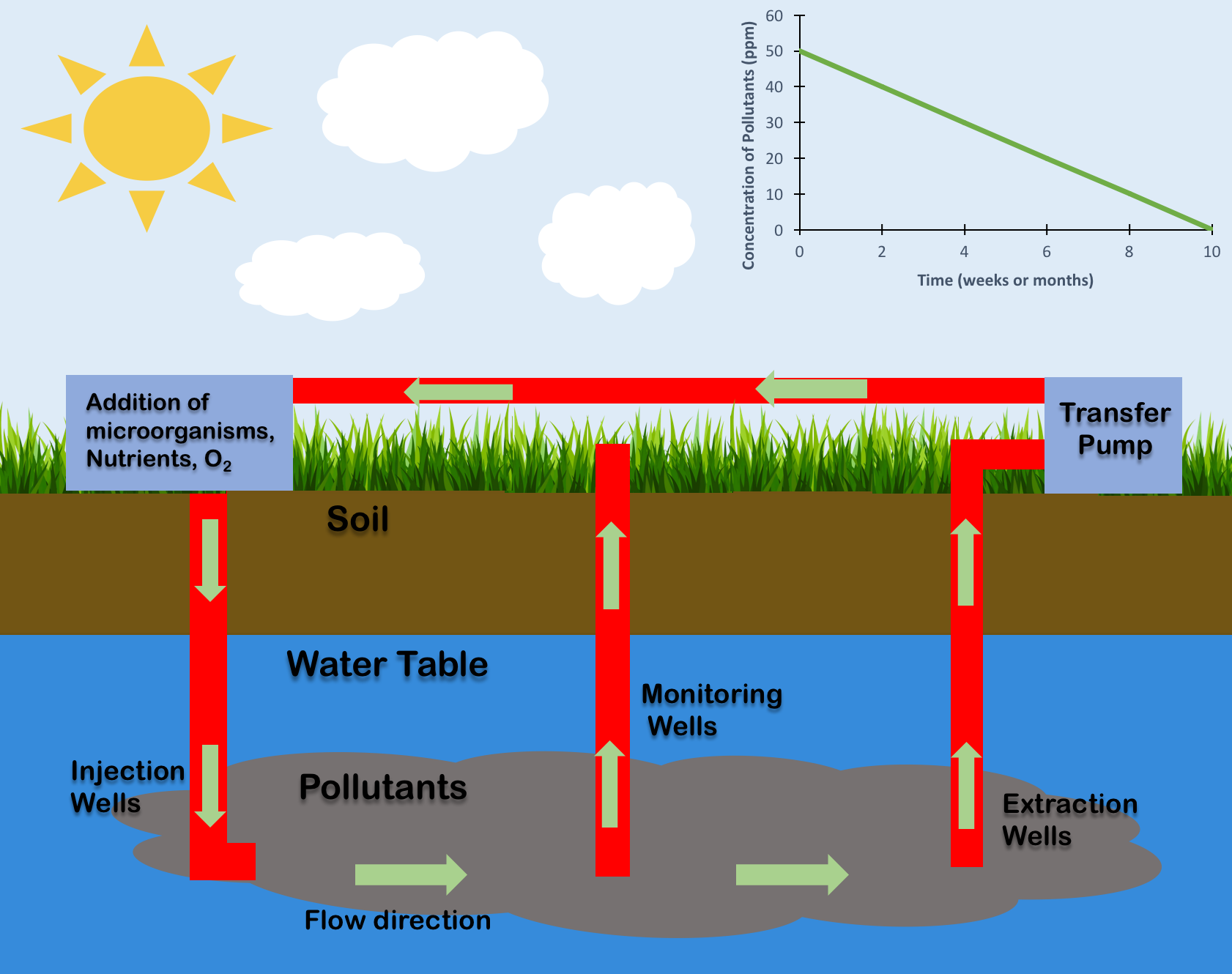
Bioremediation
Bioremediation broadly refers to any process wherein a biological system (typically bacteria, microalgae, fungi, and plants), living or dead, is employed for removing environmental pollutants from air, water, soil, flue gasses, industrial effluents etc., in natural or artificial settings. The natural ability of organisms to adsorb, accumulate, and degrade common and emerging pollutants has attracted the use of biological resources in treatment of contaminated environment. In comparison to conventional physicochemical treatment methods bioremediation may offer considerable advantages as it aims to be sustainable, eco-friendly, cheap, and scalable. Most bioremediation is inadvertent, involving native organisms. Research on bioremediation is heavily focused on stimulating the process by inoculation of a polluted site with organisms or supplying nutrients to promote the growth. In principle, bioremediation could be used to reduce the impact of byproducts created from anthropogenic acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Association For The Advancement Of Science
The American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) is an American international non-profit organization with the stated goals of promoting cooperation among scientists, defending scientific freedom, encouraging scientific responsibility, and supporting scientific education and science outreach for the betterment of all humanity. It is the world's largest general scientific society, with over 120,000 members, and is the publisher of the well-known scientific journal ''Science''. History Creation The American Association for the Advancement of Science was created on September 20, 1848, at the Academy of Natural Sciences in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was a reformation of the Association of American Geologists and Naturalists. The society chose William Charles Redfield as their first president because he had proposed the most comprehensive plans for the organization. According to the first constitution which was agreed to at the September 20 meeting, the goal of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National University Of Cuyo
The National University of Cuyo ( es, Universidad Nacional de Cuyo, UNCuyo) is the largest center of higher education in the province of Mendoza, Argentina. As of 2005, the university had 12 academic schools in the city of Mendoza and a delegation in the city of San Rafael (province of Mendoza), in addition to the Balseiro Institute, which is the most developed institute of Physics research in Argentina, located in the city of San Carlos de Bariloche (province of Río Negro). It includes the University Technological Institute which offers technical education in four other cities in Mendoza province. Moreover, UNCuyo is also devoted to improving education due to having 7 other buildings working as High Schools: * C.U.C. (Colegio Universitario Central "Gral. Jose de San Martin") * Escuela de Comercio Martín Zapata * Liceo Agrícola Domingo Faustino Sarmiento * Escuela del Magisterio * Escuela de Agricultura * D.A.D (Departamento de Aplicación Docente) * Escuela Carmen Vera Are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mendoza, Argentina
Mendoza (, ), officially the City of Mendoza ( es, Ciudad de Mendoza) is the capital of the province of Mendoza in Argentina. It is located in the northern-central part of the province, in a region of foothills and high plains, on the eastern side of the Andes. As of the , Mendoza had a population of 115,041 with a metropolitan population of 1,055,679, making Greater Mendoza the fourth largest census metropolitan area in the country. Ruta Nacional 7, the major road running between Buenos Aires and Santiago, runs through Mendoza. The city is a frequent stopover for climbers on their way to Aconcagua (the highest mountain in the Western and Southern Hemispheres) and for adventure travelers interested in mountaineering, hiking, horse riding, rafting, and other sports. In the winter, skiers come to the city for easy access to the Andes. Two of the main industries of the Mendoza area are olive oil production and Argentine wine. The region around Greater Mendoza is the largest win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |