|
Aldhanab
Gamma Gruis or γ Gruis, formally named Aldhanab (), is a star in the southern constellation of Grus (it once belonged to the Ptolemaic constellation Piscis Austrinus). With an apparent visual magnitude of 3.0, it is the third-brightest star in Grus. Based upon parallax measurements, this star is located at a distance of roughly from the Sun. Nomenclature ''γ Gruis'' ( Latinised to ''Gamma Gruis'') is the system's Bayer designation. It bore the traditional Arabic name ''Al Dhanab'', from the Arabic الذنب ''al-dhanab'' "the tail" (of the Southern Fish). In 2016, the IAU organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) to catalog and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name ''Aldhanab'' for this star on 5 September 2017 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names. In Chinese, (), meaning '' Decayed Mortar'', refers to an asterism consisting of Gamma Gruis, Lambda Gruis, Gamma Piscis Austrini and 19 P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Star Names
Chinese star names (Chinese: , ''xīng míng'') are named according to ancient Chinese astronomy and astrology. The sky is divided into star mansions (, ''xīng xiù'', also translated as "lodges") and asterisms (, ''xīng guān''). The system of 283 asterisms under Three Enclosures and Twenty-eight Mansions was established by Chen Zhuo of the Three Kingdoms period, who synthesized ancient constellations and the asterisms created by early astronomers Shi Shen, Gan De and Wuxian. Since the Han and Jin Dynasties, stars have been given reference numbers within their asterisms in a system similar to the Bayer or Flamsteed designations, so that individual stars can be identified. For example, Deneb (α Cyg) is referred to as (''Tiān Jīn Sì'', the Fourth Star of Celestial Ford). In the Qing Dynasty, Chinese knowledge of the sky was improved by the arrival of European star charts. ''Yixiang Kaocheng'', compiled in mid-18th century by then deputy Minister of Rites Ignaz Kögler, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
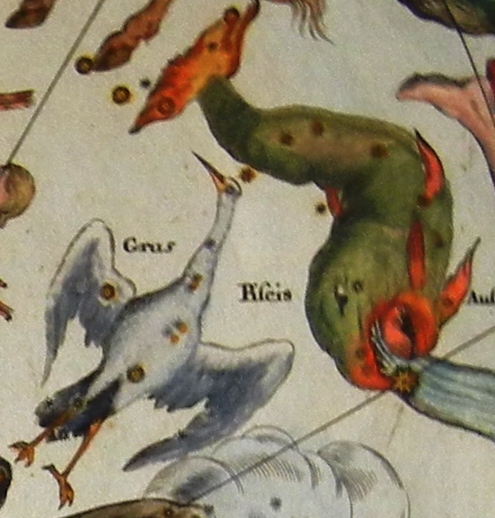
Grus (constellation)
Grus (, or colloquially ) is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the crane, a type of bird. It is one of twelve constellations conceived by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. Grus first appeared on a celestial globe published in 1598 in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius and was depicted in Johann Bayer's star atlas ''Uranometria'' of 1603. French explorer and astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille gave Bayer designations to its stars in 1756, some of which had been previously considered part of the neighbouring constellation Piscis Austrinus. The constellations Grus, Pavo, Phoenix and Tucana are collectively known as the "Southern Birds". The constellation's brightest star, Alpha Gruis, is also known as Alnair and appears as a 1.7-magnitude blue-white star. Beta Gruis is a red giant variable star with a minimum magnitude of 2.3 and a maximum magnitude of 2.0. Six star systems have been foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Rotation
Stellar rotation is the angular motion of a star about its axis. The rate of rotation can be measured from the spectrum of the star, or by timing the movements of active features on the surface. The rotation of a star produces an equatorial bulge due to centrifugal force. As stars are not solid bodies, they can also undergo differential rotation. Thus the equator of the star can rotate at a different angular velocity than the higher latitudes. These differences in the rate of rotation within a star may have a significant role in the generation of a stellar magnetic field. The magnetic field of a star interacts with the stellar wind. As the wind moves away from the star its rate of angular velocity slows. The magnetic field of the star interacts with the wind, which applies a drag to the stellar rotation. As a result, angular momentum is transferred from the star to the wind, and over time this gradually slows the star's rate of rotation. Measurement Unless a star is being observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and physicist William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin (1824–1907). The Kelvin scale is an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale, meaning it uses absolute zero as its null (zero) point. Historically, the Kelvin scale was developed by shifting the starting point of the much-older Celsius scale down from the melting point of water to absolute zero, and its increments still closely approximate the historic definition of a degree Celsius, but since 2019 the scale has been defined by fixing the Boltzmann constant to be exactly . Hence, one kelvin is equal to a change in the thermodynamic temperature that results in a change of thermal energy by . The temperature in degree Celsius is now defined as the temperature in kelvins minus 273.15, meaning t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Effective Temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature when the body's emissivity curve (as a function of wavelength) is not known. When the star's or planet's net emissivity in the relevant wavelength band is less than unity (less than that of a black body), the actual temperature of the body will be higher than the effective temperature. The net emissivity may be low due to surface or atmospheric properties, including greenhouse effect. Star The effective temperature of a star is the temperature of a black body with the same luminosity per ''surface area'' () as the star and is defined according to the Stefan–Boltzmann law . Notice that the total (bolometric) luminosity of a star is then , where is the stellar radius. The definition of the stellar radius is obviously not straightf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nanometer, nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 Hertz, PHz) to 400 nm (750 Hertz, THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionization, ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluorescence, fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. Short-wave ultraviolet light damages DNA and sterilizes surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Luminosity
The solar luminosity (), is a unit of radiant flux (power emitted in the form of photons) conventionally used by astronomers to measure the luminosity of stars, galaxies and other celestial objects in terms of the output of the Sun. One nominal solar luminosity is defined by the International Astronomical Union to be . This does not include the solar neutrino luminosity, which would add , or , i.e. a total of (the mean energy of the solar photons is 26 MeV and that of the solar neutrinos 0.59 MeV, i.e. 2.27%; the Sun emits photons and as many neutrinos each second, of which per m2 reach the Earth each second). The Sun is a weakly variable star, and its actual luminosity therefore fluctuates. The major fluctuation is the eleven-year solar cycle (sunspot cycle) that causes a quasi-periodic variation of about ±0.1%. Other variations over the last 200–300 years are thought to be much smaller than this. Determination Solar luminosity is related to solar irradiance (the solar c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luminosity
Luminosity is an absolute measure of radiated electromagnetic power (light), the radiant power emitted by a light-emitting object over time. In astronomy, luminosity is the total amount of electromagnetic energy emitted per unit of time by a star, galaxy, or other astronomical object. In SI units, luminosity is measured in joules per second, or watts. In astronomy, values for luminosity are often given in the terms of the luminosity of the Sun, ''L''⊙. Luminosity can also be given in terms of the astronomical magnitude system: the absolute bolometric magnitude (''M''bol) of an object is a logarithmic measure of its total energy emission rate, while absolute magnitude is a logarithmic measure of the luminosity within some specific wavelength range or filter band. In contrast, the term ''brightness'' in astronomy is generally used to refer to an object's apparent brightness: that is, how bright an object appears to an observer. Apparent brightness depends on both the lumin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell. Stars on this band are known as main-sequence stars or dwarf stars. These are the most numerous true stars in the universe and include the Sun. After condensation and ignition of a star, it generates thermal energy in its dense core region through nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium. During this stage of the star's lifetime, it is located on the main sequence at a position determined primarily by its mass but also based on its chemical composition and age. The cores of main-sequence stars are in hydrostatic equilibrium, where outward thermal pressure from the hot core is balanced by the inward pressure of gravitational collapse from the overlying layers. The strong dependence of the rate of energy ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Evolution
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes over the course of time. Depending on the mass of the star, its lifetime can range from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is considerably longer than the age of the universe. The table shows the lifetimes of stars as a function of their masses. All stars are formed from collapsing clouds of gas and dust, often called nebulae or molecular clouds. Over the course of millions of years, these protostars settle down into a state of equilibrium, becoming what is known as a main-sequence star. Nuclear fusion powers a star for most of its existence. Initially the energy is generated by the fusion of hydrogen atoms at the core of the main-sequence star. Later, as the preponderance of atoms at the core becomes helium, stars like the Sun begin to fuse hydrogen along a spherical shell surrounding the core. This process causes the star to gradually grow in size, passing throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giant Star
A giant star is a star with substantially larger radius and luminosity than a main sequence, main-sequence (or ''dwarf'') star of the same effective temperature, surface temperature.Giant star, entry in ''Astronomy Encyclopedia'', ed. Patrick Moore, New York: Oxford University Press, 2002. . They lie above the main sequence (luminosity class V in the Spectral classification#Yerkes spectral classification, Yerkes spectral classification) on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram and correspond to luminosity classes II and III.giant, entry in ''The Facts on File Dictionary of Astronomy'', ed. John Daintith and William Gould, New York: Facts On File, Inc., 5th ed., 2006. . The terms ''giant'' and ''dwarf'' were coined for stars of quite different luminosity despite similar temperature or spectral type by Ejnar Hertzsprung about 1905. Giant stars have radii up to a few hundred times the solar radii, Sun and luminosities between 10 and a few thousand times that of the Sun. Stars still mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their stellar spectrum, spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a Prism (optics), prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the Continuum (spectrum), rainbow of colors interspersed with spectral lines. Each line indicates a particular chemical element or molecule, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that element. The strengths of the different spectral lines vary mainly due to the temperature of the photosphere, although in some cases there are true abundance differences. The ''spectral class'' of a star is a short code primarily summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature. Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters ''O'', ''B'', ''A'', ''F'', ''G'', ''K'', and ''M'', a sequence from the hottest (''O'' type) to the coo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |