|
Alder Hey
Alder Hey Children's Hospital is a children's hospital and NHS foundation trust in West Derby, Liverpool, England. It is one of the largest children's hospitals in the United Kingdom, and one of several specialist hospitals within the Liverpool City Region, alongside the Royal Liverpool University Hospital, Liverpool Women's Hospital, Liverpool Heart and Chest Hospital, the Walton Centre, Mersey Regional Burns and Plastic Surgery Unit, and Clatterbridge Cancer Centre. History Early history The hospital was first established as a military hospital in 1914. During the First World War, the United States Army established Camp Hospital 40 on the site, operated by Hospital Unit Q and, subsequently, Unit W. American sources commonly refer to Alder Hey as being within Liverpool's Knotty Ash area. During the Second World War, parts of the hospital were again used to treat injured military personnel. The Liverpool Neonatal Surgical Unit opened at the hospital in 1953. This unit was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Children's Hospital
A children's hospital is a hospital that offers its services exclusively to infants, children, adolescents, and young adults. In certain special cases, they may also treat adults. The number of children's hospitals proliferated in the 20th century, as pediatric medical and surgical specialties separated from internal medicine and adult surgical specialties. Integration Children's hospitals are characterized by greater attention to the psychosocial support of children and their families. Some children and young people have to spend relatively long periods in hospital, so having access to play and teaching staff can also be an important part of their care. With local partnerships, this can include trips to local botanical gardens, zoos, and public libraries for instance. Designs for the new Cambridge Children's Hospital, approved in 2022, plan to fully integrate mental and physical health provision for children and young people, bringing together services of three partners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
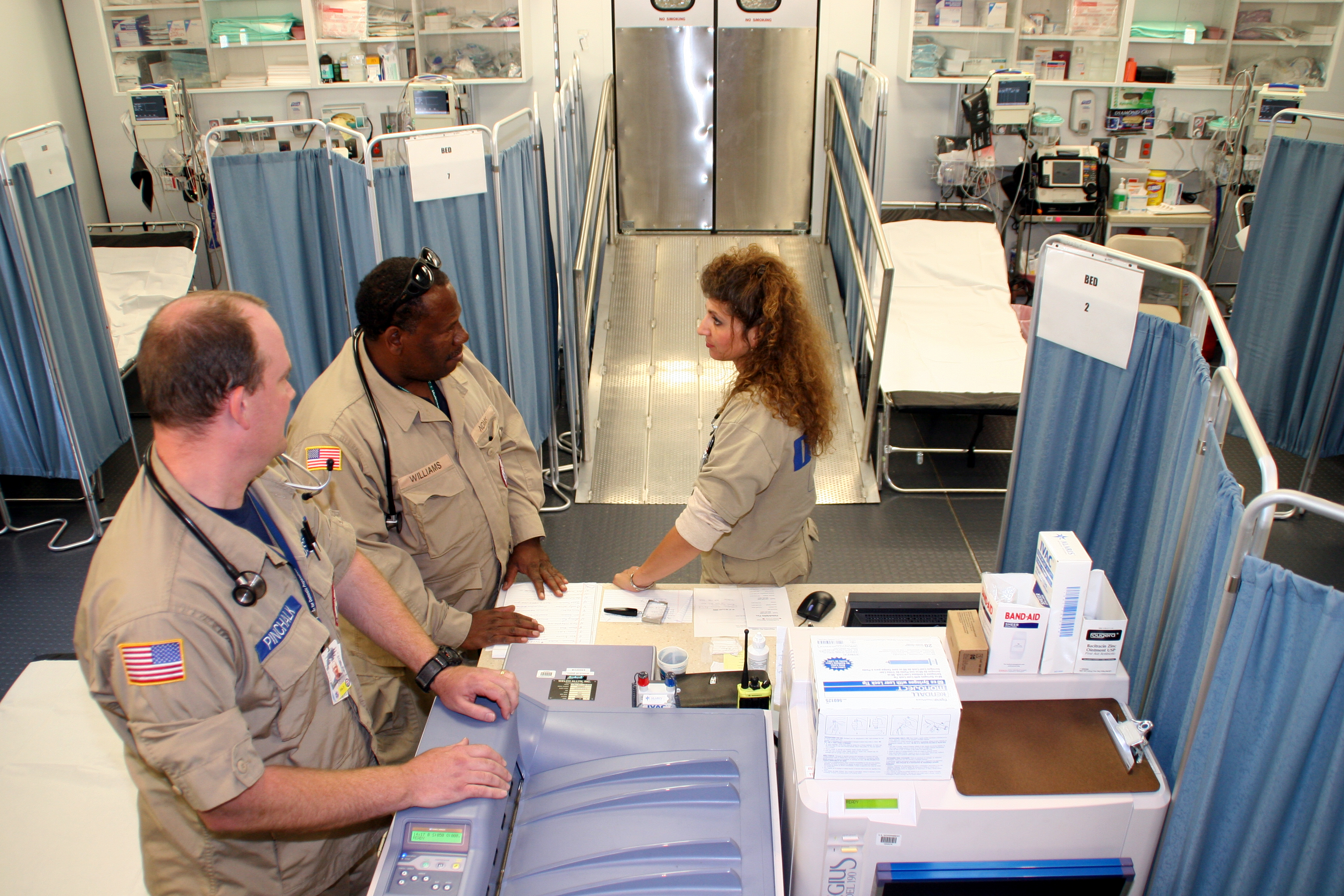
United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of the United States Constitution (1789). See alsTitle 10, Subtitle B, Chapter 301, Section 3001 The oldest and most senior branch of the U.S. military in order of precedence, the modern U.S. Army has its roots in the Continental Army, which was formed 14 June 1775 to fight the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783)—before the United States was established as a country. After the Revolutionary War, the Congress of the Confederation created the United States Army on 3 June 1784 to replace the disbanded Continental Army.Library of CongressJournals of the Continental Congress, Volume 27/ref> The United States Army considers itself to be a continuation of the Continental Army, and thus considers its institutional inception to be th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Private Finance Initiative
The private finance initiative (PFI) was a United Kingdom government procurement policy aimed at creating "public–private partnerships" (PPPs) where private firms are contracted to complete and manage public projects. Initially launched in 1992 by Prime Minister John Major, and expanded considerably by the Blair government, PFI is part of the wider programme of privatisation and financialisation, and presented as a means for increasing accountability and efficiency for public spending. PFI was controversial in the UK. In 2003, the National Audit Office felt that it provided good value for money overall; according to critics, PFI has been used simply to place a great amount of debt "off-balance-sheet". In 2011, the parliamentary Treasury Select Committee recommended: In October 2018, the then-chancellor Philip Hammond announced that the UK government would no longer use PFI; however, PFI projects will continue to operate for some time to come. In 2021, Robert Naylor warned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alder Hey Hospital Under Construction
Alders are trees comprising the genus ''Alnus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The genus comprises about 35 species of monoecious trees and shrubs, a few reaching a large size, distributed throughout the north temperate zone with a few species extending into Central America, as well as the northern and southern Andes. Description With a few exceptions, alders are deciduous, and the leaves are alternate, simple, and serrated. The flowers are catkins with elongate male catkins on the same plant as shorter female catkins, often before leaves appear; they are mainly wind-pollinated, but also visited by bees to a small extent. These trees differ from the birches (''Betula'', another genus in the family) in that the female catkins are woody and do not disintegrate at maturity, opening to release the seeds in a similar manner to many conifer cones. The largest species are red alder (''A. rubra'') on the west coast of North America, and black alder (''A. glutinosa''), native to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Digital Exemplar
The Global Digital Exemplar (GDE) programme is an NHS England initiative to achieve digital transformation in selected exemplar organisations and to create a knowledge sharing ecosystem to spread learning from these exemplars. The programme is to enable "digitally advanced" NHS trusts to share knowledge with other NHS trusts, specifically knowledge gained during the implementation of IT systems, and especially experience from introducing electronic health record (EHR) systems. The GDE project is expected to last two to three and a half years; with the most digitally advanced trusts on the shorter time scale. Four rounds of exemplars have been announced so far — two waves of acute trust GDEs, and one wave each of ambulance trusts, and mental health trusts. In addition, eighteen acute trust "fast followers" have been partnered with the acute trusts. The programme involves the investment of £395 million. Each GDE will receive "up to £10 million" to spend on digital projects. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Tissue Act 2004
The Human Tissue Act 2004 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, that applied to England, Northern Ireland and Wales, which consolidated previous legislation and created the Human Tissue Authority to "regulate the removal, storage, use and disposal of human bodies, organs and tissue." The Act does not extend to Scotland; its counterpart there is the Human Tissue (Scotland) Act 2006. Background The Act was brought about as a consequence of, among things, the Alder Hey organs scandal, in which organs of children had been retained by the Alder Hey Children's Hospital without consent, and the Kennedy inquiry into heart surgery on children at the Bristol Royal Infirmary. A consultative exercise followed the Government's Green Paper'', Human Bodies, Human Choices'' (2002), and earlier recommendations by the Chief Medical Officer, Sir Liam Donaldson. The Act The Act allows for anonymous organ donation Organ donation is the process when a person allows an organ of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alder Hey Organs Scandal
The Alder Hey organs scandal involved the unauthorised removal, retention, and disposal of human tissue, including children’s organ (anatomy), organs, during the period 1986 to 1996. During this period organs were retained in more than 2,000 pots"Pot", in the UK, is a term of art for a plastic formalin-filled container, of any of various sizes, which is used to store tissues in a pathology lab. containing body parts from around 850 infants. These were later uncovered at Alder Hey Children's Hospital, Liverpool, during a public inquiry into the organ retention scandal. The scandal led to the Human Tissue Act 2004, which overhauled legislation regarding the handling of human tissues in the UK and created the Human Tissue Authority. History Until a public inquiry in 1999, the general public was unaware that Alder Hey and other hospitals within the National Health Service (England), National Health Service (NHS) were retaining patients' organs without family consent. The inqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NHS Hospital Trust
A hospital trust, also known as an acute trust, is an NHS trust that provides secondary health services within the English National Health Service and, until they were abolished, in NHS Wales. Hospital trusts were commissioned to provide these services by NHS primary care trusts and now by clinical commissioning groups. NHS trusts were established by the National Health Service and Community Care Act 1990 as the first step in setting up an internal market. NHS foundation trusts were regulated by Monitor until 2016, when it was merged with the NHS Trust Development Authority to form NHS Improvement. As of January 2014, there were 59 NHS hospital trusts, out of the total of 97 NHS trusts supervised by the TDA.{{cite web, url=http://www.ntda.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/winter_report_web-FINAL.pdf , title=Winter Report , publisher=NHS Trust Development Authority , access-date=29 March 2014 See also *List of NHS trusts *List of hospitals in England *List of hospitals in Wales ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emergency Department
An emergency department (ED), also known as an accident and emergency department (A&E), emergency room (ER), emergency ward (EW) or casualty department, is a medical treatment facility specializing in emergency medicine, the acute care of patients who present without prior appointment; either by their own means or by that of an ambulance. The emergency department is usually found in a hospital or other primary care center. Due to the unplanned nature of patient attendance, the department must provide initial treatment for a broad spectrum of illnesses and injuries, some of which may be life-threatening and require immediate attention. In some countries, emergency departments have become important entry points for those without other means of access to medical care. The emergency departments of most hospitals operate 24 hours a day, although staffing levels may be varied in an attempt to reflect patient volume. History Accident services were provided by workmen's compensation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isabella Forshall
Isabella Forshall FRCSE (2 October 1900 – 10 August 1989) was an English paediatric surgeon who played a leading role in the development of the speciality of paediatric surgery in the United Kingdom. She took a particular interest in neonatal surgery and was instrumental in the establishment of the Liverpool Neonatal Surgical Unit, the first neonatal intensive care unit in the UK and indeed in the world. Early life Forshall was born in Sussex, England, on 2 October 1900. She did not attend school, her education being conducted at home by her mother, a Cambridge classics graduate. She went on to study medicine at the London School of Medicine for Women and the Royal Free Hospital from where she qualified MB BS in 1927. Surgical career She worked as house surgeon at the Royal Liverpool Children's Hospital, and later at Alder Hey Children's Hospital and was to continue to work in both of these until she retired in 1965. She was elected FRCSE in 1932. In 1939, she was appointed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
A neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), also known as an intensive care nursery (ICN), is an intensive care unit (ICU) specializing in the care of ill or premature newborn infants. Neonatal refers to the first 28 days of life. Neonatal care, as known as specialized nurseries or intensive care, has been around since the 1960s. The first American newborn intensive care unit, designed by Louis Gluck, was opened in October 1960 at Yale New Haven Hospital. NICU is typically directed by one or more neonatologists and staffed by resident physicians, nurses, nurse practitioners, pharmacists, physician assistants, respiratory therapists, and dietitians. Many other ancillary disciplines and specialists are available at larger units. The term ''neonatal'' comes from ''neo'', "new", and ''natal'', "pertaining to birth or origin". Nursing and neonatal populations Healthcare institutions have varying entry-level requirements for neonatal nurses. Neonatal nurses are registered nurses (RNs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The BMJ
''The BMJ'' is a weekly peer-reviewed medical trade journal, published by the trade union the British Medical Association (BMA). ''The BMJ'' has editorial freedom from the BMA. It is one of the world's oldest general medical journals. Originally called the ''British Medical Journal'', the title was officially shortened to ''BMJ'' in 1988, and then changed to ''The BMJ'' in 2014. The journal is published by BMJ Publishing Group Ltd, a subsidiary of the British Medical Association (BMA). The editor-in-chief of ''The BMJ'' is Kamran Abbasi, who was appointed in January 2022. History The journal began publishing on 3 October 1840 as the ''Provincial Medical and Surgical Journal'' and quickly attracted the attention of physicians around the world through its publication of high-impact original research articles and unique case reports. The ''BMJ''s first editors were P. Hennis Green, lecturer on the diseases of children at the Hunterian School of Medicine, who also was its fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |