|
Albertirsa
Albertirsa (formerly ''Alberti-Irsa'', sk, Irša) is a town in '' Ceglédi kistérség'', ''Pest megye'', and the middle of the Great Hungarian Plain. History Initially Albertirsa was two separate inhabitations: ''Alberti'' and ''Irsa'', having joined in 1950. * 1277: King Ladislaus IV mentions the name of Alberti (as ''Alberth'') tenure in one of his charters * 1368: The chapter of Buda mentions ''Irsa'' (from Slavic *''jelsa'') as an inhabitation * 1597: Both villages got emptied after the 1241 Mongol invasion and the Ottoman conquest in the 16th century * September 29, 1711: Local landlord András Váracskay brings settlers to populate the grassland of Alberti-Irsa. 24 chariots of Slovak settlers arrive to Alberti * 1714: Royal endowment letter grants the ownership of Alberti to Márton Szeleczky * 1719: András Irsay has one third of Irsa of Pest shire * 1731: Beginning of mandatory lecturing for commons in local landlord funded school * 1784: Descendants of Márton Sz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albertirsa–Zakhidnoukrainska–Vinnytsia Powerline
The Albertirsa–Zakhidnoukrainska–Vinnytsia powerline is a power transmission line between Ukraine and Hungary. It is a part of the former "Mir" transmission system between the Soviet Union and Comecon countries. As of today, it is the only 750 kV-powerline in Hungary and one of the few powerlines operated with this voltage in the European Union. History On 28 February 1974, the USSR, Bulgaria, Hungary, GDR, Poland and Czechoslovakia signed a cooperation agreement on construction of the 750 kV-line between Vinnytsia and Albertirsa, and substations Vinnytsia, Zakhidnoukrainska and Albertirsa. Construction started in 1975 and it went in service in 1979. Since the synchronization of the power grid of Hungary with that of the synchronous grid of Continental Europe (ENTSO-E) and because of economic reasons, the powerline went out of service in 1993, but was put in service again in 2002 after some new equipment was installed. Technical description The long power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ádám Politzer
Ádám Politzer ( hu, Politzer Ádám; 1 October 1835, Albertirsa, Pest, Hungary – 10 August 1920, in Vienna) was a Hungarian and Austrian physician and one of the pioneers and founders of otology. Life Ádám Politzer was born in Alberti (now part of Albertirsa), near the city of Budapest, to a well-to-do Jewish family. He studied medicine in the University of Vienna. Some of his teachers belonged to the Second " Vienna School", including Carl Freiherr von Rokitansky (1804–1878) and Josef Skoda (1805–1881) (its founders), as well as Joseph Hyrtl (1810–1894), Johann Ritter von Oppolzer (1808–1871), and the physiologist Carl Ludwig (1816–1895). The last two took interest in Politzer and were influential in his subsequent career. Politzer received his M.D. in 1859 and started to work in Carl Ludwig's laboratory. His interest since that time was mainly the physics of the auditory system. There, he was the first to demonstrate physiologically that the innervation of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Róza Csillag
Róza Csillag or Rosa Herrmann-Csillag (born ''Róza Goldstein'', 23 October 1832 – 20 February 1892) was an Austro-Hungarian mezzo-soprano opera singer. Csillag was born in the Jewish community of Irsa in central Hungary (today Albertirsa), and her father was Moritz Goldstein, a hazzan of Irsa. She first attracted attention in the chorus of the Hungarian National Theatre at Budapest, where by 1849 she was playing the roles of Nancy in Flotow's ''Martha'' and Mátyás Hunyadi in Erkel's ''Hunyadi László''. Recommended to the Vienna Court Opera in 1850 by the singer Anna de La Grange, she received further training from Heinrich Proch and made her initial appearances there, most notably as Fidès in Meyerbeer's ''Le prophète''. She delighted audiences with her beautiful mezzo-soprano voice and remained a favorite member of the company of the Vienna Court Opera until 1873. She also toured widely around Europe with much success, and in 1870 appeared in New York. In 1852 she marr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaggiano
Gaggiano ( lmo, Gaggian or ''Gasgian'' ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Milan in the Italian region Lombardy, located about southwest of Milan. As of 31 December 2004, it had a population of 8,360 and an area of .All demographics and other statistics: Italian statistical institute Istat. Gaggiano borders the following municipalities: Cusago, Cisliano, Albairate, Trezzano sul Naviglio, Vermezzo, Zibido San Giacomo, Gudo Visconti, Noviglio, Rosate. Gaggiano is served by Gaggiano railway station. Here, in 1849 Pope Francis' great-grandfather was born. Demographic evolution Colors= id:lightgrey value:gray(0.9) id:darkgrey value:gray(0.8) id:sfondo value:rgb(1,1,1) id:barra value:rgb(0.6,0.7,0.8) ImageSize = width:455 height:303 PlotArea = left:50 bottom:50 top:30 right:30 DateFormat = x.y Period = from:0 till:8500 TimeAxis = orientation:vertical AlignBars = justify ScaleMajor = gridcolor:darkgrey increment:500 start:0 ScaleMinor = gridcolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
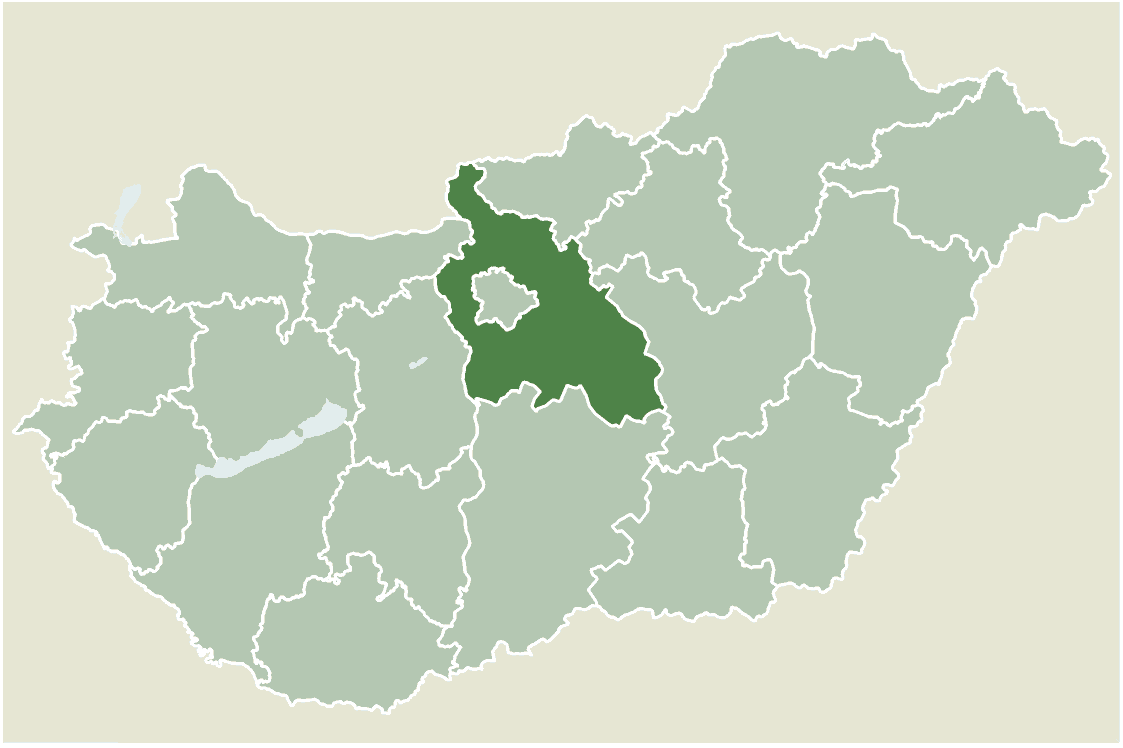
Cegléd District
Cegléd ( hu, Ceglédi járás) is a district in south-eastern part of Pest County. ''Cegléd'' is also the name of the town where the district seat is found. The district is located in the Central Hungary Statistical Region. Geography Cegléd District borders with Nagykáta District to the north, Szolnok District ''(Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok County)'' to the east, Tiszakécske District ''(Bács-Kiskun County)'' and Nagykőrös District to the south, Kecskemét District ''(Bács-Kiskun County)'' to the southwest, Dabas District to the west, Monor District to the northwest. The number of the inhabited places in Cegléd District is 12. Municipalities The district has 3 towns and 9 villages. (ordered by population, as of 1 January 2013) The bolded municipalities are cities. Demographics In 2011, it had a population of 88,952 and the population density was 100/km². Ethnicity Besides the Hungarian majority, the main minorities are the Roma (approx. 1,800), German (950) and Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cegléd
Cegléd (; german: Zieglet) is a city in Pest County, Pest county, Hungary, approximately southeast of the Hungarian capital, Budapest. Name The name of the town is of disputed origin. The name may be derived from the word "szeglet" (meaning "corner") due to its being a junction point of several important routes, while it may also have been derived from a Noun, proper name, i. e. from the name of a man called "Cegléd". The most likely explanation derives the name from the noun "cigle" or "cegle", the old Hungarian name of a rivercoast willow. History Its area has been inhabited since the Copper Age. It was first mentioned in 1290 in a decree by Ladislaus IV of Hungary. The town prospered under the Árpád dynasty until the 13th century Mongols, Mongol invasion of Hungary left it in ruins. It was reinhabitated later, and on May 8, 1364 Louis I of Hungary relieved the town from paying customs. The king gave the town to his queen, Elizabeth of Poland, Queen of Hungary, Elisabeth, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Hungary
Hungary in its modern (post-1946) borders roughly corresponds to the Great Hungarian Plain (the Pannonian Basin). During the Iron Age, it was located at the crossroads between the cultural spheres of the Celtic tribes (such as the Scordisci, Boii and Veneti), Dalmatian tribes (such as the Dalmatae, Histri and Liburni) and the Germanic tribes (such as the Lugii and Marcomanni). The name "Pannonian" comes from Pannonia, a province of the Roman Empire. Only the western part of the territory (the so-called Transdanubia) of modern Hungary formed part of Pannonia. The Roman control collapsed with the Hunnic invasions of 370–410, and Pannonia was part of the Ostrogothic Kingdom during the late 5th to mid 6th century, succeeded by the Avar Khaganate (6th to 9th centuries). The Magyar invasion took place during the 9th century. The Magyars were Christianized at the end of the 10th century, and the Christian Kingdom of Hungary was established in AD 1000, ruled by the Árpád dynast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sister City
A sister city or a twin town relationship is a form of legal or social agreement between two geographically and politically distinct localities for the purpose of promoting cultural and commercial ties. While there are early examples of international links between municipalities akin to what are known as sister cities or twin towns today dating back to the 9th century, the modern concept was first established and adopted worldwide during World War II. Origins of the modern concept The modern concept of town twinning has its roots in the Second World War. More specifically, it was inspired by the bombing of Coventry on 14 November 1940, known as the Coventry Blitz. First conceived by the then Mayor of Coventry, Alfred Robert Grindlay, culminating in his renowned telegram to the people of Stalingrad (now Volgograd) in 1942, the idea emerged as a way of establishing solidarity links between cities in allied countries that went through similar devastating events. The comradesh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synagogue (Irsa)
A synagogue, ', 'house of assembly', or ', "house of prayer"; Yiddish: ''shul'', Ladino: or ' (from synagogue); or ', "community". sometimes referred to by the Yiddish term shul and often used interchangeably with the word temple, is a Jewish house of worship. Synagogues have a place for prayer (the main sanctuary and sometimes smaller chapels), where Jews attend religious Services or special ceremonies (including Weddings, Bar Mitzvahs or Bat Mitzvahs, Confirmations, choir performances, or even children's plays), have rooms for study, social hall(s), administrative and charitable offices, classrooms for religious school and Hebrew school, sometimes Jewish preschools, and often have many places to sit and congregate; display commemorative, historic, or modern artwork throughout; and sometimes have items of some Jewish historical significance or history about the Synagogue itself, on display. Synagogues are consecrated spaces used for the purpose of Jewish prayer, stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
.jpg)