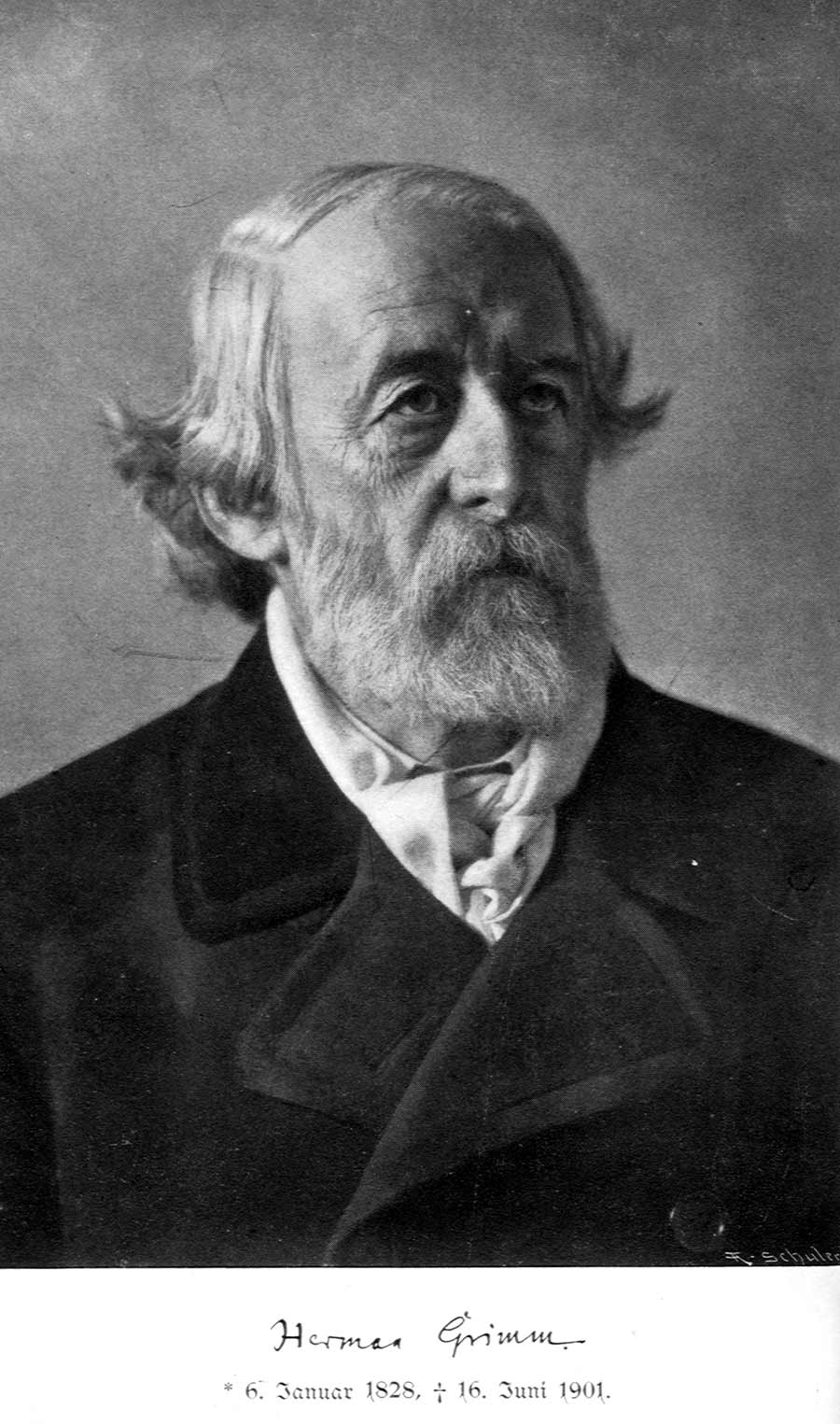|
Albert Göring
Albert Günther Göring (9 March 1895 – 20 December 1966) was a German engineer, businessman, and the younger brother of Hermann Göring (the head of the German ''Luftwaffe'' and a leading member of the Nazi Party). In contrast to his brother, Albert was opposed to Nazism, and he helped Jews and others who were persecuted in Nazi Germany. He was shunned in post-war Germany because of his family name, and he died without any public recognition and received very little attention for his humanitarian efforts until decades after his death.Burke, pp. 205–214. Family background Albert Göring was born on 9 March 1895 in the Berlin suburb of Friedenau. He was the fifth child of the former Reichskommissar to German South-West Africa and German Consul General to Haiti, Heinrich Ernst Göring, and his wife, Franziska "Fanny" Tiefenbrunn, who came from a Bavarian peasant family. The Görings were relatives of numerous residents of the Eberle/Eberlin area in Switzerland and Germany ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedenau
Friedenau () is a locality (''Ortsteil'') within the borough (''Bezirk'') of Tempelhof-Schöneberg in Berlin, Germany. Relatively small by area, its population density is the highest in the city. Geography Friedenau is part of the southwestern suburbs, right at the border with the inner city Schöneberg district, separated by the Berlin Ringbahn and the BAB 100 motorway (''Stadtring''). It borders the Wilmersdorf locality to the west and Steglitz to the south. The streets and squares are laid out according to a geometric urban design with an almost complete assembly of ''Gründerzeit'' buildings, which survived the bombing of Berlin in World War II. Urban planning The characteristic feature of Friedenau its Carstenn layout, named after urban developer Johann Anton Wilhelm von Carsten. This symmetrical layout consists of an avenue dividing a circular road, which is demarcated by four town squares. Some streets in Friedenau were named after rivers in Alsace-Lorraine to commemo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island which it shares with the Dominican Republic. To its south-west lies the small Navassa Island, which is claimed by Haiti but is disputed as a United States territory under federal administration."Haiti" ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Haiti is in size, the third largest country in the Caribbean by area, and has an estimated population of 11.4 million, making it the most populous country in the Caribb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ritter
Ritter (German for "knight") is a designation used as a title of nobility in German-speaking areas. Traditionally it denotes the second-lowest rank within the nobility, standing above "Edler" and below "Freiherr" (Baron). As with most titles and designations within the nobility in German-speaking areas, the rank was hereditary and generally was used with the nobiliary particle of von or zu before a family name. For its historical association with warfare and the landed gentry in the Middle Ages, the title of Ritter can be considered roughly equal to the titles of "Knight", but it is hereditary like the British title of "Baronet". The wife of a Ritter was called a "Frau" (in this sense "Lady") and not Ritterin. In heraldry, from the late 18th century a Ritter was often indicated by the use of a coronet with five points, although not everyone who was a Ritter and displayed arms made use of such a coronet. In the Austrian Empire and Austria-Hungary the title of "Ritter von" was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Epenstein
Hermann or Herrmann may refer to: * Hermann (name), list of people with this name * Arminius, chieftain of the Germanic Cherusci tribe in the 1st century, known as Hermann in the German language * Éditions Hermann, French publisher * Hermann, Missouri, a town on the Missouri River in the United States ** Hermann AVA, Missouri wine region * The German SC1000 bomb of World War II was nicknamed the "Hermann" by the British, in reference to Hermann Göring * Herrmann Hall, the former Hotel Del Monte, at the Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, California * Memorial Hermann Healthcare System, a large health system in Southeast Texas * The Herrmann Brain Dominance Instrument (HBDI), a system to measure and describe thinking preferences in people * Hermann station (other), stations of the name * Hermann (crater), a small lunar impact crater in the western Oceanus Procellarum * Hermann Huppen, a Belgian comic book artist * Hermann 19, an American sailboat design built by Ted Herm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Godparent
In infant baptism and denominations of Christianity, a godparent (also known as a sponsor, or '' gossiprede'') is someone who bears witness to a child's christening and later is willing to help in their catechesis, as well as their lifelong spiritual formation. In the past, in some countries, the role carried some legal obligations as well as religious responsibilities. In both religious and civil views, a godparent tends to be an individual chosen by the parents to take an interest in the child's upbringing and personal development, to offer mentorship or claim legal guardianship of the child if anything should happen to the parents. A male godparent is a godfather, and a female godparent is a godmother. The child is a godchild (i.e. godson for boys and goddaughter for girls). Christianity Origins and history As early as the 2nd century AD, infant baptism had begun to gain acceptance among Catholic Christians for the spiritual purification and social initiation of infa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gertrud Von Le Fort
The Baroness Gertrud von Le Fort (full name ''Gertrud Auguste Lina Elsbeth Mathilde Petrea Freiherr, Freiin von Le Fort''; 11 October 1876 – 1 November 1971) was a German writer of novels, poems and essays. Life Le Fort was born in the city of Minden, in the former Province of Westphalia, then the Kingdom of Prussia within the German Empire. She was the daughter of a colonel in the Prussian Army, who was of Swiss people, Swiss Huguenot descent. She was educated as a young girl in Hildesheim, and went on to study at universities at University of Heidelberg, Heidelberg, University of Marburg, Marburg and University of Berlin, Berlin. She made her home in Bavaria in 1918, living in Baierbrunn until 1939. Despite publishing some minor works previously, Le Fort's writing career really began with the publication in 1925 of the posthumous work ''Glaubenslehre'' by her mentor, Ernst Troeltsch, a major scholar in the field of the philosophy of religion, which she had edited. She reli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merck KGaA
The Merck Group, branded and commonly known as Merck, is a German multinational science and technology company headquartered in Darmstadt, with about 60,000 employees and present in 66 countries. The group includes around 250 companies; the main company is Merck KGaA in Germany. The company is divided into three business lines: Healthcare, Life Sciences and Electronics. Merck was founded in 1668 and is the world's oldest operating chemical and pharmaceutical company, as well as one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. Merck operates in Europe, Africa, Asia, Oceania and the Americas. It has major research and development centres in Darmstadt, Boston, Tokyo and Beijing, as well as other Research and Development units in Taiwan, France, Israel, South Korea, India and in the UK. Merck pioneered the commercial manufacture of morphine in the 19th century and for a time held a virtual monopoly on cocaine. Merck was privately owned until going public on the Frankfurt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merck Family
The Merck family is a German family of industrialists and bankers, known for establishing the world's oldest pharmaceutical company Merck, its American former subsidiary Merck & Co. (MSD), which is now an independent company, as well as the Hamburg merchant bank H. J. Merck & Co. The family still owns the majority of the pharmaceutical company Merck. History The family first appeared in Hammelburg in the 15th century. The family has a long history in pharmacy going back to the 17th century. In 1668 Friedrich Jacob Merck purchased the second town pharmacy in Darmstadt, known as the Engel-Apotheke or Angel Pharmacy, which would evolve into the major company Merck, the world's oldest operating pharmaceutical and chemical company. When Friedrich died, the pharmacy was passed on to his nephew and it has been owned by the family ever since. The sixth person in this series of pharmacists was Heinrich Emanuel Merck who in 1827 established the chemical-pharmaceutical factory in Darmst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Jacob Burckhardt
Carl Jacob Burckhardt (September 10, 1891 – March 3, 1974) was a Swiss diplomat and historian. His career alternated between periods of academic historical research and diplomatic postings; the most prominent of the latter were League of Nations High Commissioner for the Free City of Danzig (1937–39) and President of the International Committee of the Red Cross (1945–48). Biography Burckhardt was born in Basel to Carl Christoph Burckhardt, a member of the patrician Burckhardt family, and attended gymnasium in Basel and Glarisegg (in Steckborn). He subsequently studied at the universities of Basel, Zürich, Munich, and Göttingen, being particularly influenced by professors Ernst Gagliardi and Heinrich Wölfflin. He gained his first diplomatic experience in the Swiss legation in Austria from 1918 to 1922, a chaotic period following the collapse of Austria-Hungary. While there, he became acquainted with Hugo von Hofmannsthal. Burckhardt earned his doctorate in 1922, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Red Cross
The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC; french: Comité international de la Croix-Rouge) is a humanitarian organization which is based in Geneva, Switzerland, and it is also a three-time Nobel Prize Laureate. State parties (signatories) to the Geneva Convention of 1949 and its Additional Protocols of 1977 ( Protocol I, Protocol II) and 2005 have given the ICRC a mandate to protect victims of international and internal armed conflicts. Such victims include war wounded persons, prisoners, refugees, civilians, and other non-combatants. The ICRC is part of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement, along with the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC) and 192 National Societies. It is the oldest and most honoured organization within the movement and one of the most widely recognized organizations in the world, having won three Nobel Peace Prizes (in 1917, 1944, and 1963). History Solferino, Henry Dunant and the foundat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacob Burckhardt
Carl Jacob Christoph Burckhardt (25 May 1818 – 8 August 1897) was a Swiss historian of art and culture and an influential figure in the historiography of both fields. He is known as one of the major progenitors of cultural history. Sigfried Giedion described Burckhardt's achievement in the following terms: "The great discoverer of the age of the Renaissance, he first showed how a period should be treated in its entirety, with regard not only for its painting, sculpture and architecture, but for the social institutions of its daily life as well." His best known work is ''The Civilization of the Renaissance in Italy'' (1860). Life The son of a Protestant clergyman, Burckhardt was born and died in Basel, where he studied theology in the hope of taking holy orders; however, under the influence of Wilhelm Martin Leberecht de Wette, he chose not to become a clergyman. He was a member of the patrician Burckhardt family. He finished his degree in 1839 and went to the Universi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herman Grimm
Herman Grimm (6 January 1828 in Kassel16 June 1901 in Berlin) was a German academic and writer. Family and education Grimm's father was Wilhelm Grimm (1786–1859), and his uncle Jakob Grimm (1785–1863), the philologist compilers of indigenous folk tales ("Brothers Grimm"). His other uncle was the painter engraver Ludwig Emil Grimm (1790–1863). Herman Grimm is believed to have had only one (known) child at a young age, Martin Grimm. From 1841 Herman attended the Friedrich Wilhelm Gymnasium in Berlin. He belonged to a clique associated with Bettina von Arnim (1785–1859), wife of the late poet Achim von Arnim (1781–1831), and started publishing drama and novels. He began legal and philological studies at the universities of Berlin and Bonn. Career In 1857 he visited Rome where the artistic circle of Peter von Cornelius brought his interests to art. In 1859, he married Gisela von Arnim (1827–1889), the Arnim's daughter, and published his treatise, ''Die Akademie der Kü ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |