|
Albert E. Green
Albert Edward Green (11 November 1912, London – 12 August 1999) was a British applied mathematician and research scientist in theoretical and applied mechanics. Biography Green studied mathematics at Jesus College, Cambridge, where he attended lectures by Sydney Goldstein, Arthur Eddington and G. I. Taylor. In 1932 he attained a first in the first part of the Tripos examinations in mathematics and in 1934 was Wrangler in the second part. After his first very promising publications he was named the 1936 Fellow of Jesus College, received the 1936 Smith Prize, and in 1937 received his PhD under Taylor. With Taylor he published in the 1930s and 1940s a series of works on stress distribution in anisotropic plates. In 1939 Green became a lecturer at the University of Durham and then in 1948 a professor of applied mathematics at the University of Newcastle upon Tyne (at that time called King´s College of the University of Durham). In Newcastle he chaired the mathematical faculty with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a major settlement for two millennia. The City of London, its ancient core and financial centre, was founded by the Romans as '' Londinium'' and retains its medieval boundaries.See also: Independent city § National capitals The City of Westminster, to the west of the City of London, has for centuries hosted the national government and parliament. Since the 19th century, the name "London" has also referred to the metropolis around this core, historically split between the counties of Middlesex, Essex, Surrey, Kent, and Hertfordshire, which largely comprises Greater London, governed by the Greater London Authority.The Greater London Authority consists of the Mayor of London and the London Assembly. The London Mayor is distinguished fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal Fluid
In physics, a perfect fluid is a fluid that can be completely characterized by its rest frame mass density \rho_m and ''isotropic'' pressure ''p''. Real fluids are "sticky" and contain (and conduct) heat. Perfect fluids are idealized models in which these possibilities are neglected. Specifically, perfect fluids have no shear stresses, viscosity, or heat conduction. Quark–gluon plasma is the closest known substance to a perfect fluid. In space-positive metric signature tensor notation, the stress–energy tensor of a perfect fluid can be written in the form :T^ = \left( \rho_m + \frac \right) \, U^\mu U^\nu + p \, \eta^\, where ''U'' is the 4-velocity vector field of the fluid and where \eta_ = \operatorname(-1,1,1,1) is the metric tensor of Minkowski spacetime. In time-positive metric signature tensor notation, the stress–energy tensor of a perfect fluid can be written in the form :T^ = \left( \rho_\text + \frac \right) \, U^\mu U^\nu - p \, \eta^\, where ''U'' is the 4-vel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1912 Births
Year 191 ( CXCI) was a common year starting on Friday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Apronianus and Bradua (or, less frequently, year 944 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 191 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Parthia * King Vologases IV of Parthia dies after a 44-year reign, and is succeeded by his son Vologases V. China * A coalition of Chinese warlords from the east of Hangu Pass launches a punitive campaign against the warlord Dong Zhuo, who seized control of the central government in 189, and held the figurehead Emperor Xian hostage. After suffering some defeats against the coalition forces, Dong Zhuo forcefully relocates the imperial capital from Luoyang to Chang'an. Before leaving, Dong Zhuo orders his troops to loot the tombs of the H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academics Of Newcastle University
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 385 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, ''Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions into a method of teaching philosophy and in 387 BC, established what is known today as the Old Academy. By extension, ''academia'' has come to mean the accumulation, dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellows Of The Royal Society
Fellowship of the Royal Society (FRS, ForMemRS and HonFRS) is an award granted by the judges of the Royal Society of London to individuals who have made a "substantial contribution to the improvement of natural knowledge, including mathematics, engineering science, and medical science". Fellowship of the Society, the oldest known scientific academy in continuous existence, is a significant honour. It has been awarded to many eminent scientists throughout history, including Isaac Newton (1672), Michael Faraday (1824), Charles Darwin (1839), Ernest Rutherford (1903), Srinivasa Ramanujan (1918), Albert Einstein (1921), Paul Dirac (1930), Winston Churchill (1941), Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar (1944), Dorothy Hodgkin (1947), Alan Turing (1951), Lise Meitner (1955) and Francis Crick (1959). More recently, fellowship has been awarded to Stephen Hawking (1974), David Attenborough (1983), Tim Hunt (1991), Elizabeth Blackburn (1992), Tim Berners-Lee (2001), Venki Ramakrishnan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellows Of Jesus College, Cambridge
{{disambiguation ...
Fellows may refer to Fellow, in plural form. Fellows or Fellowes may also refer to: Places * Fellows, California, USA * Fellows, Wisconsin, ghost town, USA Other uses * Fellows Auctioneers, established in 1876. *Fellowes, Inc., manufacturer of workspace products *Fellows, a partner in the firm of English canal carriers, Fellows Morton & Clayton * Fellows (surname) See also *North Fellows Historic District, listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Wapello County, Iowa *Justice Fellows (other) Justice Fellows may refer to: * Grant Fellows (1865–1929), associate justice of the Michigan Supreme Court * Raymond Fellows (1885–1957), associate justice of the Maine Supreme Judicial Court {{disambiguation, tndis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedleian Professors Of Natural Philosophy
The Sedleian Professor of Natural Philosophy is the name of a chair at the Mathematical Institute of the University of Oxford. Overview The Sedleian Chair was founded by Sir William Sedley who, by his will dated 20 October 1618, left the sum of £2,000 to the University of Oxford for purchase of lands for its endowment. Sedley's bequest took effect in 1621 with the purchase of an estate at Waddesdon in Buckinghamshire to produce the necessary income. It is regarded as the oldest of Oxford's scientific chairs. Holders of the Sedleian Professorship have, since the mid 19th century, worked in a range of areas of applied mathematics and mathematical physics. They are simultaneously elected to fellowships at Queen's College, Oxford. The Sedleian Professors in the past century have been Augustus Love (1899-1940), who was distinguished for his work in the mathematical theory of elasticity, Sydney Chapman (1946-1953), who is renowned for his contributions to the kinetic theory of g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alumni Of Jesus College, Cambridge
Alumni (singular: alumnus (masculine) or alumna (feminine)) are former students of a school, college, or university who have either attended or graduated in some fashion from the institution. The feminine plural alumnae is sometimes used for groups of women. The word is Latin and means "one who is being (or has been) nourished". The term is not synonymous with "graduate"; one can be an alumnus without graduating ( Burt Reynolds, alumnus but not graduate of Florida State, is an example). The term is sometimes used to refer to a former employee or member of an organization, contributor, or inmate. Etymology The Latin noun ''alumnus'' means "foster son" or "pupil". It is derived from PIE ''*h₂el-'' (grow, nourish), and it is a variant of the Latin verb ''alere'' "to nourish".Merriam-Webster: alumnus .. Separate, but from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornelis Benjamin Biezeno
Cornelis Benjamin Biezeno (2 March 1888 in Delft – 5 September 1975 in Wageningen) was a Dutch applied mathematician and scientist in engineering mechanics. He was a professor at TU Delft. Biography Biezeno studied mechanical engineering from 1904 to 1909 (graduating ''cum laude'') at TU Delft. Subsequently he was a lecturer, first for mechanical engineering and then for mathematics at Delft. In 1914, he became a professor of mechanics at Delft. From 1937 to 1938 and from 1949 to 1951 he was rector magnificus at TU Delft. His book ''Technische Dynamik'', written with Richard Grammel, was a standard reference in its era. Biezeno was one of the organizers of the first Internationalen Congress of Applied Mechanics held at Delft in 1924. His doctoral students include Warner T. Koiter and Adriaan van Wijngaarden. Biezeno was given honorary doctorates by the University of Ghent, the University of Amsterdam, and the Free University of Brussels. In 1939 he was elected a member of the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
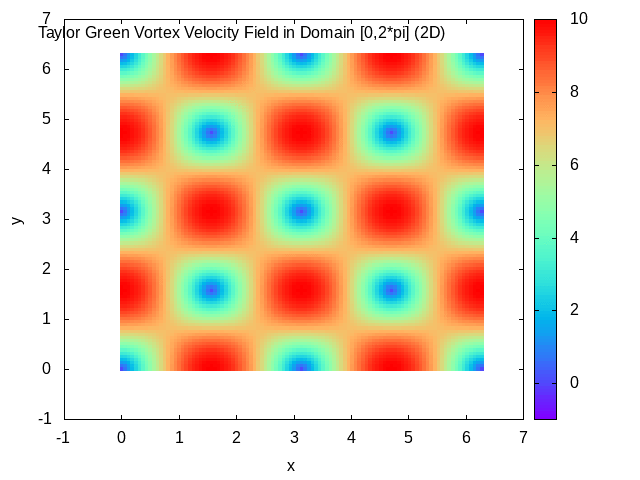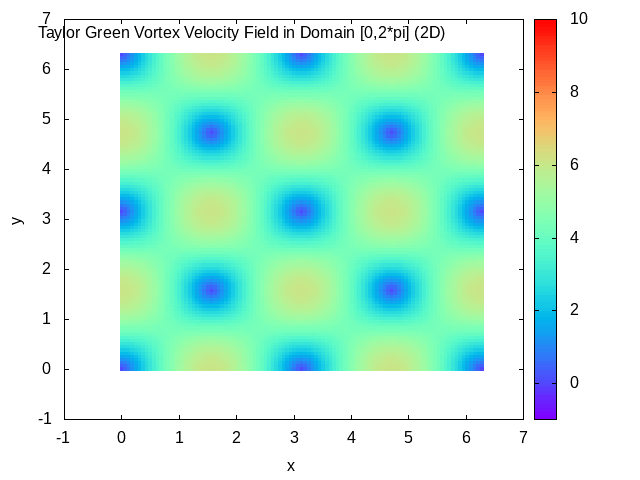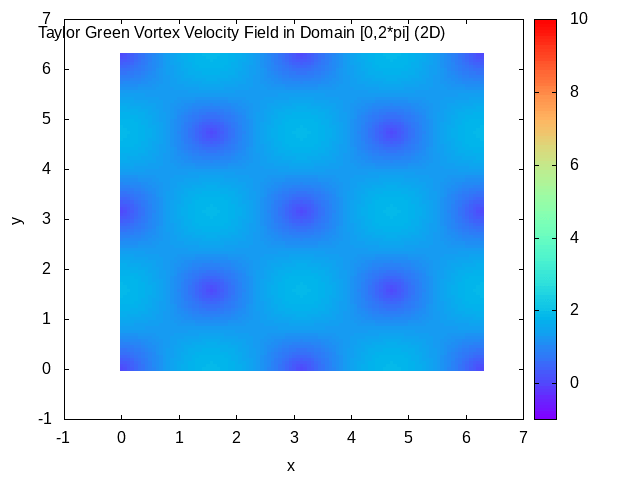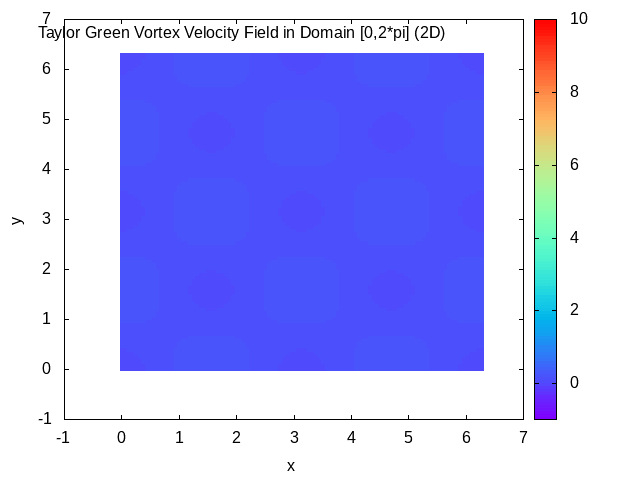
Taylor–Green Vortex
In fluid dynamics, the Taylor–Green vortex is an unsteady flow of a decaying vortex, which has an exact closed form solution of the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations in Cartesian coordinates. It is named after the British physicist and mathematician Geoffrey Ingram Taylor and his collaborator A. E. Green. Taylor, G. I. and Green, A. E., ''Mechanism of the Production of Small Eddies from Large Ones'', Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A, 158, 499–521 (1937). Original work In the original work of Taylor and Green, a particular flow is analyzed in three spatial dimensions, with the three velocity components \mathbf=(u,v,w) at time t=0 specified by : u = A \cos ax \sin by \sin cz, : v = B \sin ax \cos by \sin cz, : w = C \sin ax \sin by \cos cz. The continuity equation \nabla \cdot \mathbf=0 determines that Aa+Bb+Cc=0. The small time behavior of the flow is then found through simplification of the incompressible Navier–Stokes equations using the initial flow to give a step- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Von Karman Medal
The Theodore von Karman Medal in Engineering Mechanics is awarded annually to an individual in recognition of his distinguished achievement in engineering mechanics, applicable to any branch of civil engineering. This award was established and endowed in 1960 in honor of Theodore von Kármán by the Engineering Mechanics Division of the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE). List of recipients SourceASCE See also *List of engineering awards *List of prizes named after people This is a list of awards that are named after people. A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P R S T U - V W Y Z See also *Lists of awards Lists of awards cover awards given in various fields, i ... References {{reflist Awards established in 1960 Awards of the American Society of Civil Engineers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |