|
Albert Bachmann (philologist)
Johann Albert Bachmann (12 November 1863, in Hüttwilen – 30 January 1934, in Samedan) was a Swiss lexicographer and dialectologist, professor for Germanic philology at Zürich University from 1896. From 1892 he was an editor of the ''Schweizerisches Idiotikon'' dictionary, acting as editor-in-chief from 1896 until his death. Bachmann specialized on Swiss German dialects. He edited the series ''Beiträge zur Schweizerdeutschen Grammatik'' (20 vols) and founded, together with Louis Gauchat, the Phonographic Archive of Zurich University in 1913. Works *''Beiträge zur Geschichte der schweizerischen Gutturallaute.'' Genossenschafts-Buchdruckerei, diss. Zürich 1886. *(ed., with Samuel Singer): ''Deutsche Volksbücher aus einer Zürcher Handschrift des fünfzehnten Jahrhunderts.'' Litterarischer Verein in Stuttgart, Tübingen 1889 (Bibliothek des Litterarischen Vereins in Stuttgart 185). *(ed.): ''Morgant der Riese.'' Litterarischer Verein in Stuttgart, Tübingen 1890 (Bibliothek d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Bachmann (1863–1934)
Albert "Bert" Bachmann (26 November 1929 in Zurich - 12 April 2011 in Ireland) was a Swiss military intelligence officer. Early life Bachmann was born in Albisrieden and worked as a printer after leaving school at age 14. As a young man he flirted with communism, joining the youth wing of the PdA. Following the 1948 Communist seizure of power in Czechoslovakia, he changed course and became strongly patriotic. While doing his military service he applied for officer training, and went into military intelligence. Civil Defence booklet controversy In 1968, he was the lead author of an official civil defence booklet that was distributed throughout the country which provided instructions on how to respond to invasion, through the character of "Wilhelm Eiferli". Its warning of the danger from collaborationist elements in the Swiss Left made it the subject of national debate. 'Défense civile' has since been translated for distribution in Japan and Egypt; an attempt by Franco's Spain to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hüttwilen
Hüttwilen is a municipality in Frauenfeld District in the canton of Thurgau in Switzerland. History Archeological sites and scattered, individual items indicate that there was a mesolithic settlement in the ''Seebachtal'' near Hüttwilen. In 1928 a Roman era estate was discovered in Stutheien which proves that there was a Roman settlement in the area. The modern municipality of Hüttwilen is first mentioned in 1255 as ''Hutewiler''. In 1466 the village came the rule of the Carthusian monastery at Ittingen. The monastery held the majority of the lower court authority over the village until 1798. In 1466 the church was built in the village, under the monastery's authority. During the Protestant Reformation in 1529 the village converted to the new faith. The Catholic nobles in the village were able to reinstate the Catholic Mass at the church in 1551. Until 1961 the church was used by both denominations. In 1962 a new Reformed church was built. It was followed in 1964 b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samedan
Samedan (, ) is a town and municipality in the Maloja Region in the Swiss canton of Grisons. It is served by Samedan railway station on the Rhaetian Railway network and by the Samedan Airport. History Samedan is first mentioned in 1139 as ''Samaden''. In 1334 it was mentioned as ''Semeden'', in 1367 as ''Semaden'', in 1498 as ''Sumada'' and in 1527 as ''Sameden''. Johann Heinrich Müller, 1825-1894 J08 Samaden.JPG, Samedan c. 1870 with the Bernina hotel (opened in 1865), one of the oldest hotels in the Engadin. Etching by Heinrich Müller Samedan circa 1870.jpg, A photograph of Samedan in the circa 1870s Samedan circa 1870 B.jpg, Another photographic view of Samedan in the circa 1870s ETH-BIB-Samedan-LBS H1-017880.tif, Aerial view (1954) Geography Samedan has an area, (as of the 2004/09 survey) of . Of this area, about 15.5% is used for agricultural purposes, while 9.7% is forested. Of the rest of the land, 1.9% is settled (buildings or roads) and 72.9% is unproductive la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Philology
Germanic philology is the philological study of the Germanic languages, particularly from a comparative or historical perspective. The beginnings of research into the Germanic languages began in the 16th century, with the discovery of literary texts in the earlier phases of the languages. Early modern publications dealing with Old Norse culture appeared in the 16th century, e.g. ''Historia de gentibus septentrionalibus'' (Olaus Magnus, 1555) and the first edition of the 13th century ''Gesta Danorum'' (Saxo Grammaticus), in 1514. In 1603, Melchior Goldast made the first edition of Middle High German poetry, Tyrol and Winsbeck, including a commentary which focused on linguistic problems and set the tone for the approach to such works in the subsequent centuries. He later gave similar attention to the Old High German Benedictine Rule. In England, Cotton's studies of the manuscripts in his collection marks the beginnings of work on Old English language. The pace of publication increas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Zurich
The University of Zürich (UZH, german: Universität Zürich) is a public research university located in the city of Zürich, Switzerland. It is the largest university in Switzerland, with its 28,000 enrolled students. It was founded in 1833 from the existing colleges of theology, law, medicine which go back to 1525, and a new faculty of philosophy. Currently, the university has seven faculties: Philosophy, Human Medicine, Economic Sciences, Law, Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Theology and Veterinary Medicine. The university offers the widest range of subjects and courses of any Swiss higher education institution. History The University of Zurich was founded on April 29, 1833, when the existing colleges of theology, the ''Carolinum'' founded by Huldrych Zwingli in 1525, law and medicine were merged with a new faculty of Philosophy. It was the first university in Europe to be founded by the state rather than a monarch or church. In the university's early years, the 183 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
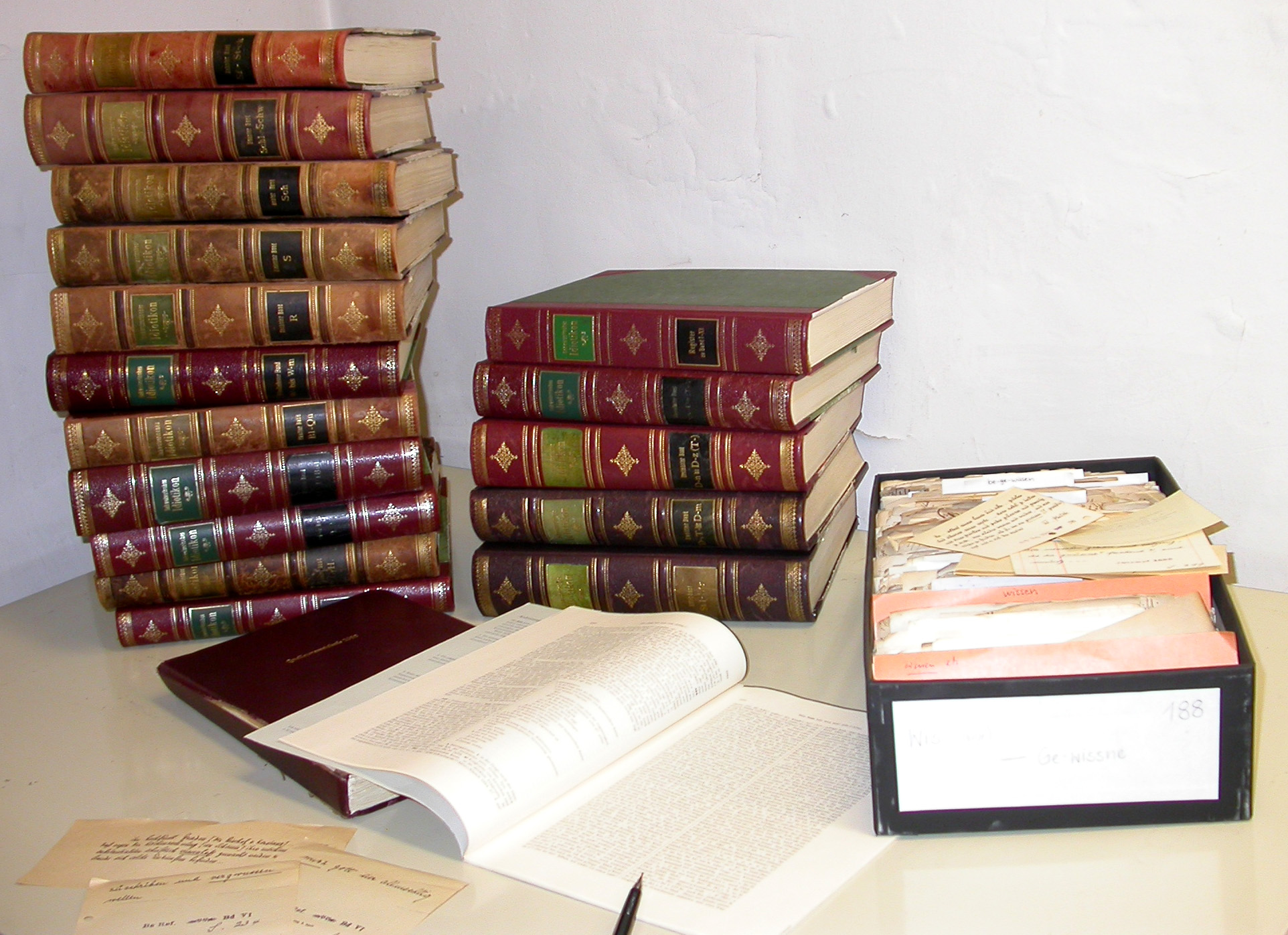
Schweizerisches Idiotikon
''Schweizerisches Idiotikon'' ("the Swiss idioticon", also known as ''Wörterbuch der schweizerdeutschen Sprache'' "Dictionary of the Swiss German language") is an ongoing, major project of lexicography of the Swiss German dialects. Publication began in 1881 and is projected to be complete by 2022. Its scope includes the language since the end of the classical Middle High German period (13th century) and as such also represents the historical dictionary of the dialects of German-speaking Switzerland, and is one of the most detailed treatments of the Early Modern High German language in general. As of 2010, it contains 150,000 words. The history of the project began in 1862 with the foundation of a ''Verein für das Schweizerdeutsche Wörterbuch'', led by Friedrich Staub (1826–1896). Originally envisaged as a dictionary in four volumes, the first fascicle was published in 1881. From 1896, the project was led by Albert Bachmann (philologist), Albert Bachmann (1863–1934), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss German
Swiss German (Standard German: , gsw, Schwiizerdütsch, Schwyzerdütsch, Schwiizertüütsch, Schwizertitsch Mundart,Because of the many different dialects, and because there is no defined orthography for any of them, many different spellings can be found. and others) is any of the Alemannic dialects spoken in the German-speaking part of Switzerland and in some Alpine communities in Northern Italy bordering Switzerland. Occasionally, the Alemannic dialects spoken in other countries are grouped together with Swiss German as well, especially the dialects of Liechtenstein and Austrian Vorarlberg, which are closely associated to Switzerland's. Linguistically, Alemannic is divided into Low, High and Highest Alemannic, varieties all of which are spoken both inside and outside Switzerland. The only exception within German-speaking Switzerland is the municipality of Samnaun, where a Bavarian dialect is spoken. The reason Swiss German dialects constitute a special group is their a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Gauchat
Louis Gauchat (born 12 January 1866 in Les Brenets, Switzerland; died 22 August 1942 in Lenzerheide) was a Swiss linguist. He studied at the University of Zürich under Heinrich Morf and in Paris as a pupil of Gaston Paris, receiving his doctorate in 1890 with the dissertation ''Le patois de Dompierre''. He later worked as a lecturer at Bern (1893–96) and Zürich (1897–1902), and in 1902 was named a professor of Romance philology at the University of Bern. In 1907 he succeeded Jakob Ulrich at the University of Zürich, where he taught classes until 1931.Gauchat, Louis Historischen Lexikon der Schweiz In 1909, with Albert Bachmann, he founded the |
Eugen Dieth
Eugen Dieth (18 November 1893, in Neukirch an der Thur – 24 May 1956, in Zollikon) was a Swiss linguist, phonetician and dialectologist. He is well known for his work in English and German phonetics, and for co-initiating the Survey of English Dialects. Biography Eugen Dieth studied General Linguistics, English and German at the University of Zurich and the University of Geneva. He got his PhD in 1919 with a dissertation on Middle English syntax. Between 1922 and 1927 he was ''lecturer in German'' in Aberdeen. In 1927 he became Professor extraordinarius and in 1947 Professor ordinarius for English, Old Norse and General Phonetics at the University of Zurich. He founded the Phonetics Laboratory of the University of Zurich in 1935. Between 1927 and 1936 he worked as a part-time editor for the Schweizerisches Idiotikon and between 1934 and his unexpected death from a stroke in 1956 he was the director of the Phonogram Archives of the University of Zurich. He married Hilde Martha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emil Ermatinger
Emil Ermatinger (21 May 1873 in Schaffhausen, Switzerland – 17 September 1953 in Zurich) was a Swiss professor for Germanic philology. Ermatinger studied classical philology in Zurich and Berlin. 1897 he wrote his Ph.D. thesis at the University of Zurich.''Die attische Autochthonensage bis auf Euripides. Mit einer einleitenden Darstellung der Bedeutung und Entwicklung der attischen Sage bis auf Euripides''. Berlin: Mayer und Müller, 1897. (Diss. Univ. Zürich, 1897.) His doctoral advisor was the classical archaeologist and philologist Hugo Blümner. 1909 Ermatinger became a professor for Germanic philology at ETH Zurich. 1912 till 1943 he was professor at the University of Zurich. 1939 he was visiting professor at the Columbia University in New York City. References Works *''Gottfried Keller Gottfried Keller (19 July 1819 – 15 July 1890) was a Swiss poet and writer of German literature. Best known for his novel '' Green Henry'' (German: ''Der grüne Heinrich'') and h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1863 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – Abraham Lincoln signs the Emancipation Proclamation during the third year of the American Civil War, making the abolition of slavery in the Confederate states an official war goal. It proclaims the freedom of 3.1 million of the nation's four million slaves and immediately frees 50,000 of them, with the rest freed as Union armies advance. * January 2 – Lucius Tar Painting Master Company (''Teerfarbenfabrik Meirter Lucius''), predecessor of Hoechst, as a worldwide chemical manufacturing brand, founded in a suburb of Frankfurt am Main, Germany. * January 4 – The New Apostolic Church, a Christian and chiliastic church, is established in Hamburg, Germany. * January 7 – In the Swiss canton of Ticino, the village of Bedretto is partly destroyed and 29 killed, by an avalanche. * January 8 ** The Yorkshire County Cricket Club is founded at the Adelphi Hotel, in Sheffield, England. ** American Civil War – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)