|
Albatros L 73
__NOTOC__ The Albatros L 73 was a German twin-engined biplane airliner of the 1920s. Of conventional configuration, it featured a streamlined, boat-like fuselage and engine nacelles. All four manufactured aircraft of that type were operated by Deutsche Luft Hansa, one of which (''Brandenburg'', ''D-961'') crashed near Babekuhl on 28 May 1928. Variants ;L 73a: powered by two Siemens-built Bristol Jupiter. ;L 73b:version with Junkers L5 engines ;L 73c:engines upgraded to BMW V Operators ; * Bulgarian Air Force ; *Deutsche Luft Hansa ''Deutsche Luft Hansa A.G.'' (from 1933 styled as ''Deutsche Lufthansa'' and also known as ''Luft Hansa'', ''Lufthansa'', or DLH) was a German airline, serving as flag carrier of the country during the later years of the Weimar Republic and t ... Specifications (L 73b) References Further reading * * External links German Aircraft between 1919-1945 {{Albatros aircraft L 073 1920s German airliners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inline Engine (aviation)
In aviation, an inline engine is a reciprocating engine with banks of cylinders, one behind another, rather than rows of cylinders, with each bank having any number of cylinders, although more than six is uncommon. The major reciprocating-engine alternative configuration is the radial engine, where the cylinders are placed in a circular or "star" arrangement. The term "inline" is used somewhat differently for aircraft engines than automotive engines. For automotive engines, the term ‘inline’ refers only to straight engines (those with a single bank of cylinders). But for aircraft, ‘inline’ can also refer to engines which are not of the straight configuration, such as V, H, or horizontally opposed. Inline engine configurations ; Straight: Engines with a single bank of cylinders which can be arranged at any angle but typically upright or inverted, (e.g. upright ADC Cirrus, inverted de Havilland Gipsy Major). ; V:Engines with two banks of cylinders with less than 180° be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water-cooled
Cooling tower and water discharge of a nuclear power plant Water cooling is a method of heat removal from components and industrial equipment. Evaporative cooling using water is often more efficient than air cooling. Water is inexpensive and non-toxic; however, it can contain impurities and cause corrosion. Water cooling is commonly used for cooling automobile internal combustion engines and power stations. Water coolers utilising convective heat transfer are used inside high-end personal computers to lower the temperature of CPUs. Other uses include the cooling of lubricant oil in pumps; for cooling purposes in heat exchangers; for cooling buildings in HVAC and in chillers. Mechanism Advantages Water is inexpensive, non-toxic, and available over most of the earth's surface. Liquid cooling offers higher thermal conductivity than air cooling. Water has unusually high specific heat capacity among commonly available liquids at room temperature and atmospheric pressure allow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
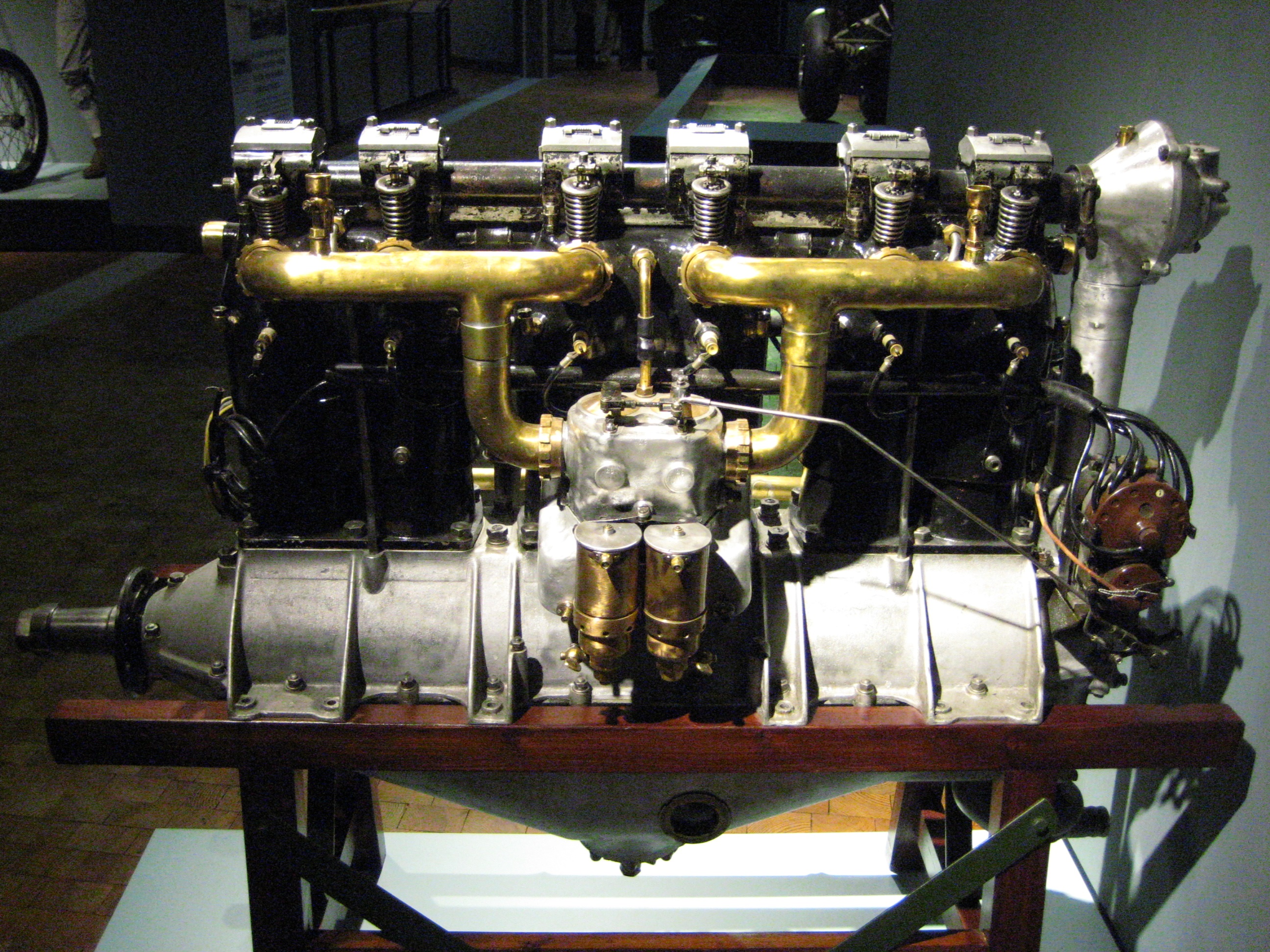
BMW IV
The BMW IV was a six-cylinder, water-cooled inline aircraft engine built in Germany in the 1920s. Power was in the 180 kW (250 hp) range. World record On 17 June 1919 Franz Zeno Diemer flew a DFW F37, powered by a BMW IV engine to an unofficial world record height of from Oberwiesenfeld, reaching that altitude in 89 minutes. Diemer stated at the time, "I could have gone much higher, but I didn't have enough oxygen." Applications * Arado SC I * Albatros L 72 * Albatros L 74 * Caspar C 27 * DFW F37 DFW may refer to: Businesses *, an early twentieth century German aircraft manufacturer *Dutch FilmWorks, a film distributor *Duty Free World, a US-based in-flight shopping company Government agencies *Division of Fisheries and Wildlife (Mass ... * Heinkel HD 22 * Heinkel HD 24 * Heinkel HD 39 * Junkers A 35 * Junkers F 13 * LFG V 59 * LFG V 60 * Polikarpov R-1 BMW (Soviet unlicensed copy of Airco DH.9A) * Rohrbach Ro VII Robbe * Rohrbach Ro VIII Rolan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flight International
''Flight International'' is a monthly magazine focused on aerospace. Published in the United Kingdom and founded in 1909 as "A Journal devoted to the Interests, Practice, and Progress of Aerial Locomotion and Transport", it is the world's oldest continuously published aviation news magazine. ''Flight International'' is published by DVV Media Group. Competitors include Jane's Information Group and ''Aviation Week''. Former editors of, and contributors include H. F. King, Bill Gunston, John W. R. Taylor and David Learmount. History The founder and first editor of ''Flight'' was Stanley Spooner. He was also the creator and editor of ''The Automotor Journal'', originally titled ''The Automotor Journal and Horseless Vehicle''.Guide To British Industrial History: Biographies: ''S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albatros L 73 3 View NACA Aircraft Circular No
An albatross is one of a family of large winged seabirds. Albatross or Albatros may also refer to: Animals * Albatross (butterfly) or ''Appias'', a genus of butterfly * Albatross (horse) (1968–1998), a Standardbred horse Literature * Albatross Books, a German publishing house that produced the first modern mass market paperback books * Albatros Literaturpreis, a literary award * "L'albatros" (poem) ("The Albatross"), 1859 poem by Charles Baudelaire * ''The Albatross'', a 1971 novella by Susan Hill * ''The Albatross'', the fictional propeller-sustained airship in Jules Verne's novel ''Robur the Conqueror'' * ''Albatross'' (novel), a 2019 novel by Terry Fallis Film and television * Films Albatros, a French film production company which operated between 1922 and 1939 * ''Albatross'' (2011 film), a British film * ''Albatross'' (2015 film), an Icelandic film * Albatross (Monty Python sketch), a sketch from ''Monty Python's Flying Circus'', first appearing in 1970 * "Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian Air Force
The Bulgarian Air Force ( bg, Военновъздушни сили, Voennovazdushni sili) is one of the three branches of the Military of Bulgaria, the other two being the Bulgarian Navy and Bulgarian land forces. Its mission is to guard and protect the sovereignty of Bulgarian airspace, and jointly with the other branches, to protect territorial integrity. The Bulgarian Air Force is one of the oldest air forces in Europe and the world. In recent times it has been actively taking part in numerous NATO missions and exercises in Europe. The current commanding officer of the Bulgarian Air Force is Major General Dimitar Hristov Petrov. History Early years The Bulgarian Air Force dates back to the end of the 19th century. At the 1892 Plovdiv International Fair, two lieutenants of the Bulgarian Army flew in the 'La France' balloon owned by the Frenchman Eugène Godard.Nedialkov, D. "Air Power of the Kingdom of Bulgaria. Part I" Later, inspired by the flight, they succeeded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMW V
__NOTOC__ The BMW V was a six-cylinder, water-cooled inline aircraft engine built in Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ... in the 1920s, with power of for the production version, the BMW Va. Specifications (BMW Va) Applications * Albatros L 73 * Albatros L 75 * Rohrbach Ro VII Robbe II References Bibliography * {{BMW aeroengines BMW aircraft engines 1920s aircraft piston engines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junkers L5
The Junkers L 5 was a six-cylinder, water-cooled, inline engine for aircraft built in Germany during the 1920s. First run in 1925, it was a much enlarged development of the Junkers L2. Design and development The Junkers L5 was a development of Junkers' first water-cooled engine, the L2, but at four times the swept volume was a much more powerful engine. It was a water-cooled upright inline 6-cylinder unit, four-stroke and petrol-fuelled, with a capacity of nearly 23 litres. It adopted some of the L2 features, having twin exhaust and inlet valves in each cylinderdriven by an overhead camshaft, twin spark plugs and twin magnetos. The splash component of the L2's lubrication was abandoned in favour of a completely forced recirculating system. The twin carburettors of the L2 were replaced with a single float chamber, dual-venturi model. Like the L2, the L5 was a direct drive engine. The compression ratio of the standard version was 5.5:1, but variants had other ratios to cope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Jupiter
The Bristol Jupiter was a British nine-cylinder single-row piston radial engine built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company. Originally designed late in World War I and known as the Cosmos Jupiter, a lengthy series of upgrades and developments turned it into one of the finest engines of its era. The Jupiter was widely used on many aircraft designs during the 1920s and 1930s. Thousands of Jupiters of all versions were produced, both by Bristol and abroad under licence. A turbo-supercharged version of the Jupiter known as the Orion suffered development problems and only a small number were produced. The "Orion" name was later re-used by Bristol for an unrelated turboprop engine. Design and development The Jupiter was designed during World War I by Roy Fedden of Brazil Straker and later Cosmos Engineering. The first Jupiter was completed by Brazil Straker in 1918 and featured three carburettors, each one feeding three of the engine's nine cylinders via a spiral deflector housed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1928 In Aviation
This is a list of aviation-related events from 1928: Events * The Soviet Unions first five-year plan (1928–1932) begins, placing a high priority on the construction of new aircraft factories. It begins a rapid expansion of the Soviet aircraft industry. * The Aeromarine Plane and Motor Company renames itself the Aeromarine-Klemm Corporation and begins to produce the German-designed Klemm aircraft. * The Douglas Company renames itself the Douglas Aircraft Company. * The Kawanishi Aircraft Company is founded. * The Mitsubishi Internal Combustion Engine Company Ltd. changes its name to Mitsubishi Aircraft Company Ltd. * Italy officially records its production rate for military aircraft at 150 per month, with a capacity to expand to 600 per month in wartime. The ''Regia Aeronautica'' (Italian Royal Air Force), meanwhile, determines that it will require a production rate of 900 aircraft per month during a war. * The United States Coast Guard establishes an Aviation Section at its h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |