|
Albania Under The Bulgarian Empire
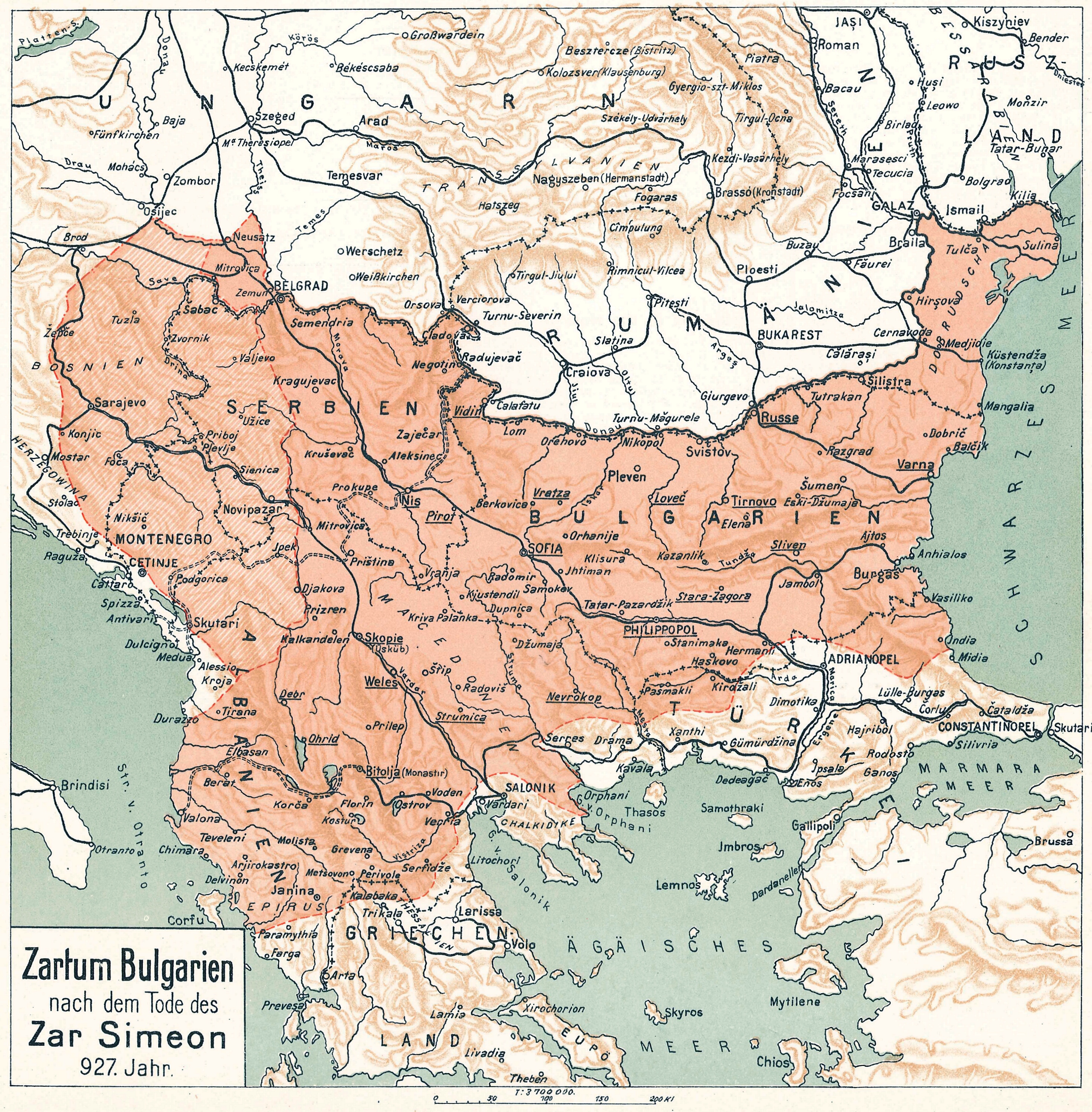
The territory of modern Albania was part of the Bulgarian Empire during certain periods in the Middle Ages and some parts in what is now eastern Albania were populated and ruled by the Bulgarians for centuries. Most of Albania became part of the First Bulgarian Empire, First Empire in the early 840s during the reign of Khan Presian of Bulgaria, Presian. Some coastal towns such as Durrës remained in the hands of the Byzantine Empire, Byzantines for most of that period. The castles of the inner mountainous country remained one of the last Bulgarian strongholds to be conquered by the Byzantines in 1018/1019 during the fall of the First Bulgarian Empire — Tomornitsa. During the Byzantine rule Albania was one of the centres of a Uprising of Peter Delyan. The last Bulgarian Emperor to govern the whole territory was Ivan Asen II of Bulgaria, Ivan Asen II (1218–1241) but after his successors the Bulgarian rule diminished. Much of that area corresponded with the Bulgarian historical regi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares land borders with Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, North Macedonia to the east and Greece to the south. Tirana is its capital and largest city, followed by Durrës, Vlorë, and Shkodër. Albania displays varied climatic, geological, hydrological, and morphological conditions, defined in an area of . It possesses significant diversity with the landscape ranging from the snow-capped mountains in the Albanian Alps as well as the Korab, Skanderbeg, Pindus and Ceraunian Mountains to the hot and sunny coasts of the Albanian Adriatic and Ionian Sea along the Mediterranean Sea. Albania has been inhabited by different civilisations over time, such as the Illyrians, Thracians, Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, Venetians, and Ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuber
Kuber, (also Kouber or Kuver), was a Bulgar leader who, according to the ''Miracles of Saint Demetrius'', liberated a mixed Bulgar and Byzantine Christian population in the 670s, whose ancestors had been transferred from the Eastern Roman Empire to the Syrmia region in Pannonia by the Avars 60 years earlier.CurtaFine According to a scholarly theory, he was a son of Kubrat, brother of Khan Asparukh and member of the Dulo clan. Origins According to the Byzantine scholar, Theophanes the Confessor, Kubrat's (unnamed) fourth son, who left the Pontic steppes after his father's death around 642, became "the subject of the of the Avars in Avar Pannonia and remained there with his army". According to a scholarly theory, first proposed by the Bulgarian historian Vasil Zlatarski, Kuber was the fourth son of Kubrat, the Christian ruler of the Onogur Bulgars in the steppes north of the Black Sea. Kuber's story is continued in the second book of the ''Miracles of Saint Demetrius''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simeon I Of Bulgaria
Tsar Simeon (also Symeon) I the Great ( cu, цѣсар҄ь Сѷмеѡ́нъ А҃ Вели́къ, cěsarĭ Sỳmeonŭ prĭvŭ Velikŭ bg, цар Симеон I Велики, Simeon I Veliki el, Συμεών Αʹ ὁ Μέγας, Sumeṓn prôtos ho Mégas) ruled over Bulgaria from 893 to 927,Lalkov, ''Rulers of Bulgaria'', pp. 23–25. during the First Bulgarian Empire. Simeon's successful campaigns against the Byzantines, Magyars and Serbs led Bulgaria to its greatest territorial expansion ever, making it the most powerful state in contemporary Eastern and Southeast Europe. His reign was also a period of unmatched cultural prosperity and enlightenment later deemed the Golden Age of Bulgarian culture. During Simeon's rule, Bulgaria spread over a territory between the Aegean, the Adriatic and the Black Sea.Bakalov, ''Istorija na Bǎlgarija'', "Simeon I Veliki". The newly independent Bulgarian Orthodox Church became the first new patriarchate besides the Pentarchy, and Bulgarian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohrid Literary School
The Ohrid Literary School or Ohrid- ''Devol'' Literary school was one of the two major cultural centres of the First Bulgarian Empire, along with the Preslav Literary School (Pliska Literary School). The school was established in Ohrid (in what is now North Macedonia). Another center was Devol (modern-day Albania) as well as Drembica, Glavinica and Velika with unknown location. All the school centers were located in a then Bulgarian province known as Kutmichevitsa. It was founded in 886 by Saint Clement of Ohrid on the order of Boris I of Bulgaria simultaneously or shortly after the establishment of the Preslav Literary School. After Clement was ordained bishop of Drembica, Velika (bishopric) in 893, the position of head of the school was assumed by Naum of Preslav. The Ohrid Literary School used the Glagolitic alphabet from its establishment until the 12th century and Cyrillic from the end of the 9th century onward. Between 990 and 1015, Ohrid was the capital of the Bulgarian Em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballsh
Ballsh ( sq-definite, Ballshi) is a town and a former municipality in Fier County, southern Albania. At the 2015 local government reform it became a subdivision and the seat of the municipality Mallakastër. It was the seat of the former District of Mallakastër. The population at the 2011 census was 7,657.2011 census results Name It was centre of Malkasra (Turkish of "") kaza in in Yanya Vilayet during Ottoman rule between 1670 and 1912. ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berat
Berat (; sq-definite, Berati) is the ninth most populous city of Albania and the seat of Berat County and Berat Municipality. By air, it is north of Gjirokastër, west of Korçë, south of Tirana, and east of Fier. Berat is located in the south of the country. It is surrounded by mountains and hills, including Tomorr on the east that was declared a national park. The river Osum (total length ) runs through the city before it empties into the Seman within the Myzeqe Plain. The municipality of Berat was formed at the 2015 local government reform by the merger of the former municipalities Berat, Otllak, Roshnik, Sinjë, and Velabisht, that became municipal units. The seat of the municipality is the city Berat. The total population is 60,031 (2011 census), in a total area of . The population of the former municipality at the 2011 census was 32,606. Berat, designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2008, comprises a unique style of architecture with influences from several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devol (Albania)
Devol ( bg, Девол) also Deabolis or Diabolis, ( el, Δεάβολις) was a medieval fortress and bishopric in western Macedonia, located south of Lake Ohrid in what is today the south-eastern corner of Albania (Devoll District). Its precise location is unknown today, but it is thought to have been located by the river of the same name (today Devoll River), and on the Roman Via Egnatia road. It is first mentioned in historical sources in John Skylitzes' account of the Byzantine-Bulgarian Wars under Emperor Basil II, whose general Eustathios Daphnomeles is said to have subdued some of the last Bulgarian resisting forces concentrated in Deabolis in 1018. The place is also mentioned in a 1019 charter granted by Basil to the Bulgarian church, as a ''kastron'' (castle) under the jurisdiction of the bishop of Kastoria. It is not precisely known when Deabolis became a bishopric. Saint Clement of Ohrid (ca. 840–916), an eminent early Macedonian writer, is supposed to have been i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boris I Of Bulgaria
Boris I, also known as Boris-Mihail (Michael) and ''Bogoris'' ( cu, Борисъ А҃ / Борисъ-Михаилъ bg, Борис I / Борис-Михаил; died 2 May 907), was the ruler of the First Bulgarian Empire in 852–889. At the time of his baptism in 864, Boris was named Michael after his godfather, Emperor Michael III. The historian Steven Runciman called him one of the greatest persons in history. Despite a number of military setbacks, the reign of Boris I was marked with significant events that shaped Bulgarian and European history. With the Christianization of Bulgaria in 864 paganism (i.e. Tengrism) was abolished. A skillful diplomat, Boris I successfully exploited the conflict between the Patriarchate of Constantinople and the Papacy to secure an autocephalous Bulgarian Church, thus dealing with the nobility's concerns about Byzantine interference in Bulgaria's internal affairs. When in 885 the disciples of Saints Cyril and Methodius were banished ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianization Of Bulgaria
The Christianization of Bulgaria was the process by which 9th-century medieval Bulgaria converted to Christianity. It reflected the need of unity within the religiously divided Bulgarian state as well as the need for equal acceptance on the international stage in Christian Europe. This process was characterized by the shifting political alliances of Boris I of Bulgaria (ruled 852-889) with the kingdom of the East Franks and with the Byzantine Empire, as well as his diplomatic correspondence with the Pope. Because of Bulgaria's strategic position, the churches of both Rome and Constantinople each wanted Bulgaria in their sphere of influence. They regarded Christianization as a means of integrating Slavs into their region. After some overtures to each side, the Khan adopted Christianity from Constantinople in 870. As a result, he achieved his goal of gaining an independent Bulgarian national church and having an archbishop appointed to head it. Background When Khan Boris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isbul
Isbul ( bg, Исбул) ( fl. 820s–830s) was the ''kavhan'', or first minister, of the First Bulgarian Empire during the reigns of Omurtag, Malamir and Presian I. Appointed to the ''kavhan'' office under Omurtag, Isbul was a regent or co-ruler of the underage Malamir and his successor Presian. Under Malamir and Presian, Isbul headed Bulgaria's successful campaigns against the Byzantines in southern Thrace and Macedonia, which led to a significant territorial expansion of the Bulgarian realm. As a co-ruler of Malamir, Isbul also financed the construction of a water conduit in the capital Pliska. As second-in-command, Isbul held enormous power and wealth, and was unusually often mentioned beside the name of the ruler in inscriptions. Due to his merits, Isbul has been described as an architect of medieval Bulgarian statehood by historians. Biography The office of the ''kavhan'' was a hereditary title in the First Bulgarian Empire, monopolised by the members of the tentatively ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kavkhan (title)
The ''kavkhan'' ( grc-x-byzant, καυχάνος; bg, кавха̀н) was one of the most important officials in the First Bulgarian Empire. Role and status According to the generally accepted opinion, he was the second most important person in the state after the Bulgarian ruler. He had a number of responsibilities and concentrated huge power and authority. The ''kavkhan'' was a commander-in-chief of the Bulgarian army and one of the primary diplomats in the state. He was a member of the ' Bolyar Counsel' and one of the most important advisers to the Bulgarian ruler; the ''kavkhan'' was sometimes his regent or co-ruler. The ''kavkhan'' was a high magistrate and substitute to the ruler when the latter is absent from the capital. He is also attributed to have been a judge. It is assumed that there was a prominent bolyar family in Bulgaria from which the ''kavkhan'' was chosen generation after generation - the so-called "''kavkhan'' kin". The title was therefore hereditary and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |