|
Alaska Plaice
Alaska plaice (''Pleuronectes quadrituberculatus'') is a saltwater fish that live in the North Pacific Ocean. Alaska plaice are right-eye flounders which live on the sandy bottoms of the continental shelf, up to 600 metres deep. Their geographic range is from the Gulf of Alaska in the east, to the Chukchi Sea in the north, to the Sea of Japan in the west. Alaska plaice feed mostly on polychaetes, but also eat amphipods and echiurans. Most commercial fisheries do not target Alaska plaice, and bycatch by commercial trawlers targeting other groundfish is the sole source of significant harvest of this species. Large schools of Alaska plaice are commonly associated with schools of Yellowfin sole, and bycatch rates can reach relatively high levels. The 2005 total allowable catch in the Bering Sea and Aleutian Islands management area (BSAI) was reached before the end of May of that year. Alaska plaice can live for up to 30 years, and grow to 60 centimetres (24 inches) long, but mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Simon Pallas
Peter Simon Pallas Fellow of the Royal Society, FRS FRSE (22 September 1741 – 8 September 1811) was a Prussian zoologist and botanist who worked in Russia between 1767 and 1810. Life and work Peter Simon Pallas was born in Berlin, the son of Professor of Surgery Simon Pallas. He studied with private tutors and took an interest in natural history, later attending the University of Halle and the University of Göttingen. In 1760, he moved to the University of Leiden and passed his doctor's degree at the age of 19. Pallas travelled throughout the Netherlands and to London, improving his medical and surgical knowledge. He then settled at The Hague, and his new system of animal classification was praised by Georges Cuvier. Pallas wrote ''Miscellanea Zoologica'' (1766), which included descriptions of several vertebrates new to science which he had discovered in the Dutch museum collections. A planned voyage to southern Africa and the East Indies fell through when his father reca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class (biology), class of generally marine invertebrate, marine annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are made of chitin. More than 10,000 species are described in this class. Common representatives include the lugworm (''Arenicola marina'') and the Alitta virens, sandworm or Alitta succinea, clam worm ''Alitta''. Polychaetes as a class are robust and widespread, with species that live in the coldest ocean temperatures of the abyssal plain, to forms which tolerate the extremely high temperatures near hydrothermal vents. Polychaetes occur throughout the Earth's oceans at all depths, from forms that live as plankton near the surface, to a 2- to 3-cm specimen (still unclassified) observed by the robot ocean probe Nereus (underwater vehicle), ''Nereus'' at the bottom of the Challenger Deep, the deepes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Marine Fisheries Service
The National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS), informally known as NOAA Fisheries, is a United States federal agency within the U.S. Department of Commerce's National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) that is responsible for the stewardship of U.S. national marine resources. It conserves and manages fisheries to promote sustainability and prevent lost economic potential associated with overfishing, declining species, and degraded habitats. History Founded in 1871 as the U.S. Commission of Fish and Fisheries, the National Marine Fisheries Service is the oldest federal conservation and environmental research agency in the United States. The commission was formed when President Ulysses S. Grant named zoologist Spencer Fullerton Baird, United States National Museum director and assistant secretary of the Smithsonian Institution, the first commissioner of the United States Fish Commission. The commission was divided into three research categories: the study of U.S. wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
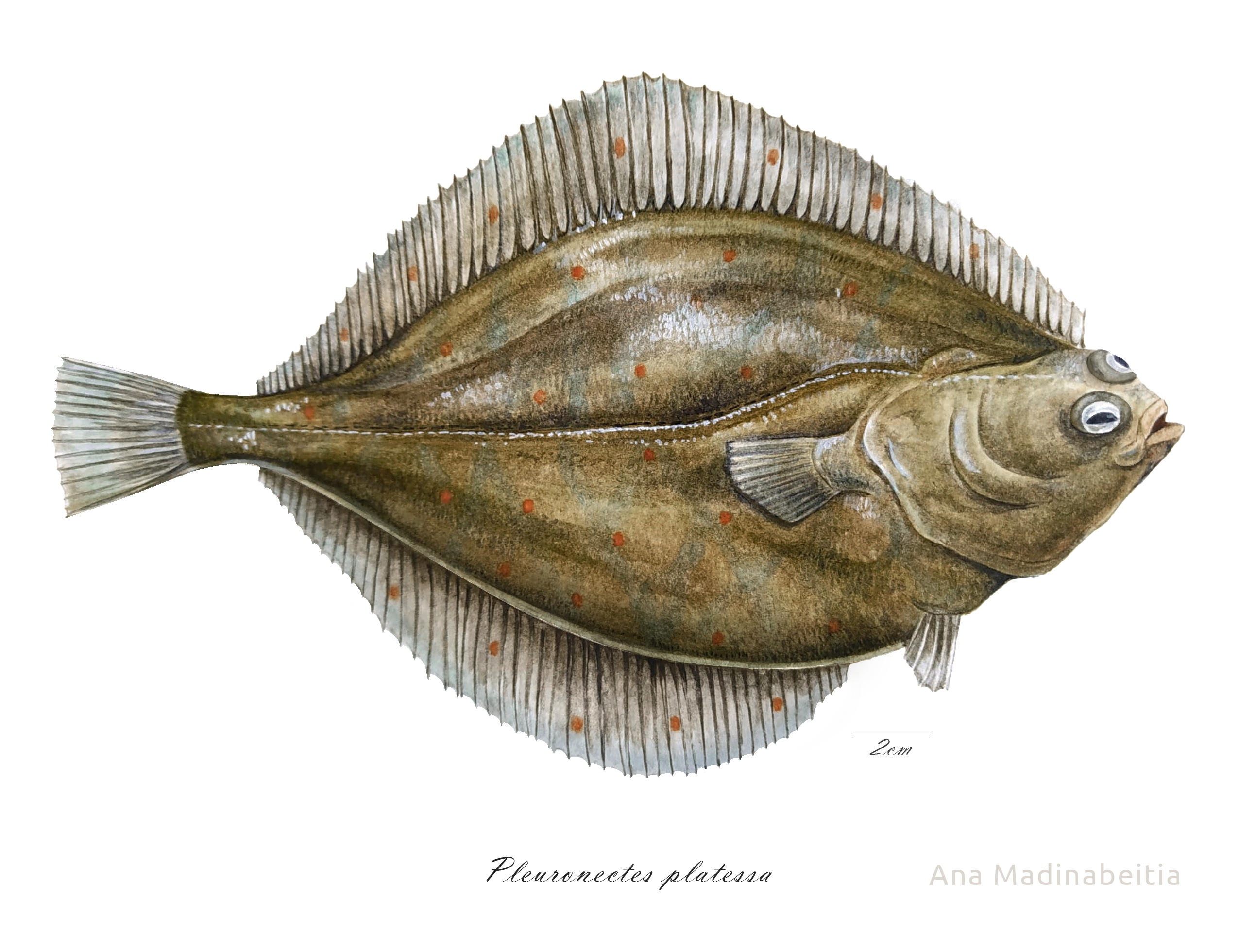
European Plaice
The European plaice (''Pleuronectes platessa''), commonly referred to as simply plaice, is a species of marine flatfish in the genus Pleuronectes of the family Pleuronectidae. Description The European plaice is characterized, on their dorsal side, by their dark green to dark brown skin, blotched with conspicuous, but irregularly distributed, orange spots. The ventral side is pearly white. The skin is smooth with small scales. They are able to adapt their colour somewhat to match that of their surroundings, but the orange spots always remain visible. The skin lacks any prickles. The outline of adults is oval. The head is rather small and is less than 25% of the total length. The pointed mouth is terminal and fairly small with its maxilla reaching just below the right eye. Both eyes are located at the right side of the body. The bony ridge behind the eyes is another characteristic for this species. The lateral line curves slightly above the pectoral fin. The dorsal fin reaches t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Plaice
The American plaice, American sole or long rough dab (''Hippoglossoides platessoides'') is a North Atlantic flatfish that belongs, along with other right-eyed flounders, to the family Pleuronectidae. In the northwest Atlantic (''H. p. platessoides'') it ranges from Greenland and Labrador to Rhode Island, and in the northeast Atlantic (''H. p. limandoides'') it ranges from Murmansk to the English Channel, Ireland and Iceland.Muus, B., J. G. Nielsen, P. Dahlstrom and B. Nystrom (1999). ''Sea Fish.'' pp. 260-261. They live on soft bottoms at depths of , but mainly between . In the Gulf of Maine spawning peaks in April and May. They grow to a maximum length of . The species is considered by the Northwest Atlantic Fisheries Organization to be overfished, with no signs of recovery. On the other hand, the Canadian government believes the species is abundant, and counts it as the second most caught flatfish, totalling 50% of the flatfish caught by Canadian fishermen. A 1997 study reports ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellowfin Sole
The yellowfin sole (''Limanda aspera'') is a flatfish of the family Pleuronectidae. It is a demersal fish that lives on soft, sandy bottoms at depths of up to , though it is most commonly found at depths of around . Its native habitat is the temperate waters of the northern Pacific, from Korea and the Sea of Japan to the Sea of Okhotsk, the Bering Sea and Barkley Sound on the west coast of Canada. Males grow up to in length, though the common length is around . The maximum recorded weight is , and the maximum recorded lifespan is 26 years. Description The yellowfin sole has a deep body, with a small mouth, moderately large and closely situated eyes, and a slightly pronounced snout. The upper side of the body is olive to brown in colour, with dark mottling, and dorsal and anal fins are yellowish on both sides of the body, with faint dark bars and a narrow dark line at the base. Scales are rough on both sides of the body. Taxonomy The yellowfin sole was originally described ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commercial Trawler
A fishing trawler is a commercial fishing vessel designed to operate fishing trawls. Trawling is a method of fishing that involves actively dragging or pulling a trawl through the water behind one or more trawlers. Trawls are fishing nets that are pulled along the bottom of the sea or in midwater at a specified depth. A trawler may also operate two or more trawl nets simultaneously (double-rig and multi-rig). There are many variants of trawling gear. They vary according to local traditions, bottom conditions, and how large and powerful the trawling boats are. A trawling boat can be a small open boat with only 30 horsepower (22 kW) or a large factory ship with 10,000 horsepower (7457 kW). Trawl variants include beam trawls, large-opening midwater trawls, and large bottom trawls, such as "rock hoppers" that are rigged with heavy rubber wheels that let the net crawl over rocky bottom. History During the 17th century, the British developed the Dogger, an ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fishery
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life; or more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a. fishing ground). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both in freshwater waterbodies (about 10% of all catch) and the oceans (about 90%). About 500 million people worldwide are economically dependent on fisheries. 171 million tonnes of fish were produced in 2016, but overfishing is an increasing problem — causing declines in some populations. Because of their economic and social importance, fisheries are governed by complex fisheries management practices and legal regimes that vary widely across countries. Historically, fisheries were treated with a " first-come, first-served " approach, but recent threats by human overfishing and environmental issues have required increased regulation of fisheries to prevent conflict and increase profitable economic activity on the fishery. Modern jurisdictio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echiura
The Echiura, or spoon worms, are a small group of marine animals. Once treated as a separate phylum, they are now considered to belong to Annelida. Annelids typically have their bodies divided into segments, but echiurans have secondarily lost their segmentation. The majority of echiurans live in burrows in soft sediment in shallow water, but some live in rock crevices or under boulders, and there are also deep sea forms. More than 230 species have been described. Spoon worms are cylindrical, soft-bodied animals usually possessing a non-retractable proboscis which can be rolled into a scoop-shape to feed. In some species the proboscis is ribbon-like, longer than the trunk and may have a forked tip. Spoon worms vary in size from less than a centimetre in length to more than a metre. Most are deposit feeders, collecting detritus from the sea floor. Fossils of these worms are seldom found and the earliest known fossil specimen is from the Upper Carboniferous ( Pennsylvanian). T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphipoda
Amphipoda is an order of malacostracan crustaceans with no carapace and generally with laterally compressed bodies. Amphipods range in size from and are mostly detritivores or scavengers. There are more than 9,900 amphipod species so far described. They are mostly marine animals, but are found in almost all aquatic environments. Some 1,900 species live in fresh water, and the order also includes the terrestrial sandhoppers such as ''Talitrus saltator''. Etymology and names The name ''Amphipoda'' comes, via New Latin ', from the Greek roots 'on both/all sides' and 'foot'. This contrasts with the related Isopoda, which have a single kind of thoracic leg. Particularly among anglers, amphipods are known as ''freshwater shrimp'', ''scuds'', or ''sideswimmers''. Description Anatomy The body of an amphipod is divided into 13 segments, which can be grouped into a head, a thorax and an abdomen. The head is fused to the thorax, and bears two pairs of antennae and one pair of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Of Japan
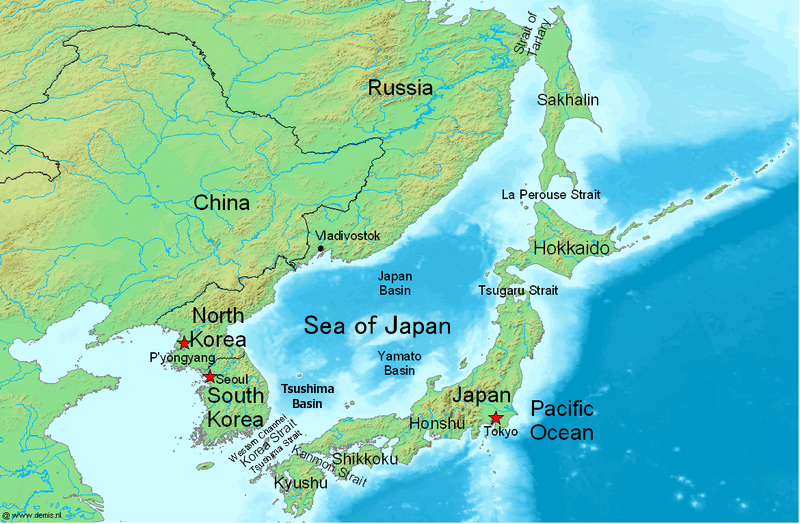
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific Ocean. This isolation also affects faunal diversity and salinity, both of which are lower than in the open ocean. The sea has no large islands, bays or capes. Its water balance is mostly determined by the inflow and outflow through the straits connecting it to the neighboring seas and the Pacific Ocean. Few rivers discharge into the sea and their total contribution to the water exchange is within 1%. The seawater has an elevated concentration of dissolved oxygen that results in high biological productivity. Therefore, fishing is the dominant economic activity in the region. The intensity of shipments across the sea has been moderate owing to political issues, but it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Steindachner
Franz Steindachner (11 November 1834 in Vienna – 10 December 1919 in Vienna) was an Austrian Zoology, zoologist, ichthyologist, and herpetologist. He published over 200 papers on fishes and over 50 papers on reptiles and amphibians. Steindachner described hundreds of new species of fish and dozens of new amphibians and reptiles. At least seven species of reptile have been named after him. Work and career Being interested in natural history, Steindachner took up the study of fossil fishes on the recommendation of his friend Eduard Suess (1831–1914). In 1860 he was appointed to the position of director of the fish collection at the Naturhistorisches Museum, a position which had remained vacant since the death of Johann Jakob Heckel (1790–1857). (in German). Steindachner's reputation as an Ichthyology, ichthyologist grew, and in 1868 he was invited by Louis Agassiz (1807–1873) to accept a position at the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. Steindachner took ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |