|
Alaska Native Corporation
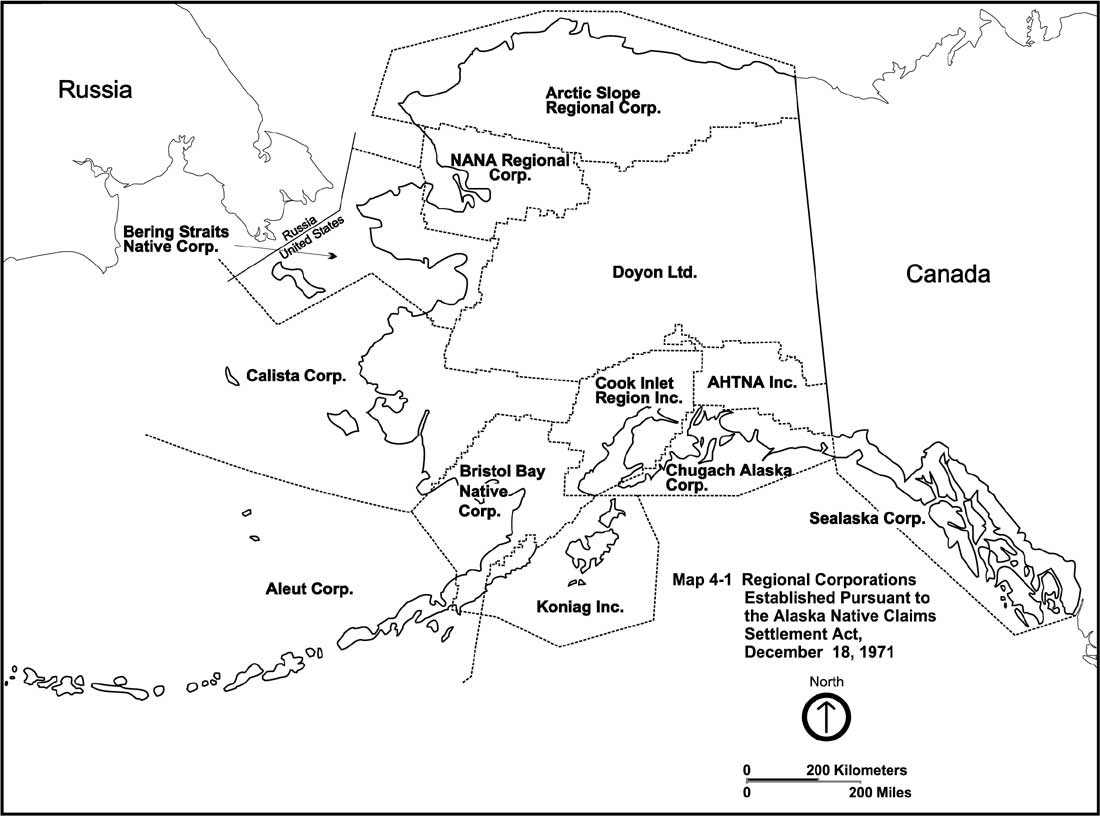
The Alaska Native Regional Corporations were established in 1971 when the United States Congress passed the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act (ANCSA) which settled land and financial claims made by the Alaska Natives and provided for the establishment of 13 regional corporations to administer those claims. Associations, regional and village corporations Under ANCSA the state was originally divided into twelve regions, each represented by a "Native association" responsible for the enrollment of past and present residents of the region. Individual Alaska Natives enrolled in these associations, and their village level equivalents, were made shareholder in the Regional and Village Corporations created by the Act. The twelve for-profit regional corporations, and a thirteenth region representing those Alaska Natives who were no longer residents of Alaska in 1971, were awarded the monetary and property compensation created by ANCSA. Village corporations and their shareholders received ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washington, D.C. Senators and representatives are chosen through direct election, though vacancies in the Senate may be filled by a governor's appointment. Congress has 535 voting members: 100 senators and 435 representatives. The U.S. vice president has a vote in the Senate only when senators are evenly divided. The House of Representatives has six non-voting members. The sitting of a Congress is for a two-year term, at present, beginning every other January. Elections are held every even-numbered year on Election Day. The members of the House of Representatives are elected for the two-year term of a Congress. The Reapportionment Act of 1929 establishes that there be 435 representatives and the Uniform Congressional Redistricting Act requires ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kotzebue, Alaska
Kotzebue ( ) or Qikiqtaġruk ( , ) is a city in the Northwest Arctic Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. It is the borough's seat, by far its largest community and the economic and transportation hub of the subregion of Alaska encompassing the borough. The population of the city was 3,102 as of the 2020 census, down from 3,201 in 2010. The city has received an All-America City award. History Etymology and prehistory Owing to its location and relative size, Kotzebue served as a trading and gathering center for the various communities in the region. The Noatak, Selawik and Kobuk Rivers drain into the Kotzebue Sound near Kotzebue to form a center for transportation to points inland. In addition to people from interior villages, inhabitants of far-eastern Asia, now the Russian Far East, came to trade at Kotzebue. Furs, seal-oil, hides, rifles, ammunition, and seal skins were some of the items traded. People also gathered for competitions like the current World Eskimo Indian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pribilof Islands
The Pribilof Islands (formerly the Northern Fur Seal Islands; ale, Amiq, russian: Острова Прибылова, Ostrova Pribylova) are a group of four volcanic islands off the coast of mainland Alaska, in the Bering Sea, about north of Unalaska and 200 miles (320 km) southwest of Cape Newenham. The Siberian coast is roughly northwest. About in total area, they are mostly rocky and are covered with tundra, with a population of 572 as of the 2010 census. Principal islands The principal islands are Saint Paul and Saint George. The former was named for the Feast of Saints Peter and Paul, on the day of which the island was first encountered by the Russian explorer Gavriil Pribylov; the latter was probably named for the ship sailed by Pribylov. The Otter and Walrus islets are near St. Paul. The total land area of all the islands is . The islands are part of the Bering Sea unit of the Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuge. Fur trade While oral traditions of the Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands (; ; ale, Unangam Tanangin,”Land of the Aleuts", possibly from Chukchi language, Chukchi ''aliat'', "island"), also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large volcanic islands and 55 smaller islands. Most of the Aleutian Islands belong to the U.S. state of Alaska, but some belong to the Russian Federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of Kamchatka Krai. They form part of the Aleutian Arc in the Northern Pacific Ocean, occupying a land area of 6,821 sq mi (17,666 km2) and extending about westward from the Alaska Peninsula toward the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, and act as a border between the Bering Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Crossing 180th meridian, longitude 180°, at which point east and west longitude end, the archipelago contains both the westernmost part of the United States by longitude (Amatignak Island) and the easternmost by longitude ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska Peninsula
The Alaska Peninsula (also called Aleut Peninsula or Aleutian Peninsula, ale, Alasxix̂; Sugpiaq: ''Aluuwiq'', ''Al'uwiq'') is a peninsula extending about to the southwest from the mainland of Alaska and ending in the Aleutian Islands. The peninsula separates the Pacific Ocean from Bristol Bay, an arm of the Bering Sea. In literature (especially Russian) the term "Alaska Peninsula" was used to denote the entire northwestern protrusion of the North American continent, or all of what is now the state of Alaska, exclusive of its panhandle and islands. The Lake and Peninsula borough, the Alaskan equivalent of a county, is named after the peninsula. The Alaska/Aleutian Peninsula is also grouped into Southwest Alaska. The other largest peninsulas in Alaska include the Kenai Peninsula and Seward Peninsula. Geography The base of the Alaska Peninsula extends out from the end of the Alaska Range. The Aleutian Range is a highly active volcanic mountain range which runs a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dillingham, Alaska
Dillingham ( esu, Curyung; russian: Диллингхем ), also known as Curyung, is a city in Dillingham Census Area, Alaska, United States. Incorporated in 1963, it is an important commercial fishing port on Nushagak Bay. As of the 2020 census, the population of the city was 2,249, down from 2,329 in 2010. Geography Dillingham is on Nushagak Bay at the mouth of the Nushagak River, an inlet of Bristol Bay, an arm of the Bering Sea in the North Pacific, in southwestern Alaska. It is located at (59.046751, -158.508665). According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of . of it is land, and of it (7.64%) is water. This may change as the City of Dillingham will likely petition the State of Alaska to increase the size of its boundaries to include most of Nushagak Bay and Wood River, to gain revenue from the Nushagak District and Wood River Special Harvest Area commercial salmon fisheries. Dillingham is located in the 37th district of the Alaska House ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliamna, Alaska
Iliamna ( Dena'ina: ) is a census-designated place (CDP) in Lake and Peninsula Borough, Alaska, United States. The population was 108 at the 2020 census, slightly down from 109 in 2010. History Iliamna was originally the name of an Athabaskan village at the point where the Iliamna River flows into Iliamna Lake, about east of present-day Iliamna. That site is now called Old Iliamna ( Dena'ina: ''Nuch'ak'dalitnu’''). In 1935, the residents of Old Iliamna moved to the present-day location. The first sport fishing lodge in Iliamna was built in the 1930s, and the second was built in the 1950s. Many more were built later in the 20th century. Iliamna's economy has two main elements: subsistence fishing and hunting and sport fishing lodges. Year-round residents largely pursue subsistence activities, while summer workers from other areas work in the lodges. Around 1913, Herman Gartelmann, Jack Kinney, and Ed Ahola built a roadhouse here, taking advantage of air travel through Lak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eklutna, Alaska
Eklutna (; Dena'ina: ''Idlughet''; Ahtna: ''Zdlaaygha'') is a native village within the Municipality of Anchorage in the U.S. state of Alaska. The Tribal Council estimates the population at 70; many tribal members live in the surrounding communities. About Eklutna lies northeast of Anchorage near the intersection of Mi. 142 of the Alaska Railroad and the Mile 26 of the Glenn Highway from the mouth of the Eklutna River at the head of the Knik Arm of Cook Inlet, at in the Anchorage Recording District. The Dena'ina Athabascan village of Eklutna is the last of eight villages that existed before construction of the Alaska Railroad brought an influx of American colonists around 1915. First settled more than 800 years ago, it is the oldest inhabited location in the Anchorage area. Its Dena'ina name is ''Idlughet'' ("by the objects", referring to two nearby hills); the name "Eklutna" derives from ''Idluytnu'', the name for Eklutna River, meaning "(plural) objects river". Russian O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyonek, Alaska
Tyonek or Present / New Tyonek ( Dena'ina: ''Qaggeyshlat'' - ″little place between toes") is a census-designated place (CDP) in Kenai Peninsula Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. As of the 2020 census the population was 152, down from 171 in 2010. In 1973, the community formed the Tyonek Native Corporation (TNC) under the Alaska Native Claims Settlement Act and is federally recognized. History A Dena'ina Alaska Native village at Tyonek was noted by the explorer James Cook in 1778. The Lebedev-Lastochkin Company, a Russian fur trade venture, maintained a small trapping station on the site of Tyonek.Solojova, Katerina and Aleksandra Vovnyanko. ''The Rise and Decline of the Lebedev-Lastochkin Company: Russian Colonization of South Central Alaska, 1787-1798.'' The Pacific Northwest Quarterly 90, No. 4 (1999), pp. 191-205. A detachment of the Vancouver Expedition under Joseph Whidbey visited the trading post in May 1794. Whidbey found that the LLC maintained "one large house, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenai, Alaska
Kenai (, ) ( Dena'ina: ; russian: Кенай, ''Kenay'') is a city in the Kenai Peninsula Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. It is one hundred and fifty-eight miles by road southwest from Anchorage. The population was 7,424 as of the 2020 census, up from 7,100 in 2010, the fifteenth-most populated city in the state. History The city of Kenai is named after the local Dena'ina word 'ken' or 'kena', which means 'flat, meadow, open area with few trees; base, low ridge', according to the Dena'ina Topical Dictionary by James Kari, Ph.D., published in 2007. This describes the area along the mouth and portion of the Kenai River near the City of Kenai. Archaeological evidence suggests that the area was first occupied by the Kachemak people from 1000 B.C., until they were displaced by the Dena'ina Athabaskan people around 1000 A.D. Before the arrival of the Russians, Kenai was a Dena'ina village called ''Shk'ituk't'', meaning "where we slide down." When Russian fur traders first a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanana River
The Tanana River (Lower Tanana: Tth'eetoo', Upper Tanana: ''Tth’iitu’ Niign'') is a tributary of the Yukon River in the U.S. state of Alaska. According to linguist and anthropologist William Bright, the name is from the Koyukon (Athabaskan) ''tene no'', ''tenene'', literally "trail river". The river's headwaters are located at the confluence of the Chisana and Nabesna rivers just north of Northway in eastern Alaska. The Tanana flows in a northwest direction from near the border with the Yukon Territory, and laterally along the northern slope of the Alaska Range, roughly paralleled by the Alaska Highway. In central Alaska, it emerges into a lowland marsh region known as the Tanana Valley and passes south of the city of Fairbanks. In the marsh regions it is joined by several large tributaries, including the Nenana (near the city of Nenana) and the Kantishna. It passes the village of Manley Hot Springs and empties into the Yukon near the town of Tanana. Ice on the riv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koyukuk, Alaska
Koyukuk () (Koyukon: ) is a city in Yukon-Koyukuk Census Area, Alaska, United States. At the 2010 census the population was 96, down from 101 in 2000. , Koyukuk is one of a number of Alaskan communities threatened by erosion. History The Koyukon Athabascans had seasonal camps and moved when the wild game migrated. There were 12 summer fish camps located on the Yukon River between the Koyukuk River and the Nowitna River. Trading between the Koyukon and Inupiat of the Kobuk River area has occurred before the arrival of Europeans. After the Alaska Purchase, a United States military telegraph line was constructed along the north side of the Yukon River and Koyukuk became the site of a telegraph station. A trading post opened around 1880, just before the gold rush of 1884–85. Steamboats on the Yukon, which supplied gold prospectors ran before and after 1900 with 46 boats in operation on the river in the peak year of 1900. A measles epidemic and food shortages during 1900 red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |