|
Alain Chabaud
Alain Chabaud (13 March 1923 – 11 March 2013) was a French parasitologist, mainly a specialist of nematodes and sporozoa. He was the Director of the Laboratoire de Zoologie (Vers) in the Muséum National d'Histoire Naturelle in Paris from 1960 to 1989. He was one of the founders of the Société Française de Parasitologie in 1962 and its president until 1975, and president of the Société zoologique de France in 1967. Taxa named in his honour Chabaud's name is honoured in many parasite taxa described by his colleagues. The most famous species named in the honour of Chabaud is ''Plasmodium chabaudi'' Landau, 1965, a species studied in many laboratories. Several genera of Nematoda were named in the honour of Chabaud, including '' Chabaudacuaria'' Mutafchiev & Kinsella, 2012, '' Chabaudechina'' Smales, 1999, '' Chabaudgolvania'' Freitas, 1958 (also honouring French parasitologist Jean-Yves Golvan). '' Chabaudus chabaudi'' Inglis & Ogden, 1965 has both genus and species names ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L'Aigle
L'Aigle is a commune in the Orne department in Normandy in northwestern France. Before 1961, the commune was known as ''Laigle''. According to Orderic Vitalis, the nest of an eagle (''aigle'' in French) was discovered during the construction of the castle. The river Risle flows through the commune. L'Aigle station has rail connections to Argentan, Paris and Granville. Meteorite On 26 April 1803 a meteoroid entered the Earth's atmosphere and air burst over L'Aigle. Population Heraldry Events * 8 January 1354 : Assassination of the constable of France, Charles d'Espagne, by men of Charles the Bad, king of Navarre. * 26 April 1803 - meteorite falls. Twin towns – sister cities L'Aigle is twinned with: * Aigle, Switzerland * Clausthal-Zellerfeld, Germany * Spišská Nová Ves, Slovakia See also * Communes of the Orne department * L'Aigle station * L'Aigle family The l'Aigle family was a Norman family that derived from the town of L'Aigle, on the southeastern borders of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phlebotomus
''Phlebotomus'' is a genus of " sand flies" in the Diptera family Psychodidae. In the past, they have sometimes been considered to belong in a separate family, Phlebotomidae, but this alternative classification has not gained wide acceptance. Epidemiology In the Old World, ''Phlebotomus'' sand flies are primarily responsible for the transmission of leishmaniasis, an important parasitic disease, while transmission in the New World, is generally via sand flies of the genus ''Lutzomyia''. The protozoan parasite itself is a species of the genus ''Leishmania''. Leishmaniasis normally finds a mammalian reservoir in rodents and other small animals such as canids ( canine leishmaniasis) and hyraxes. The female sand fly carries the ''Leishmania'' protozoa from infected animals after feeding, thus transmitting the disease, while the male feeds on plant nectar. The parasite ''Leishmania donovani'' is the main causative agent of visceral leishmaniasis (VL) in India, Nepal, and Bangladesh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fleas
Flea, the common name for the order Siphonaptera, includes 2,500 species of small flightless insects that live as external parasites of mammals and birds. Fleas live by ingesting the blood of their hosts. Adult fleas grow to about long, are usually brown, and have bodies that are "flattened" sideways or narrow, enabling them to move through their hosts' fur or feathers. They lack wings; their hind legs are extremely well adapted for jumping. Their claws keep them from being dislodged, and their mouthparts are adapted for piercing skin and sucking blood. They can leap 50 times their body length, a feat second only to jumps made by another group of insects, the superfamily of froghoppers. Flea larvae are worm-like, with no limbs; they have chewing mouthparts and feed on organic debris left on their hosts' skin. Genetic evidence indicates that fleas are a specialised lineage of parasitic scorpionflies (Mecoptera) ''sensu lato'', most closely related to the family Nannochorist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acari
Mites are small arachnids (eight-legged arthropods). Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari, but genetic analysis does not show clear evidence of a close relationship. Most mites are tiny, less than in length, and have a simple, unsegmented body plan. The small size of most species makes them easily overlooked; some species live in water, many live in soil as decomposers, others live on plants, sometimes creating galls, while others again are predators or parasites. This last type includes the commercially destructive ''Varroa'' parasite of honey bees, as well as scabies mites of humans. Most species are harmless to humans, but a few are associated with allergies or may transmit diseases. The scientific discipline devoted to the study of mites is called acarology. Evolution and taxonomy The mites are not a defined taxon, but is used for two distinct groups of arachni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligochaeta
Oligochaeta () is a subclass of animals in the phylum Annelida, which is made up of many types of aquatic and terrestrial worms, including all of the various earthworms. Specifically, oligochaetes comprise the terrestrial megadrile earthworms (some of which are semiaquatic or fully aquatic), and freshwater or semiterrestrial microdrile forms, including the tubificids, pot worms and ice worms ( Enchytraeidae), blackworms ( Lumbriculidae) and several interstitial marine worms. With around 10,000 known species, the Oligochaeta make up about half of the phylum Annelida. These worms usually have few setae (chaetae) or "bristles" on their outer body surfaces, and lack parapodia, unlike polychaeta. Diversity Oligochaetes are well-segmented worms and most have a spacious body cavity (coelom) used as a hydroskeleton. They range in length from less than up to in the 'giant' species such as the giant Gippsland earthworm (''Megascolides australis'') and the Mekong worm (''Amynth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Euzet
Louis Euzet (27 July 1923 in Lézignan-Corbières, France – 24 September 2013 in Sète, France) was a French parasitologist. Education Louis Euzet was a high-school student in Narbonne, France, and a student of the University of Montpellier (in the then “''Faculté des Sciences''”). He obtained his bachelor's degree (''Licence'') in 1947. He prepared his doctoral thesis in the Station de Biologie Marine at Sète, under the direction of Paul Mathias and Jean-George Baer; the thesis, on tetraphyllidean cestodes, was accepted on 16 June 1956. Career Louis Euzet was a junior lecturer at the Station de Biologie Marine in Sète in 1947. He was appointed Professor in the recently created “''Collège Scientifique Universitaire''” at Perpignan in 1959. He moved in 1969 to the University of Montpellier, where he established his ''Laboratoire de Parasitologie Comparée'' (Laboratory of Comparative Parasitology). He retired in 1991, became an Emeritus Professor in 1992 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monogenea
Monogeneans are a group of ectoparasitic flatworms commonly found on the skin, gills, or fins of fish. They have a direct lifecycle and do not require an intermediate host. Adults are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive structures.L.A. Tubbsa et al. (2005). "Effects of temperature on fecundity in vitro, egg hatching and reproductive development of ''Benedenia seriolae'' and ''Zeuxapta seriolae'' (Monogenea) parasitic on yellowtail kingfish Seriola lalandi". ''International Journal for Parasitology''(35), 315–327. Some monogeneans are oviparous (egg-laying) and some are viviparous (live-bearing). Oviparous varieties release eggs into the water. Viviparous varieties release larvae, which immediately attach to another host. The genus ''Gyrodactylus'' is an example of a viviparous variety, while the genus ''Dactylogyrus'' is an example of an oviparous variety. Signs and symptoms Freshwater fish that become infected with this parasite become let ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert-Philippe Dollfus
Robert-Philippe Dollfus (20 July 1887 in Paris, France – 19 February 1976 in Paris, France) was a French zoologist and parasitologist. Stunkard, H.W. 1977. In Memoriam Robert-Philippe Dollfus (1887–1976). Journal of Parasitology 63: 706 & 727. Grabda, E. 1977. Robert Ph. Dollfus (1887–1976) Wspomnienie Pośmiertne. ''Wiadomości Parazytologiczne'' 23: 463–465. Career Robert-Philippe Dollfus was born in Paris on July 20, 1887, in a family of Protestant tradition. His father was Gustave Frédéric Dollfus, famous French geologist and malacologist. Very early on, he attended the laboratories of Alfred Giard and that of Alfred Blanchard. As early as 1912, at the age of 25, he established the notion of metacercaria, a stage of the lifecycle of Digenea. In 1914, he was on an oceanographic mission aboard the Research Vessel "Pourquoi Pas?" under the orders of Jean-Baptiste Charcot. During the Second World War, he was a stretcher bearer and auxiliary doctor. Between the wars, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cestoda
Cestoda is a class of parasitic worms in the flatworm phylum (Platyhelminthes). Most of the species—and the best-known—are those in the subclass Eucestoda; they are ribbon-like worms as adults, known as tapeworms. Their bodies consist of many similar units known as proglottids—essentially packages of eggs which are regularly shed into the environment to infect other organisms. Species of the other subclass, Cestodaria, are mainly fish infecting parasites. All cestodes are parasitic; many have complex life histories, including a stage in a definitive (main) host in which the adults grow and reproduce, often for years, and one or two intermediate stages in which the larvae develop in other hosts. Typically the adults live in the digestive tracts of vertebrates, while the larvae often live in the bodies of other animals, either vertebrates or invertebrates. For example, '' Diphyllobothrium'' has at least two intermediate hosts, a crustacean and then one or more freshwater fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digenea
Digenea (Gr. ''Dis'' – double, ''Genos'' – race) is a class of trematodes in the Platyhelminthes phylum, consisting of parasitic flatworms (known as ''flukes'') with a syncytial tegument and, usually, two suckers, one ventral and one oral. Adults commonly live within the digestive tract, but occur throughout the organ systems of all classes of vertebrates. Once thought to be related to the Monogenea, it is now recognised that they are closest to the Aspidogastrea and that the Monogenea are more closely allied with the Cestoda. Around 6,000 species have been described to date. Morphology Key features Characteristic features of the Digenea include a syncytial tegument; that is, a tegument where the junctions between cells are broken down and a single continuous cytoplasm surrounds the entire animal. A similar tegument is found in other members of the Neodermata; a group of platyhelminths comprising the Digenea, Aspidogastrea, Monogenea and Cestoda. Digeneans possess a vermifo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
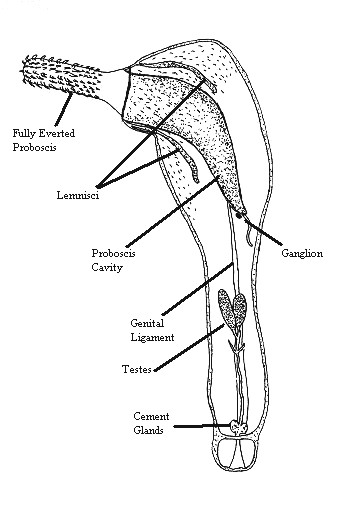
Acanthocephala
Acanthocephala (Greek , ', thorn + , ', head) is a phylum of parasitic worms known as acanthocephalans, thorny-headed worms, or spiny-headed worms, characterized by the presence of an eversible proboscis, armed with spines, which it uses to pierce and hold the gut wall of its host. Acanthocephalans have complex life cycles, involving at least two hosts, which may include invertebrates, fish, amphibians, birds, and mammals. About 1420 species have been described. The Acanthocephala were thought to be a discrete phylum. Recent genome analysis has shown that they are descended from, and should be considered as, highly modified rotifers. This unified taxon is known as Syndermata. History The earliest recognisable description of Acanthocephala – a worm with a proboscis armed with hooks – was made by Italian author Francesco Redi (1684).Crompton 1985, p. 27 In 1771, Joseph Koelreuter proposed the name Acanthocephala. Philipp Ludwig Statius Müller independently called th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_Lorryia_formosa_2_edit.jpg)