|
Alaborg
Álaborg or Áluborg is the name of a Varangian fort mentioned in the Norse sagas about Halfdan Eysteinsson and Hrolf Ganger. The first saga indicates that it was possible to sail from Aldeigjuborg (Ladoga) to Alaborg northward by sea, but a more rapid and practicable way was by land eastward. The text implies that Alaborg and Aldeigjuborg were two rivals, situated at a short distance from each other. In 1989, Tatiana Jackson demonstrated that the only location conforming to this description is the so-called "Gorodishche" (literally, "abandoned fortress") on the Syas River. It was the only sizable settlement in the area east of Ladoga until the 13th or 14th century. Its Norse name may derive from the Valya River that flows in the vicinity. Archaeology Nikolay Repnikov was the first historian to recognize the archaeological importance of the village Gorodishche on the Syas River (russian: Сясьское городище). Repnikov published his observations in 1900 but it wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rus' Khaganate
The Rusʹ Khaganate ( be, Рускі каганат, ''Ruski kahanat'', russian: Русский каганат, ''Russkiy kaganat'', uk, Руський каганат, ''Ruśkyj kahanat''), is the name applied by some modern historians to a polity postulated to have existed during a poorly documented period in the history of Eastern Europe in the 9th century AD. It was suggested that the Rusʹ Khaganate was a state, or a cluster of city-states, set up by a people called ''Rusʹ'' (characterised in all contemporary sources as Norsemen) somewhere in what is today European Russia and Ukraine as a chronological predecessor to the Rurik Dynasty and Kievan Rusʹ. The region's population at that time was composed of Slavic, Turkic, Baltic, Finnic, Hungarian and Norse peoples. The region was also a place of operations for Varangians, eastern Scandinavian adventurers, merchants, and pirates.Franklin, Simon and Jonathan Shepard. ''The Emergence of Rus 750–1200.'' London: Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syas River
The Syas () is a river in Lyubytinsky District of Novgorod Oblast and Tikhvinsky and Volkhovsky Districts of Leningrad Oblast, Russia. The Syas flows from the Valdai Hills north into Lake Ladoga. The town of Syasstroy is located at its mouth. It is long, and the area of its basin . The largest tributary of the Syas is the Tikhvinka (right). The source of the Syas is in the Valday Hills north of the settlement of Nebolchi. The river flows north and enters Leningrad Oblast. It crosses the Tikhvin Ridge from the south to the north. Further north, it accepts the Tikhvinka from the right and turns west. There it accepts the Lunenka from the left, turns northwest and crosses into Volkhovsky District. The mouth of the Syas is downstream from the city of Syasstroy. The river basin of the Syas comprises parts of Volkhovsky, Tikhvinsky, and Boksitogorsky Districts of Leningrad Oblast and Lyubytinsky District of Novgorod Oblast. In the west and the south, it is separated from the river ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Building Ships By Roerich
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volga
The Volga (; russian: Во́лга, a=Ru-Волга.ogg, p=ˈvoɫɡə) is the List of rivers of Europe#Rivers of Europe by length, longest river in Europe. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment area of «Река Волга» , Russian State Water Registry which is more than twice the size of Ukraine. It is also Europe's largest river in terms of average discharge (hydrology), discharge at delta – between and – and of drainage basin. It is widely regarded as the Rivers in Russia, national river of Russia. The hypothetical old Russian state, the Rus' Khaganate, arose along the Volga . Historically, the river served as an important meeting place of various Eurasian civilizations. The river flows in Russia through forests, Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Russia
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Leningrad Oblast
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dmitry Machinsky
Dmitry Alexeyevich Machinsky (russian: Дмитрий Алексеевич Мачинский, 1937 – 8 January 2012) was a Russian archaeologist. He lived in Saint Petersburg and worked in the Hermitage Museum. Machinsky is particularly well known for having excavated Lyubsha and other Varangians, Viking settlements along the Volkhov River. Machinsky attributed these settlements to the Rus' Khaganate, whose capital — as he believed — was Staraya Ladoga, Ladoga. External linksBibliography of Dmitry Machinsky Archaeologists from Saint Petersburg 1937 births 2012 deaths {{Russia-scientist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vadim The Bold
Vadim the Bold was a legendary chieftain of the Ilmen Slavs who led their struggle against Rurik and the Varangians in the 9th century. According to the Nikon Chronicle, a historic 16th-century Muscovite chronicle that covered events of 859–1520 CE, the Novgorodians broke into rebellion against Rurik, their ruler, but his Varangian druzhina managed to quell the riots and murdered their leader, Vadim. The first Russian historian, Vasily Tatishchev, conjectured that Vadim's mother was the elder daughter of Gostomysl. Hence, Vadim was Rurik's elder cousin and had a better claim to the throne. In Russian literature After Tatischev's publications, Vadim became one of the most popular characters in the 18th-century Russian literature. Yakov Knyazhnin, a leading playwright, penned a play in which he contrasted Vadim, a defender of Novgorod's ancient freedom, with the authoritarian Rurik. When the play appeared in 1791, Catherine the Great was enraged, although she had fictionalized Vadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine Zuckerman
Constantin Zuckerman (; born 1957) is a French historian and Professor of Byzantine studies at the Ecole Pratique des Hautes Etudes in Paris. Biography Academic rank: professor. Highest degree: doctorate. Job title: The Deputy Director of the Centre for History and Civilization of Byzantium, Collège de France. Zuckerman is the author of numerous articles about the Byzantine Empire, the Goths, the Armenians, the Huns, the Turkic peoples, the Khazars, the Magyars and the early Rus, among other peoples. In "On the Date of the Khazars' Conversion to Judaism and the Chronology of the Kings of the Rus Oleg and Igor," Zuckerman used Khazar documents (the Kievian Letter, Khazar Correspondence, and Schechter Letter) to call into question the traditional dates for early Kievan Rus leaders. In the same article he asserted that the Khazars converted to Judaism in 861, during the visit of Saint Cyril. Bibliography *La Crimee entre Byzance et le Khaganat khazar. Ed. Constantin Zuckerman. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duboviki
Novyye Duboviki (russian: Новые Дубовики; literally: "New Oak Grove") is an archaeological site in Leningrad Oblast of Russia, located about south of Ladoga upstream the Volkhov River, at the head of the lower Volkhov rapids. In the Early Middle Ages, Novyye Duboviki was the site of a Norse-Slavic fort, which guarded the crossing of the rapids. The settlement flourished in the late 9th century, but was burned to the ground in the early 10th century. It was later revived on a much smaller scale, and was operated by the Novgorod Republic in the High Middle Ages, as a minor pogost. Although the site is seriously damaged by modern building activities, a series of excavations, undertaken since 1884, revealed traces of a predominantly Scandinavian settlement, covering no less than six hectares. The fort was ringed by at least ten burial mounds, ranging from seven to ten metres in height. The tallest barrow, built around a 9-metre-high vertical pole, stands high. Recent re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
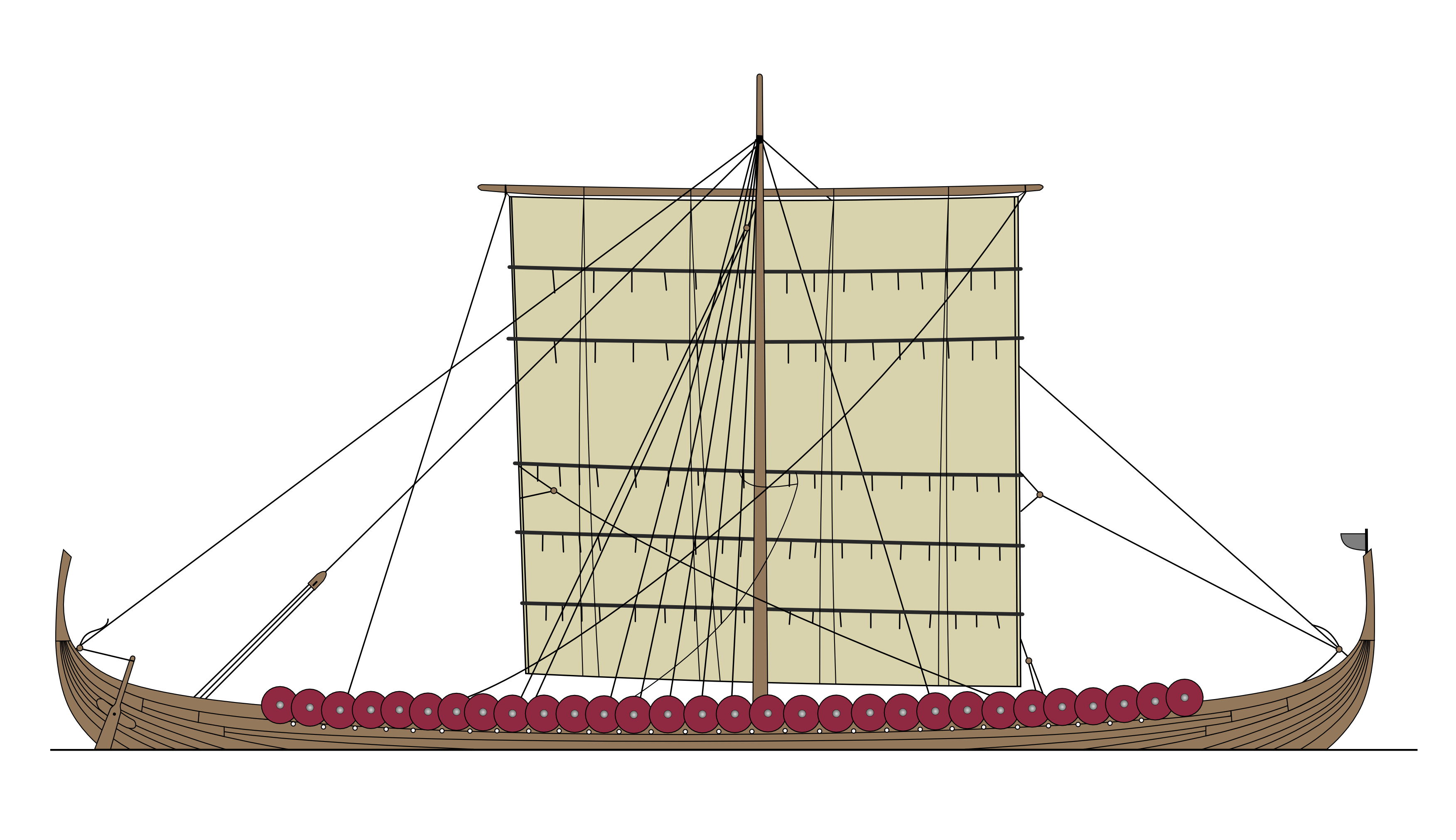
Longship
Longships were a type of specialised Scandinavian warships that have a long history in Scandinavia, with their existence being archaeologically proven and documented from at least the fourth century BC. Originally invented and used by the Norsemen (commonly known as the Vikings) for commerce, exploration, and warfare during the Viking Age, many of the longship's characteristics were adopted by other cultures, like Anglo-Saxons, and continued to influence shipbuilding for centuries. The longship's design evolved over many centuries, and continuing up until the sixth century with clinker-built ships like Nydam. The longship appeared in its complete form between the ninth and 13th centuries. The character and appearance of these ships have been reflected in Scandinavian boatbuilding traditions to the present day. The particular skills and methods employed in making longships are still used worldwide, often with modern adaptations. They were all made out of wood, with cloth sails ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Druzhina
In the medieval history of Kievan Rus' and Early Poland, a druzhina, drużyna, or družyna ( Slovak and cz, družina; pl, drużyna; ; , ''druzhýna'' literally a "fellowship") was a retinue in service of a Slavic chieftain, also called ''knyaz.'' The name is derived from the Slavic word ''drug'' ( друг) with the meaning of "companion, friend". Early Rus' In Early Rus', a druzhina helped the prince administer his principality and constituted the area's military force. The first members of a druzhina were the Varangians, whose princes established control there in the 9th century. Soon, members of the local Slavic aristocracy and adventurers of a variety of other nationalities became druzhinniki. The druzhina's organization varied with time and survived in one form or another until the 16th century. The druzhina was composed of two groups: the senior members, later known as boyars, and the junior members, later known as boyar scions. The boyars were the prince's closest a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)