|
Akbariyya
Akbari Sufism or Akbarism (Arabic: أكبرية: ''Akbariyya'') is a branch of Sufi metaphysics based on the teachings of Ibn Arabi, an Andalusian Sufi who was a gnostic and philosopher. The word is derived from Ibn Arabi's nickname, "Shaykh al-Akbar," meaning "the greatest master." 'Akbariyya' or 'Akbaris' have never been used to indicate a specific Sufi group or society. It is now used to refer to all historical or contemporary Sufi metaphysicians and Sufis influenced by Ibn Arabi's doctrine of ''Wahdat al-Wujud''. It is not to be confused with Al Akbariyya, a secret Sufi society founded by Swedish Sufi 'Abdu l-Hadi Aguéli. Wahdat al-Wujud Wahdat al-Wajud (Arabic: وحدة الوجود Persian: وحدت وجود) meaning the "unity of being" is a Sufi philosophy emphasizing that "there is no true existence except the Ultimate Truth (God)", that is, that the only truth within the universe is God, and that all things exist within God only. Ibn Arabi is most often char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Aguéli
Ivan Aguéli (born ''John Gustaf Agelii'') (May 24, 1869 – October 1, 1917) also named Shaykh ʿAbd al-Hādī al-ʿAqīlī ( ar, شيخ عبد الهادی عقیلی) upon his conversion to Islam, was a Swedish wandering Sufi, painter and author. As a devotee of Ibn Arabi, his metaphysics applied to the study of Islamic esoterism and its similarities with other esoteric traditions of the world. He was one of the initiators of René Guénon into Sufism and founder of the Parisian ''Al Akbariyya'' society. His art was a unique form of miniature Post-Impressionism where he used the blend of colours to create a sense of depth and distance. His unique style of art made him one of the founders of the Swedish contemporary art movement. Childhood and youth Ivan Aguéli was born ''John Gustaf Agelii'' in the small Swedish town of Sala in 1869, the son of veterinarian ''Johan Gabriel Agelii''. Through his mother, he was related to the 18th century Swedish metaphysician Emanuel Swe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
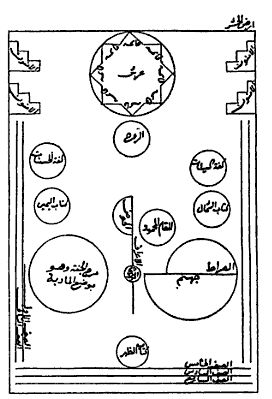
Ibn Arabi
Ibn ʿArabī ( ar, ابن عربي, ; full name: , ; 1165–1240), nicknamed al-Qushayrī (, ) and Sulṭān al-ʿĀrifīn (, , 'Sultan of the Knowers'), was an Arab Andalusian Muslim scholar, mystic, poet, and philosopher, extremely influential within Islamic thought. Out of the 850 works attributed to him, some 700 are authentic while over 400 are still extant. His cosmological teachings became the dominant worldview in many parts of the Muslim world. His traditional titular is ''Muḥyīddīn'' ( ar, محيي الدين; ''The Reviver of Religion''). After he passed away, among practitioners of sufism he is renowned by the honorific title ''Shaykh al-Akbar'' ( ar, الشيخ الأكبر) which the "Akbarian" school derives its name, and make him known as ''Doctor Maximus'' (The Greatest Teacher) in medieval Europe. Ibn ʿArabī was considered as a saint by some scholars and Muslim community. Al-Suyuti, Tanbih al-Ghabi fi Tanzih Ibn ‘Arabi (p. 17-21) Biography Ibn ʿAra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dawūd Al-Qayṣarī
Dawūd al-Qayṣarī (c.1260-c.1350) was an early Ottoman Sufi scholar, philosopher and mystic. He was born in Kayseri, in central Anatolia and was the student of the Iranian scholar, Abd al-Razzaq Kāshānī (d. 1329). He was the author of over a dozen philosophical texts, many of which are still important textbooks in Shi'ite religious schools. The most important is the commentary on Ibn al-'Arabi's ''Fusus al-Hikam'' and his criticism of Ibn al-Farid's poetry. Sultan Orhan Gazi built a school for him in the town of İznik, the first case of an Ottoman state-established medrese. See also * Akbariyya Akbari Sufism or Akbarism (Arabic: أكبرية: ''Akbariyya'') is a branch of Sufi metaphysics based on the teachings of Ibn Arabi, an Andalusian Sufi who was a gnostic and philosopher. The word is derived from Ibn Arabi's nickname, " Sh ... References Sufi mystics Akbarian Sufis 14th-century Muslim theologians Non-fiction writers from the Ottoman Empire {{ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sufi Metaphysics
In Islamic philosophy, Sufi metaphysics is centered on the concept of ar, وحدة, waḥdah, unity, label=none or ar, توحيد, tawhid, label=none. Two main Sufi philosophies prevail on this topic. literally means "the Unity of Existence" or "the Unity of Being." , meaning "existence" or "presence", here refers to God. On the other hand, , meaning "Apparentism" or "Monotheism of Witness", holds that God and his creation are entirely separate. Some scholars have claimed that the difference between the two philosophies differ only in semantics and that the entire debate is merely a collection of "verbal controversies" which have come about because of ambiguous language. However, the concept of the relationship between God and the universe is still actively debated both among Sufis and between Sufis and non-Sufi Muslims. Waḥdat al-Wujūd (unity of existence) The mystical thinker and theologian Abu Saeed Mubarak Makhzoomi discussed this concept in his book called ''Tohfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miguel Asín Palacios
Miguel Asín Palacios (5 July 1871 – 12 August 1944) was a Spanish scholar of Islamic studies and the Arabic language, and a Roman Catholic priest. He is primarily known for suggesting Muslim sources for ideas and motifs present in Dante's Divine Comedy, which he discusses in his book ''La Escatología musulmana en la Divina Comedia'' (1919). He wrote on medieval Islam, extensively on al-Ghazali (Latin: Algazel). A major book ''El Islam cristianizado'' (1931) presents a study of Sufism through the works of Muhyiddin ibn 'Arabi ( Sp: Mohidín Abenarabe) of Murcia in Andalusia (medieval Al-Andalus). Asín also published other comparative articles regarding certain Islamic influences on Christianity and on mysticism in Spain. Life Miguel Asín Palacios was born in Zaragoza, Aragón, on 5 July 1871, into the modest commercial family of Don Pablo Asín and Doña Filomena Palacios. His older brother Luis, his younger sister Dolores, and he were little children when their father died ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sachiko Murata
Sachiko Murata (村田幸子, born 1943) is Japanese scholar of comparative philosophy and mysticism and a professor of religion and Asian studies at Stony Brook University. She is a 2011 Guggenheim Fellow. Life She received her B.A. in family law from Chiba University in Japan, worked at a law firm in Tokyo for a year, and later attended Iran's University of Tehran, where she was the first woman and first non-Muslim to study ''fiqh'' (Islamic jurisprudence). She received her PhD in Persian literature in 1971, and then moved to the faculty of theology. She received her MA in Islamic jurisprudence in 1975, but shortly before completing her PhD in ''fiqh'', the Iranian Revolution caused her and her husband William Chittick to leave the country. Murata resettled at SUNY Stony Brook in Stony Brook, New York, where she teaches Islam, Confucianism, Taoism, and Buddhism Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Chittick
William C. Chittick (born 29 June 1943) is an American philosopher, writer, translator and interpreter of classical Islamic philosophical and mystical texts. He is best known for his work on Rumi and Ibn 'Arabi, and has written extensively on the school of Ibn 'Arabi, Islamic philosophy, and Islamic cosmology. Biography Born in Milford, Connecticut, Chittick finished his BA at the College of Wooster in Ohio, and then went on to complete a PhD in Persian literature at University of Tehran under the supervision of Seyyed Hossein Nasr in 1974. He taught comparative religion at Tehran's Aryamehr Technical University and left Iran before the revolution. Chittick is currently Distinguished Professor in the Department of Asian and Asian American Studies at Stony Brook University. He was awarded the Guggenheim Fellowship for his academic contributions in 2014. Major works Chittick has published 30 books and numerous articles on Islamic intellectual history, Sufism and Islamic philosop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James W
James is a common English language surname and given name: *James (name), the typically masculine first name James * James (surname), various people with the last name James James or James City may also refer to: People * King James (other), various kings named James * Saint James (other) * James (musician) * James, brother of Jesus Places Canada * James Bay, a large body of water * James, Ontario United Kingdom * James College, a college of the University of York United States * James, Georgia, an unincorporated community * James, Iowa, an unincorporated community * James City, North Carolina * James City County, Virginia ** James City (Virginia Company) ** James City Shire * James City, Pennsylvania * St. James City, Florida Arts, entertainment, and media * ''James'' (2005 film), a Bollywood film * ''James'' (2008 film), an Irish short film * ''James'' (2022 film), an Indian Kannada-language film * James the Red Engine, a character in ''Thomas the Tank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Lings
Martin Lings (24 January 1909 – 12 May 2005), also known as Abū Bakr Sirāj ad-Dīn, was an English writer, Islamic scholar, and philosopher. A student of the Swiss metaphysician Frithjof Schuon and an authority on the work of William Shakespeare, he is best known as the author of '' Muhammad: His Life Based on the Earliest Sources'', first published in 1983 and still in print. Early life and education Lings was born in Burnage, Manchester, in 1909 to a Protestant family. The young Lings gained an introduction to travelling at a young age, spending significant time in the United States because of his father's employment. Lings attended Clifton College and went on to Magdalen College, Oxford, where he gained a BA in English Language and Literature. At Magdalen, he was a student and then a close friend of C. S. Lewis. After graduating from Oxford Lings went to Vytautas Magnus University, in Lithuania, where he taught Anglo-Saxon and Middle English. For Lings himself, howeve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titus Burckhardt
Titus Burckhardt (24 October 1908 – 15 January 1984) was a Swiss writer and a leading member of the Perennialist or Traditionalist School. He was the author of numerous works on metaphysics, cosmology, anthropology, esoterism, alchemy, Sufism, symbolism and sacred art. Life Scion of a patrician family of Basel, Switzerland, Titus Burckhardt was the son of the sculptor Carl Burckhardt (1878–1923) and the grand-nephew of Jacob Burckhardt (1818–1897), an art historian and Renaissance specialist. His genealogical tree also includes John Lewis Burckhardt (1784–1817), the explorer who discovered the Nabatean city of Petra and the Egyptian temples of Abu Simbel. He was born in Florence, Italy, on October 24, 1908. The following year his family settled in Basel. He attended the same primary school as Frithjof Schuon, who became a lifelong friend. In 1920, his family left Basel for Ligornetto in the Swiss canton of Ticino, where his father died three years later. Around 1927, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frithjof Schuon
Frithjof Schuon (, , ; 18 June 1907 – 5 May 1998) was a Swiss metaphysician of German descent, belonging to the Perennialist or Traditionalist School of thought. He was the author of more than twenty works in French on metaphysics, spirituality, the religious phenomenon, anthropology and art, which have been translated into English and many other languages. He was also a painter and a poet. With René Guénon and Ananda Coomaraswamy, Schuon is recognized as one of the major 20th-century representatives of the ''philosophia perennis''. Like them, he affirmed the reality of an absolute Principle – God – from which the universe emanates, and maintained that all divine revelations, despite their differences, possess a common essence: one and the same Truth. He also shared with them the certitude that man is potentially capable of supra-rational knowledge, and undertook a sustained critique of the modern mentality severed from its traditional roots. Following Plato, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)
