|
Aisin-Gioro Ulhicun
Aisin-Gioro Ulhicun (born 1958) is a Chinese linguistics, linguist of Manchu ethnicity who is known for her studies of the Manchu language, Manchu, Jurchen language, Jurchen and Khitan language, Khitan languages and scripts. She is also known as a historian of the Liao Dynasty, Liao and Jin dynasty (1115–1234), Jin dynasties. Her works include a grammar of Manchu (1983), a dictionary of Jurchen (2003), and a study of Khitan memorial inscriptions (2005), as well as various studies on the phonology and grammar of the Khitan language. Biography Aisin-Gioro Ulhicun was born in Beijing, the second daughter of Jin Qizong (1918–2004), and the granddaughter of Jin Guangping (1899–1966), both of whom were also renowned scholars of Manchu and Jurchen. She is a direct descendant of the Qianlong Emperor as Jin Guangping was a sixth generation descendant of Qianlong's fifth son, Yongqi, Prince Rong, Prince Rongchun (Aisin-Gioro Yongqi). Other ancestors include the poet Gu Taiqing, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aisin-Gioro
The House of Aisin-Gioro was a Manchu people, Manchu clan that ruled the Later Jin (1616–1636), Later Jin dynasty (1616–1636), the Qing dynasty (1636–1912), and Manchukuo (1932–1945) in the history of China. Under the Ming dynasty, members of the Aisin Gioro clan served as chiefs of the Jianzhou Jurchens, one of the three major Jurchen tribes at this time. Qing bannermen passed through the gates of the Great Wall of China, Great Wall in 1644, conquered the short-lived Shun dynasty and the Southern Ming, Southern Ming dynasty. The Qing dynasty later expanded into other adjacent regions, including Xinjiang under Qing rule, Xinjiang, Tibet under Qing rule, Tibet, Mongolia under Qing rule, Outer Mongolia, and Taiwan under Qing rule, Taiwan, gaining total control of China. The dynasty reached High Qing era, its zenith during the High Qing era and under the Qianlong Emperor, who reigned from 1735 to 1796. This reign was followed by a century of gradual decline. The house lost po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beppu, Ōita
is a city in Ōita Prefecture on the island of Kyushu, Japan. As of March 31, 2017, the city had a population of 122,643"Statistics: Population" Beppu City Government website . Accessed 21 April 2017. and a of . The total area is . Beppu is famous for its hot springs. Geography Beppu is situated at the west end of , around the east central prefecture. The north, west, and east of the city are the mountains or highlands with elevations of several hundreds meters above sea level. Most of those mountains are the fourth-pe ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguists Of The Khitan Language
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science,Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). or part of the humanities. Traditional areas of linguistic analysis correspond to phenomena found in human linguistic systems, such as syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences); semantics (meaning); morphology (structure of words); phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages); phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language); and pragmatics (how social co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguists Of The Jurchen Language
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science,Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). or part of the humanities. Traditional areas of linguistic analysis correspond to phenomena found in human linguistic systems, such as syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences); semantics (meaning); morphology (structure of words); phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages); phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language); and pragmatics (how social conte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguists From China
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguistics is concerned with both the cognitive and social aspects of language. It is considered a scientific field as well as an academic discipline; it has been classified as a social science, natural science, cognitive science,Thagard, PaulCognitive Science, The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (Fall 2008 Edition), Edward N. Zalta (ed.). or part of the humanities. Traditional areas of linguistic analysis correspond to phenomena found in human linguistic systems, such as syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences); semantics (meaning); morphology (structure of words); phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages); phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language); and pragmatics (how social co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1958 Births
Events January * January 1 – The European Economic Community (EEC) comes into being. * January 3 – The West Indies Federation is formed. * January 4 ** Edmund Hillary's Commonwealth Trans-Antarctic Expedition completes the third overland journey to the South Pole, the first to use powered vehicles. ** Sputnik 1 (launched on October 4, 1957) falls to Earth from its orbit, and burns up. * January 13 – Battle of Edchera: The Moroccan Army of Liberation ambushes a Spanish patrol. * January 27 – A Soviet-American executive agreement on cultural, educational and scientific exchanges, also known as the "Lacy-Zarubin Agreement, Lacy–Zarubin Agreement", is signed in Washington, D.C. * January 31 – The first successful American satellite, Explorer 1, is launched into orbit. February * February 1 – Egypt and Syria unite, to form the United Arab Republic. * February 6 – Seven Manchester United F.C., Manchester United footballers are among the 21 people killed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paiza
A paiza or paizi or gerege ( xng, Гэрэгэ, mn, Пайз, fa, پایزه ''pāiza'', ''páizi'') was a tablet carried by Mongol officials and envoys to signify certain privileges and authority. They enabled Mongol nobles and officials to demand goods and services from civilian populations. Although only someone with a paiza was required to be supplied with mounts and served specified rations, those carrying military rarities used the yam even without a paiza. The officials and nobles of the Mongol Empire issued paizas unofficially and abused civilians. Therefore, Ögedei Khan (r. 1229–1241) prohibited the nobility from issuing paizas and jarliqs. To attract foreign or overseas merchants and talents, the Great Khans gave them paiza exempting them from taxes and allowing them to use relay stations. Most of these merchants were business partners of the Mongols, known as ortoq. However, Möngke Khan (r. 1251–1259) limited notorious abuses and sent imperial investigators t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
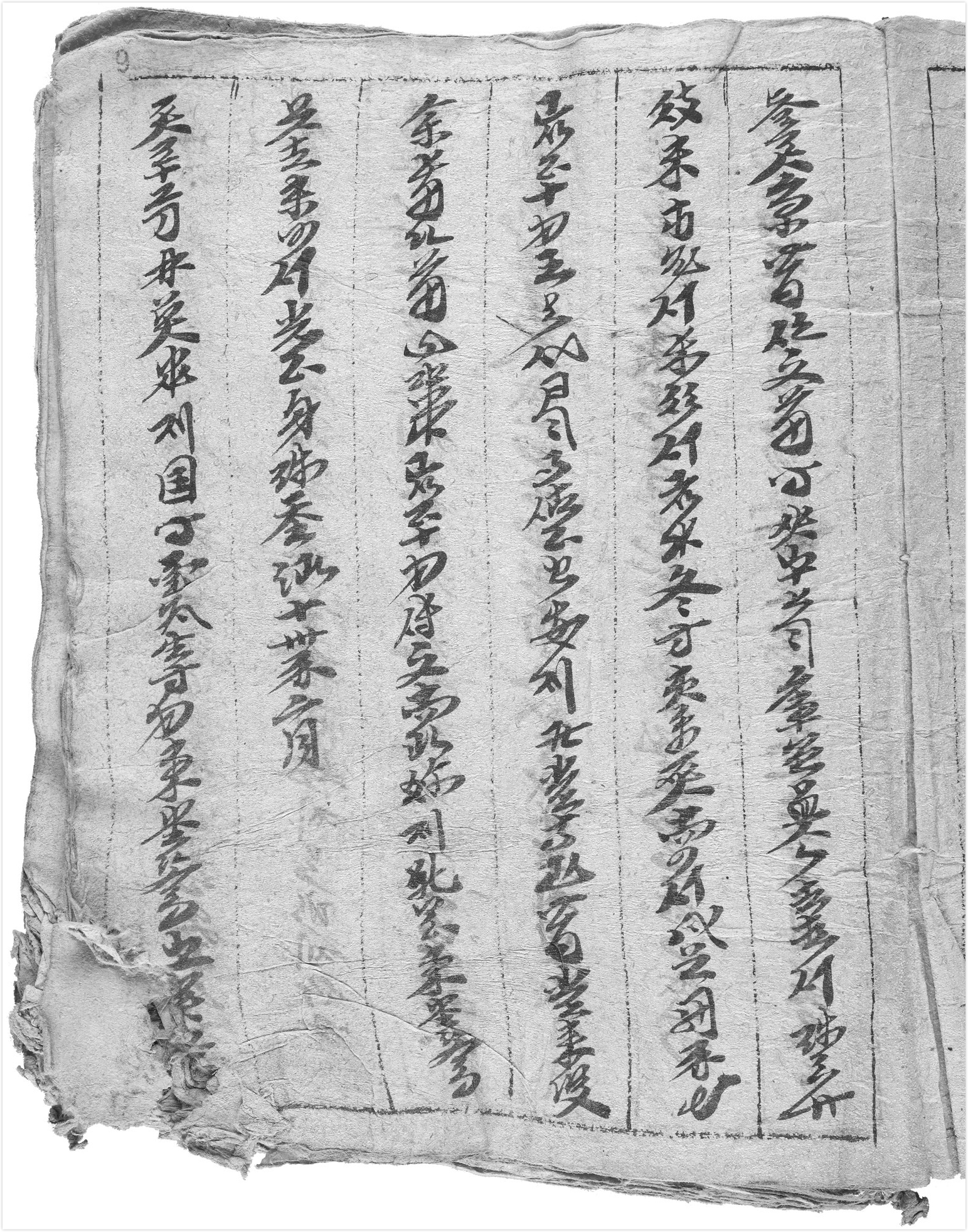
List Of Jurchen Inscriptions
The list of Jurchen inscriptions comprises a list of the corpus of known inscriptions written in the Jurchen language using the Jurchen script. There are ten monumental inscriptions, mostly dating to the Jin dynasty (1115–1234), but the latest monument dates to the early Ming Dynasty (1413). There are also a number of short Jurchen inscriptions on portable artefacts such as mirrors, seals and paiza A paiza or paizi or gerege ( xng, Гэрэгэ, mn, Пайз, fa, پایزه ''pāiza'', ''páizi'') was a tablet carried by Mongol officials and envoys to signify certain privileges and authority. They enabled Mongol nobles and officials to dem .... In contrast with inscriptions in Khitan scripts, there are no known examples of stone-inscribed epitaphs in the Jurchen script. Monumental inscriptions in the Jurchen script Other inscriptions in the Jurchen script See also * List of Khitan inscriptions Notes Footnotes References * * External links {{DEFAULT ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khitan Small Script
The Khitan small script () was one of two writing systems used for the now-extinct Khitan language (the other was the Khitan large script). It was used during the 10th–12th century by the Khitan people, who had created the Liao Empire in present-day northeastern China. In addition to the small script, the Khitans simultaneously also used a functionally independent writing system known as the Khitan large script. Both Khitan scripts continued to be in use to some extent by the Jurchens for several decades after the fall of the Liao dynasty, until the Jurchens fully switched to a script of their own. Examples of the scripts appeared most often on epitaphs and monuments, although other fragments sometimes surface. History The Khitan small script was invented in about 924 or 925 CE by a scholar named Yelü Diela. He drew his inspiration from "the Uyghur language and script", which he was shown by a visiting Uyghur ambassador at the Khitan court. For this reason, Khitan small scrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khitan Large Script
The Khitan large script () was one of two writing systems used for the now-extinct Khitan language (the other was the Khitan small script). It was used during the 10th–12th centuries by the Khitan people, who had created the Liao Empire in north-eastern China. In addition to the large script, the Khitans simultaneously also used a functionally independent writing system known as the Khitan small script. Both Khitan scripts continued to be in use to some extent by the Jurchens for several decades after the fall of the Liao dynasty, until the Jurchens fully switched to a script of their own. Examples of the scripts appeared most often on epitaphs and monuments, although other fragments sometimes surface. History Abaoji of the Yelü clan, founder of the Khitan, or Liao, dynasty, introduced the original Khitan script in 920 CE. The "large script", or "big characters" (), as it was referred to in some Chinese sources, was established to keep the record of the new Khitan state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Xizong Of Jin
Emperor Xizong of Jin (28 February 1119 – 9 January 1150), personal name Hela, sinicised name Wanyan Dan, was the third emperor of the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty of China. He reigned for about 15 years from 1135 to 1150. During his reign, the Jin dynasty launched several military campaigns against the Han-led Southern Song dynasty in southern China. Early life Hela was the eldest son of Shengguo (繩果; also known as Wanyan Zongjun 完顏宗峻), the eldest son of Aguda (Emperor Taizu), the founder and first emperor of the Jin dynasty. His mother was Lady Pucha (蒲察氏), whom he posthumously honoured as "Empress Huizhao" (惠昭皇后). When Emperor Taizu died in 1123, the throne was passed on to his younger brother, Wuqimai (Emperor Taizong). Wanyan Zonghan and Wanyan Xiyin, who used to be Emperor Taizu's chief advisers, convinced Emperor Taizong to designate Hela as his heir apparent (''anban bojilie''; 諳班勃極烈) in 1132, so Hela became the new emperor in 1135 w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)