|
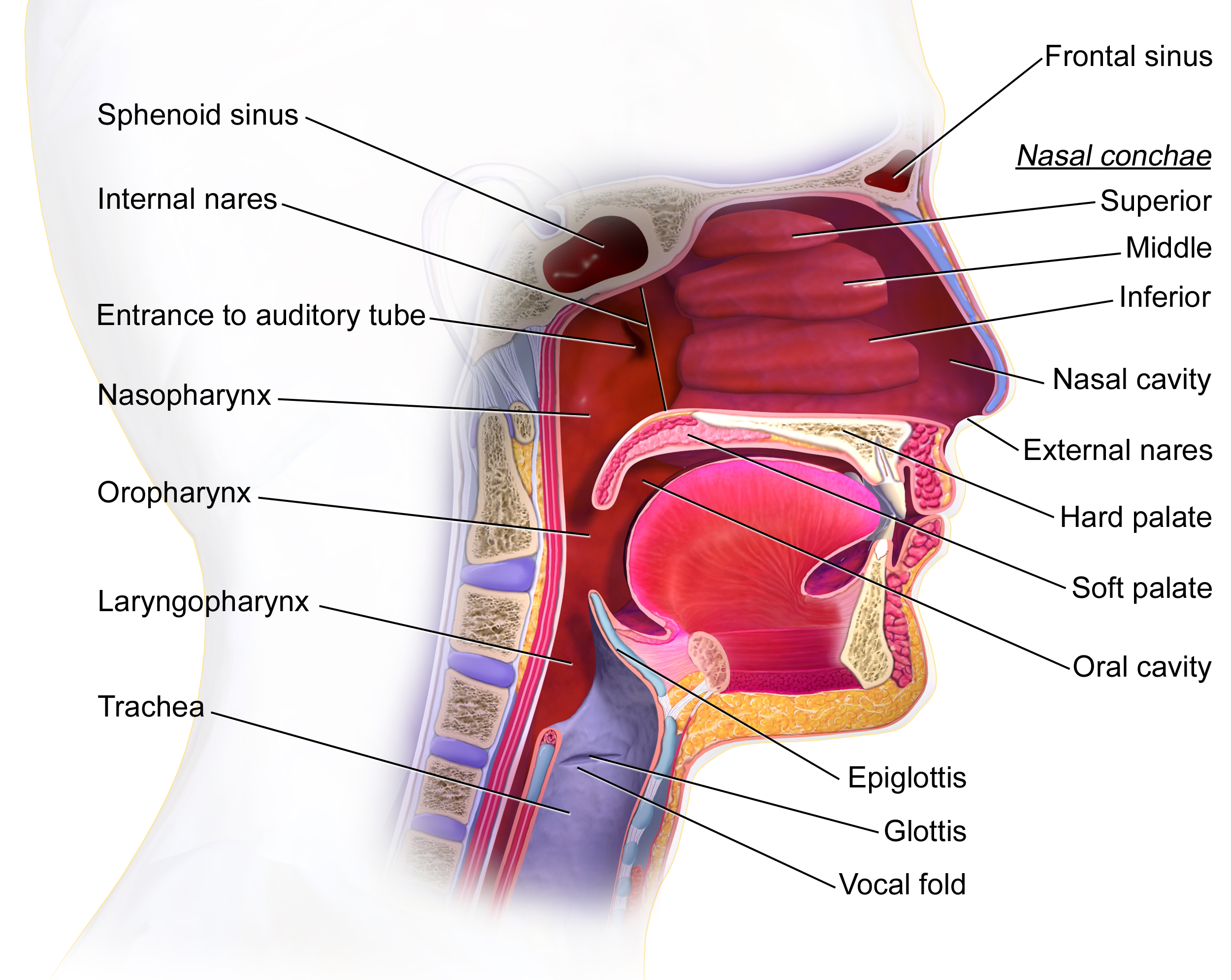
Airway Access
Surgical airway management (bronchotomy or laryngotomy) is the medical procedure ensuring an open airway between a patient’s lungs and the outside world. Surgical methods for airway management rely on making a surgical incision below the glottis in order to achieve direct access to the lower respiratory tract, bypassing the upper respiratory tract. Surgical airway management is often performed as a last resort in cases where orotracheal and nasotracheal intubation are impossible or contraindicated. Surgical airway management is also used when a person will need a mechanical ventilator for a longer period. The surgical creation of a permanent opening in the larynx is referred to as laryngostomy. Surgical airway management is a primary consideration in anaesthesia, emergency medicine and intensive care medicine. Surgical methods for airway management include cricothyrotomy and tracheostomy History Asclepiades of Bithynia is credited with being the first person who propos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cricothyrotomy
A cricothyrotomy (also called cricothyroidotomy) is an incision made through the skin and cricothyroid membrane to establish a patent airway during certain life-threatening situations, such as airway obstruction by a foreign body, angioedema, or massive facial trauma. Cricothyrotomy is nearly always performed as a last resort in cases where other means of tracheal intubation are impossible or impractical. Compared with tracheotomy, cricothyrotomy is quicker and easier to perform, does not require manipulation of the cervical spine, and is associated with fewer complications. However, while cricothyrotomy may be life-saving in extreme circumstances, this technique is only intended to be a temporizing measure until a definitive airway can be established. Indications A cricothyrotomy is often used as an airway of last resort given the numerous other airway options available including standard tracheal intubation and rapid sequence induction which are the common means of establishing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intensive Care Medicine
Intensive care medicine, also called critical care medicine, is a medical specialty that deals with seriously or critically ill patients who have, are at risk of, or are recovering from conditions that may be life-threatening. It includes providing life support, invasive monitoring techniques, resuscitation, and end-of-life care. Doctors in this specialty are often called intensive care physicians, critical care physicians or intensivists. Intensive care relies on multidisciplinary teams composed of many different health professionals. Such teams often include doctors, nurses, physical therapists, respiratory therapists, and pharmacists, among others. They usually work together in intensive care units (ICUs) within a hospital. Scope Patients are admitted to the intensive care unit if their medical needs are greater than what the general hospital ward can provide. Indications for the ICU include blood pressure support for cardiovascular instability ( hypertension/hypote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyrotomy
:''Thyrotomy may also refer to the cutting or biopsy the thyroid gland.'' Thyrotomy (also called thyroidotomy, median laryngotomy, laryngofissure or thyrofissure) is an incision of the larynx through the thyroid cartilage. See also * Laryngotomy *Cricothyrotomy *Tracheotomy * List of surgeries by type References * ''Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary ''Dorland's'' is the brand name of a family of medical reference works (including dictionaries, spellers and word books, and spell-check software) in various media spanning printed books, CD-ROMs, and online content. The flagship products are ''Do ...'' Larynx surgery Otorhinolaryngology {{Surgery-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasive Airway Management
Advanced airway management is the subset of airway management that involves advanced training, skill, and invasiveness. It encompasses various techniques performed to create an open or patent airway – a clear path between a patient's lungs and the outside world. This is accomplished by clearing or preventing obstructions of airways. Obstructions can be caused by many things, including the patient's own tongue or other anatomical components of the airway, foreign bodies, excessive amounts of blood and body fluids, or aspiration of food particles. Unlike basic airway management such as head tilt/chin lift or jaw-thrust maneuver, advanced airway management relies on the use of medical equipment and advanced training. Certain invasive airway management techniques can be performed "blind" or with visualization of the glottis. Visualization of the glottis can be accomplished either directly by using a laryngoscope blade or by utilizing newer video technology options. In roughl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airway Management
Airway management includes a set of maneuvers and medical procedures performed to prevent and relieve airway obstruction. This ensures an open pathway for gas exchange between a patient's lungs and the atmosphere. This is accomplished by either clearing a previously obstructed airway; or by preventing airway obstruction in cases such as anaphylaxis, the obtunded patient, or medical sedation. Airway obstruction can be caused by the tongue, foreign objects, the tissues of the airway itself, and bodily fluids such as blood and gastric contents ( aspiration). Airway management is commonly divided into two categories: basic and advanced. Basic techniques are generally non-invasive and do not require specialized medical equipment or advanced training. These include head and neck maneuvers to optimize ventilation, abdominal thrusts, and back blows. Advanced techniques require specialized medical training and equipment, and are further categorized anatomically into supraglottic device ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percutaneous Transtracheal Ventilation
Percutaneous transtracheal ventilation is the delivery of oxygen to the lungs through an over-the-needle catheter inserted through the skin into the trachea using a high pressure gas source is considered a form of conventional ventilation.{{cite journal, vauthors=Mace SE, Khan N , title=Needle cricothyrotomy. , journal=Emerg Med Clin North Am , year= 2008 , volume= 26 , issue= 4 , pages= 1085–101, xi , pmid=19059102 , doi=10.1016/j.emc.2008.09.004 , url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&tool=sumsearch.org/cite&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19059102 Percutaneous transtracheal ventilation may be mistaken for transtracheal jet ventilation, which is not considered conventional ventilation and refers to high-frequency ventilation; a low tidal volume Tidal volume (symbol VT or TV) is the volume of air moved into or out of the lungs during a normal breath. In a healthy, young human adult, tidal volume is approximately 500 ml per insp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kit De Cricothyroïdotomie
Kit may refer to: Places *Kitt, Indiana, US, formerly Kit * Kit, Iran, a village in Mazandaran Province * Kit Hill, Cornwall, England People * Kit (given name), a list of people and fictional characters * Kit (surname) Animals * Young animals: ** A short form of kitten, a young cat ** A young beaver ** A young ferret ** A young fox ** A young mink ** A young rabbit ** A young raccoon ** A young skunk ** A young squirrel ** A young wolverine * Old collective noun for a group of pigeons flying together Kinds of sets * Standard equipment and attire in sports: ** Kit (association football) ** Kit (cycling) ** Kit (rugby football) * Kit (of components), a set of components such as ** Electronic kit ** Kit car or component car **Testing kit (other) Other uses * Kit lens, a low-end SLR camera lens * Kit violin or kit, a small stringed musical instrument * Tropical Storm Kit, tropical cyclones named Kit * ''Whale (film)'', 1970, Bulgarian title See also * * * KIT (disamb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angioedema
Angioedema is an area of swelling ( edema) of the lower layer of skin and tissue just under the skin or mucous membranes. The swelling may occur in the face, tongue, larynx, abdomen, or arms and legs. Often it is associated with hives, which are swelling within the upper skin. Onset is typically over minutes to hours. The underlying mechanism typically involves histamine or bradykinin. The version related to histamine is due to an allergic reaction to agents such as insect bites, foods, or medications. The version related to bradykinin may occur due to an inherited problem known as C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency, medications known as angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, or a lymphoproliferative disorder. Treatment to protect the airway may include intubation or cricothyroidotomy. Histamine-related angioedema can be treated with antihistamines, corticosteroids, and epinephrine. In those with bradykinin-related disease a C1 esterase inhibitor, ecallantide, or icati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caelius Aurelianus
Caelius Aurelianus of Sicca in Numidia was a Greco-Roman physician and writer on medical topics. He is best known for his translation from Greek to Latin of a work by Soranus of Ephesus, ''On Acute and Chronic Diseases''. He probably flourished in the 5th century, although some place him two or even three centuries earlier. In favour of the later date is the nature of his Latin, which shows a strong tendency to the Romance, and the similarity of his language to that of Cassius Felix, also an African medical writer, who about 450 wrote a short treatise, chiefly based on Galen. We possess a translation by Aurelianus of two works of Soranus of Ephesus (2nd century), the chief representative of the methodic school of medicine, on chronic and acute maladies—''Tardae'' or ''Chronicae Passiones'', in five, and ''Celeres'' or ''Acutae Passiones'' in three books. The translation, which is especially valuable since the original has been lost, shows that Soranus possessed considerable p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartilaginous
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck and the bronchial tubes, and the intervertebral discs. In other taxa, such as chondrichthyans, but also in cyclostomes, it may constitute a much greater proportion of the skeleton. It is not as hard and rigid as bone, but it is much stiffer and much less flexible than muscle. The matrix of cartilage is made up of glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, collagen fibers and, sometimes, elastin. Because of its rigidity, cartilage often serves the purpose of holding tubes open in the body. Examples include the rings of the trachea, such as the cricoid cartilage and carina. Cartilage is composed of specialized cells called chondrocytes that produce a large amount of collagenous extracellular matrix, abundant ground substance that is rich in proteoglyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choking
Choking, also known as foreign body airway obstruction (FBAO), is a phenomenon that occurs when breathing is impeded by a blockage inside of the respiratory tract. An obstruction that prevents oxygen from entering the lungs results in oxygen deprivation. Although oxygen stored in the blood and lungs can keep a person alive for several minutes after breathing stops, choking often leads to death. Over 4,000 choking-related deaths occur in the United States every year. Deaths from choking most often occur in the very young (children under 2 years old) and in the elderly (adults over 75 years). Foods that can adapt their shape to that of the pharynx (such as bananas, marshmallows, or gelatinous candies) are more dangerous. Various forms of First Aid are used to address resolve choking. Choking is the fourth leading cause of unintentional injury death in the United States. Many episodes go unreported because they are brief and resolve without needing medical attention. Of the report ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aretaeus Of Cappadocia
Aretaeus ( grc-gre, Ἀρεταῖος) is one of the most celebrated of the ancient Greek physicians. Little is known of his life. He presumably was a native or at least a citizen of Cappadocia (Roman province), Cappadocia, a Roman province in Anatolia, Asia Minor (modern day Turkey), and most likely lived in the second half of the second century AD. He is generally styled "the Cappadocian" (). Diagnostic method Aretaeus wrote in Ionic Greek. His eight treatises on diseases, which are still extant, are considered to be among the most important Greco-Roman medical works ever written. His valuable work displays great accuracy in the detail of symptoms, and in seizing the diagnostic character of diseases. In his practice he followed for the most part the method of Hippocrates, but he paid less attention to what have been styled "the natural actions" of the system; and, contrary to the practice of the ''Father of Medicine'', he did not hesitate to attempt to counteract them, when t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |