|
Air Board (Australia)
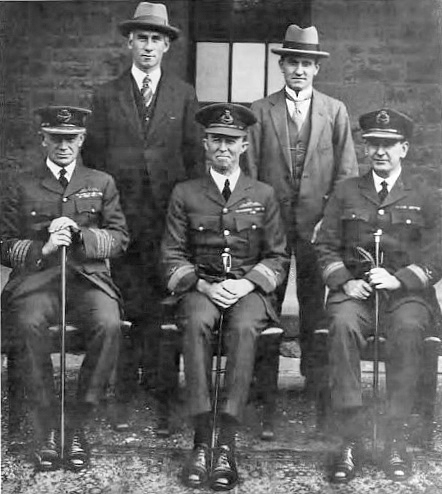
The Air Board, also known as the Administrative Air Board, or the Air Board of Administration, was the controlling body of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) from 1921 to 1976. It was composed of senior RAAF officers as well as some civilian members, and chaired by the Chief of the Air Staff (CAS). The CAS was the operational head of the Air Force, and the other board members were responsible for specific areas of the service such as personnel, supply, engineering, and finance. Initially based in Melbourne, the board relocated to Canberra in 1961. Formed in 1920, the Air Board's first task was to establish the air force that it was to administer; this took place in March 1921. The board was initially controlled by an Air Council, which included the chiefs of the Army and Navy; after the council's dissolution in 1929 the Air Board had equal status with the other service boards, reporting directly to the Minister for Defence. According to Air Force Regulations, the Air Board ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Australian Air Force
"Through Adversity to the Stars" , colours = , colours_label = , march = , mascot = , anniversaries = RAAF Anniversary Commemoration – 31 March , equipment = , equipment_label = , battles = * Second World War * Berlin Airlift * Korean War * Malayan Emergency * Indonesia–Malaysia Confrontation * Vietnam War * East Timor * War in Afghanistan * Iraq War * Military intervention against ISIL , decorations = , battle_honours = , battle_honours_label = , flying_hours = , website = , commander1 = Governor-General David Hurley as representative of Charles III as King of Australia , commander1_label = Commander-in-Chief , commander2 = General Angus Campbell , comma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Vice-marshal
Air vice-marshal (AVM) is a two-star air officer rank which originated in and continues to be used by the Royal Air Force. The rank is also used by the air forces of many countries which have historical British influence and it is sometimes used as the English translation of an equivalent rank in countries which have a non-English air force-specific rank structure. Air vice-marshal is a two-star rank and has a NATO ranking code of OF-7. It is equivalent to a rear-admiral in the Royal Navy or a major-general in the British Army or the Royal Marines. In other NATO forces, such as the United States Armed Forces and the Canadian Armed Forces, the equivalent two-star rank is major general. The rank of air vice-marshal is immediately senior to the rank air commodore and immediately subordinate to the rank of air marshal. Since before the Second World War it has been common for air officers commanding RAF groups to hold the rank of air vice-marshal. In small air forces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Williams (RAAF Officer)
Air Marshal Sir Richard Williams, (3 August 1890 – 7 February 1980), is widely regarded as the "father" of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). He was the first military pilot trained in Australia, and went on to command Australian and British fighter units in World War I. A proponent for air power independent of other branches of the armed services, Williams played a leading role in the establishment of the RAAF and became its first Chief of the Air Staff (CAS) in 1922. He served as CAS for thirteen years over three terms, longer than any other officer. Williams came from a working-class background in South Australia. He was a lieutenant in the Army when he learned to fly at Point Cook, Victoria, in 1914. As a pilot with the Australian Flying Corps (AFC) in World War I, Williams rose to command No. 1 Squadron AFC, and later 40th Wing RAF. He was awarded the Distinguished Service Order and finished the war a lieutenant colonel. Afterwards he campaigned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Blamey
Field Marshal Sir Thomas Albert Blamey, (24 January 1884 – 27 May 1951) was an Australian general of the First and Second World Wars, and the only Australian to attain the rank of field marshal. Blamey joined the Australian Army as a regular soldier in 1906, and attended the Staff College at Quetta. During the First World War he participated in the landing at Anzac Cove on 25 April 1915, and served as a staff officer in the Gallipoli Campaign, where he was mentioned in despatches for a daring raid behind enemy lines. He later served on the Western Front, where he distinguished himself in the planning for the Battle of Pozières. He rose to the rank of brigadier general, and served as chief of staff of the Australian Corps under Lieutenant General Sir John Monash, who credited him as a factor in the Corps' success in the Battle of Hamel, the Battle of Amiens and the Battle of the Hindenburg Line. After the war Blamey was Deputy Chief of the General Staff, and was invol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and the Royal Naval Air Service (RNAS). Following the Allied victory over the Central Powers in 1918, the RAF emerged as the largest air force in the world at the time. Since its formation, the RAF has taken a significant role in British military history. In particular, it played a large part in the Second World War where it fought its most famous campaign, the Battle of Britain. The RAF's mission is to support the objectives of the British Ministry of Defence (MOD), which are to "provide the capabilities needed to ensure the security and defence of the United Kingdom and overseas territories, including against terrorism; to support the Government's foreign policy objectives particularly in promoting international peace and security". T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
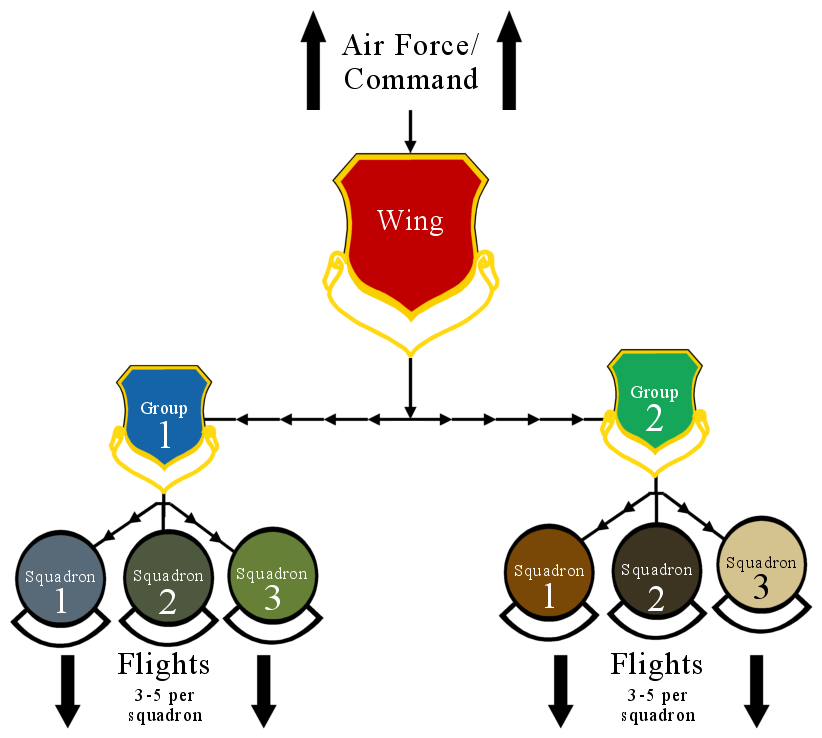
Wing (military Unit)
In military aviation, a wing is a unit of command. In most military aviation services, a wing is a relatively large formation of planes. In Commonwealth countries a wing usually comprises three squadrons, with several wings forming a group (around 10 squadrons). Each squadron will contain around 20 planes. Commonwealth usage Origins On its establishment in 1912, the British Royal Flying Corps (RFC) was intended to be an inter-service, combined force of the British Army and Royal Navy. Given the rivalry that existed between the army and navy, new terminology was used, in order to avoid marking the corps out as having an army or navy ethos. While the term "wing" had been used in the cavalry, its more general use predominated. Accordingly, the word "wing", with its allusion of flight, was chosen as the term of subdivision and the corps was split into a "Military Wing" (i.e. an army wing) and a "Naval Wing". Each wing consisted of a number of squadrons (the term "squadro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percy Grant (Royal Navy Officer)
Admiral Sir Edmund Percy Fenwick George Grant, (23 September 1867 – 8 September 1952) was a Royal Navy officer who served as First Naval Member and Chief of the Australian Naval Staff from 1919 to 1921. Naval career Grant saw service in the Egyptian War of 1882 as well as the Brazilian Naval Mutiny in 1893. He was promoted to lieutenant on 1 October 1890, posted as a lieutenant for navigation on the battleship , and promoted to commander (Navigation) on 26 June 1902. In September 1902 he was posted to for study at the Royal Naval College. He went on to serve during the First World War initially as flag captain to Vice Admiral Sir Lewis Bayly in and then as flag captain and chief of staff to Admiral Sir Cecil Burney who was then second-in-command of the Grand Fleet. In that capacity he saw his ship torpedoed and crippled at the Battle of Jutland in 1916. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chief Of Navy (Australia)
The Chief of Navy is the most senior appointment in the Royal Australian Navy The Royal Australian Navy (RAN) is the principal naval force of the Australian Defence Force (ADF). The professional head of the RAN is Chief of Navy (CN) Vice Admiral Mark Hammond AM, RAN. CN is also jointly responsible to the Minister of ..., responsible to the Chief of the Defence Force (CDF) and the Secretary of Defence. The rank associated with the position is vice admiral ( 3-star). Vice Admiral Mark Hammond is the current Chief of Navy; he assumed the position on 6 July 2022. Appointees The following list chronologically records those who have held the post of Chief of Navy or its preceding positions. Rank and honours are as at the completion of the individual's tours. Notes {{Chief of the navy by country Royal Australian Navy Royal Australian Navy admirals Leadership of the Australian Defence Force Military appointments of Australia Australia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Commonwealth Naval Board
The Australian Commonwealth Naval Board was the governing authority over the Royal Australian Navy from its inception and through World Wars I and II. The board was established on 1 March 1911 and consisted of civilian members of the Australian government The Australian Government, also known as the Commonwealth Government, is the national government of Australia, a federal parliamentary constitutional monarchy. Like other Westminster-style systems of government, the Australian Government ... as well as naval officers. References * * * History of the Royal Australian Navy {{Australia-mil-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Board (Australia)
The Military Board, also known as the Military Board of Administration, was the controlling body of the Australian Military Forces (AMF) from 1905 to 1976. It was composed of senior military and civilian members, and chaired by the Chief of the General Staff (CGS). Initially based in Melbourne, the board relocated to Canberra in 1959. On its formation in January 1905, the regular members of the Military Board were the Minister for Defence (the president of the board), the Deputy Adjutant-General, the Chief of Intelligence, the Chief of Ordnance, and a civilian Finance Member; members of the Citizens Military Force could also attend board meetings as required. The CGS position was initiated in 1909. The board as a whole was responsible for administering the AMF, subject to the control of the Minister. In November 1939 the board came under the newly formed Department of the Army in place of the Department of Defence. In July 1942 the board was dissolved and its functions assumed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Air Corps
The Australian Air Corps (AAC) was a temporary formation of the Australian military that existed in the period between the disbandment of the Australian Flying Corps (AFC) of World War I and the establishment of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) in March 1921. Raised in January 1920, the AAC was commanded by Major William Anderson, a former AFC pilot. Many of the AAC's members were also from the AFC and would go on to join the RAAF. Although part of the Australian Army, for most of its existence the AAC was overseen by a board of senior officers that included members of the Royal Australian Navy. Following the disbandment of the AFC, the AAC was a stop-gap measure intended to remain in place until the formation of a permanent and independent Australian air force. The corps' primary purpose was to maintain assets of the Central Flying School at Point Cook, Victoria, but several pioneering activities also took place under its auspices: AAC personnel set an Australian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian Flying Corps
The Australian Flying Corps (AFC) was the branch of the Australian Army responsible for operating aircraft during World War I, and the forerunner of the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF). The AFC was established in 1912, though it was not until 1914 that it began flight training. In 1911, at the Imperial Conference held in London, it was decided that aviation should be developed by the national armed forces of the British Empire. Australia became the first member of the Empire to follow this policy. By the end of 1911, the Army was advertising for pilots and mechanics. During 1912, pilots and mechanics were appointed, aircraft were ordered, the site of a flying school was chosen and the first squadron was officially raised. On 7 March 1913, the government officially announced formation of the Central Flying School (CFS) and an "Australian Aviation Corps", although that name was never widely used. AFC units were formed for service overseas with the Australian Imperial Force (A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpeg)
