|
Air-launched Cruise Missile
An air-launched cruise missile (ALCM) is a cruise missile that is launched from a military aircraft. Current versions are typically standoff weapons which are used to attack predetermined land targets with conventional, nuclear or thermonuclear payloads. Specific types of ALCMs (current, past and under development) include: * AGM-28 Hound Dog (USA) * AGM-84H/K SLAM-ER (USA) * AGM-86 ALCM (USA) * AGM-129 ACM (USA) * AGM-158 JASSM (USA) * AGM-158C LRASM (USA) * Air-Sol Moyenne Portée ASMP (France) *ASN4G (France) * BrahMos (India/Russia) * BrahMos-NG (India) * BrahMos-II (India/Russia) * CJ-10 (China) * Delilah (Israel) * Hatf-VIII (Ra'ad) (Pakistan) * Hypersonic Attack Cruise Missile USA * Ra'ad-II (Pakistan) * Joint Strike Missile (Norway/USA) * Kalibr-A (Russia) * KEPD 350 (Germany/Sweden) * Kh-20 (USSR) * Kh-32 (Russia) * Kh-35 (Russia) * Kh-55/Kh-555 (USSR/Russia) * Kh-59 (USSR/Russia) * Kh-61 (USSR/Russia) * Kh-101/102 (Russia) * KSR-5 (USSR) *LRSO (Long Range Stand Off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AGM-86 ALCM
The AGM-86 ALCM is an American subsonic air-launched cruise missile (ALCM) built by Boeing and operated by the United States Air Force. This missile was developed to increase the effectiveness and survivability of the Boeing B-52H Stratofortress strategic bomber. The missile dilutes an enemy's forces and complicates air defense of its territory. The concept started as a long-range drone aircraft that would act as a decoy, distracting Soviet air defenses from the bombers. As new lightweight nuclear weapons emerged in the 1960s, the design was modified with the intent of attacking missile and radar sites at the end of its flight. Further development extended its range so much that it emerged as a weapon allowing the B-52s to launch their attacks while still well outside Soviet airspace, saturating their defenses with hundreds of tiny, low-flying targets that were extremely difficult to see on radar. The ALCM so improved the capabilities of the US bomber force that the Soviets dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delilah (missile)
The Delilah missile is a cruise missile or loitering munition developed in Israel by Israel Military Industries (IMI). It is designed to target moving and re-locatable targets with a circular error probable (CEP) of . Unlike a typical cruise missile, which is locked onto a pre-programmed target prior to launch, the Delilah missile's unique feature, as claimed by the manufacturer, is being able to loiter and surveil an area before a remote weapon systems officer, usually from the launching fighter aircraft, identifies the specific target of the attack. Overview The name Delilah had been used by an anti-radiation attack drone configured after the US MQM-74 Chukar aerial target. It entered service in the Israeli Air Force in the mid-1980s. This air-launched drone identifies radar sites, allowing them to be found and destroyed. The Delilah missile is the name of a missile family built by IMI. Delilah was initially created as an aerial decoy, and was later developed into an offensiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kh-61
The P-800 Oniks (russian: П-800 Оникс; en, Onyx), also known in export markets as Yakhont (russian: Яхонт; en, ruby), is a Soviet / Russian supersonic anti-ship cruise missile developed by NPO Mashinostroyeniya as a ramjet version of P-80 Zubr. Its GRAU designation is 3M55, the air launched Kh-61 variant also exists. The missile has the NATO codename SS-N-26 " Strobile". Development officially started in 1983, and in the 1990s the anti-ship missile was tested on the Project 1234.7 ship. In 2002 the missile passed the whole range of trials and was commissioned. It is reportedly a replacement for the P-270 Moskit, and possibly also of the P-700 Granit. Description The missile is carried in flight by aerodynamic lift. The solid-propellant booster is located in the ramjet's combustion chamber and is ejected by the airflow after it has burned out. Advantages *Over-the-horizon firing range *Full autonomy of combat use ("fire and forget") *A set of flexible ("low-profile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kh-59
The Kh-59 ''Ovod'' (russian: Х-59 Овод 'Gadfly'; AS-13 'Kingbolt') is a Russian TV-guided cruise missile with a two-stage solid-fuel propulsion system and 200 km range. The Kh-59M ''Ovod-M'' (AS-18 'Kazoo') is a variant with a bigger warhead and turbojet engine. It is primarily a land-attack missile but the Kh-59MK variant targets ships. Development The initial design was based on the Raduga Kh-58 (AS-11 'Kilter'), but it had to be abandoned because the missile speed was too high for visual target acquisition. Raduga OKB developed the Kh-59 in the 1970s as a longer ranged version of the Kh-25 (AS-10 'Karen'), as a precision stand-off weapon for the Su-24M and late-model MiG-27's. The electro-optical sensors for this and other weapons such as the Kh-29 (AS-14 'Kedge') and KAB-500KR bombs were developed by S. A. Zverev NPO in Krasnogorsk. It is believed that development of the Kh-59M started in the 1980s. Details of the Kh-59M were first revealed in the early 1990s. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kh-55
The Kh-55 (russian: Х-55, also known as RKV-500; NATO reporting name: AS-15 "Kent") is a Soviet/Russian subsonic air-launched cruise missile, designed by MKB Raduga in the 1970s. It has a range of up to and can carry nuclear warheads. Kh-55 is launched exclusively from bomber aircraft and has spawned a number of conventionally armed variants mainly for tactical use, such as the Kh-65SE and Kh-SD, but only the Kh-101 and Kh-555 appear to have been put into service. Contrary to popular belief, the Kh-55 was not the basis of the submarine and ground-launched S-10 Granat or RK-55 ''Relief'' (SS-N-21"Sampson" and SSC-X-4"Slingshot") designed by NPO Novator. The RK-55 is very similar to the air-launched Kh-55 (AS-15 "Kent") but the Kh-55 has a drop-down turbofan engine and was designed by MKB Raduga. Development In the late 1960s, the "Ekho" study conducted by the GosNIIAS institute concluded that it would be more effective to deploy many small, subsonic cruise missiles than t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kh-35
The Zvezda Kh-35 (russian: Х-35 , AS-20 'Kayak') is a Soviet turbojet subsonic cruise anti-ship missile. The missile can be launched from helicopters, surface ships and coastal defence batteries with the help of a rocket booster, in which case it is known as ''Uran'' ('Uranus', SS-N-25 'Switchblade', GRAU 3M24) or ''Bal'' (SSC-6 'Sennight', GRAU 3K60). It is designed to attack vessels up to 5,000 tonnes. Development The previous anti-ship missiles made in USSR were highly capable, but they also were large and expensive. Therefore, the Soviet Navy found that a similar, small and very low flying missile would be useful. This new system was planned as small, cheap, and easy to install missile for a variety of platforms. This new system, called 3M24 Uran (in western nomenclature, SS-N-25) was originally meant for small surface combatants such as frigates, like the Krivak, Gepard and Neustrashimy. It was the answer to western missiles like the US Harpoon. Informally, it was also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kh-32
Kh-32 (russian: Х-32) is a Russian supersonic air-launched cruise missile with a range of 600–1000 km developed by the MKB Raduga from the Kh-22. The missile was accepted to service in 2016 as armament for the Tu-22M3M bombers. History Work on the deep modernization of the Kh-22 missile began in the late 1980s, due to the low immunity of its guidance radar operating at fixed frequencies. When the enemy was using radar jamming, the launch of the Kh-22 was impossible. State contract number 01133 for development work on the topic "Adaptation" was signed in 19 June 1990. Due to the general crisis in the country and insufficient financing, work on the topic was suspended several times. In 1998, the first missile tests were carried out on the basis of the 929th GLITS, and further work was stopped due to lack of funding from the Tupolev Design Bureau for the modernization of the aircraft-carrier. On 7 March 2008, Contract No. 83042 was signed with the Raduga State Committee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kh-20
The Raduga Kh-20 ( NATO reporting name: AS-3 Kangaroo) was an air launched cruise missile armed with a thermonuclear warhead which was developed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. The Kh-20 was designed to be air-launched. Background Kh-20 cruise missile was designed by M.I. Gurevich for the Tu-95 strategic bomber. Development began in 1954, drawing on experience with MiG-17 and MiG-19 fighters. Two Tu-95 were converted to Tu-95K missile carriers in 1955. Initial testing of the missile systems was performed using four specially modified MiG-19 fighters designated SM-20/I and SM-20/II for mothership-missile interface and airborne launch testing, and SM-K/I and SM-K/II for guidance system and ground launch testing. First SM-20/I launch from Tu-95K was made in the fall of 1956. One of the greatest challenges in the early development was starting the missile's Lyulka AL-7F turbojet engine after prolonged flight in very cold upper atmosphere. Kh-20 began flight testing on Marc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
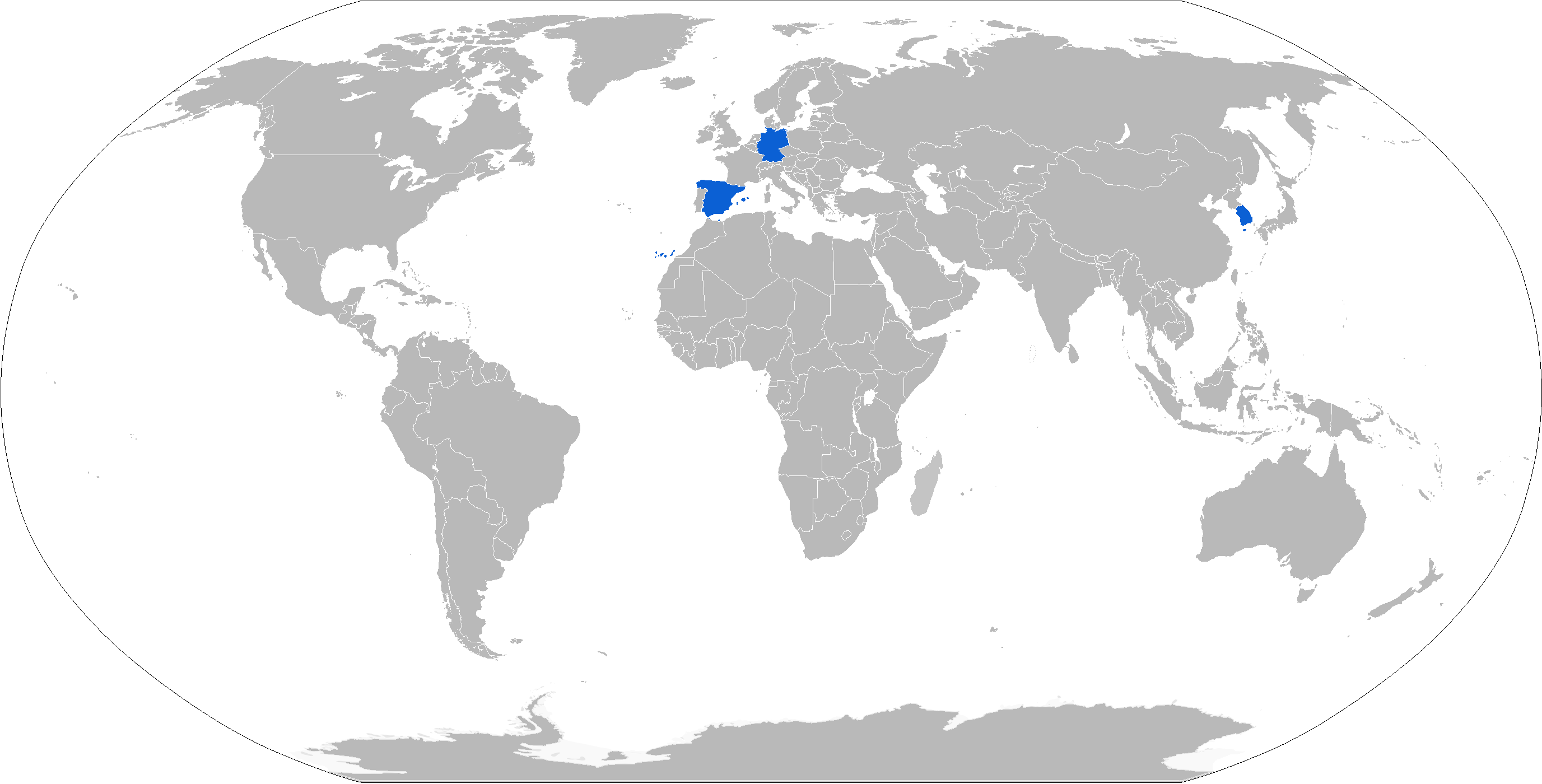
KEPD 350
Taurus KEPD 350 is a Swedish-German air-launched cruise missile, manufactured by Taurus Systems and used by Germany, Spain, and South Korea. Taurus Systems GmbH is a partnership between MBDA Deutschland GmbH (formerly LFK) and Saab Bofors Dynamics. Overview The missile incorporates stealth technology and has an official range in excess of . Taurus is powered by a turbofan engine at Mach 0.95 and can be carried by Tornado, Eurofighter Typhoon, Gripen, F/A-18, and F-15K jets. The double warhead, called Mephisto (Multi-Effect Penetrator HIghly Sophisticated and Target Optimised), features a precharge and initial penetrating charge to clear soil or enter HDBT (Hard and Deeply Buried Targets) hardened underground bunker, then a variable delay fuze to control detonation of the main warhead. The missile weighs about and has a maximum body diameter of . Intended targets are hardened bunkers; command, control, and communications facilities; airfield and port facilities; AMS and am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3M-54 Klub
The 3M-54 Kalibr, (Калибр, caliber), also referred to it as 3M54-1 Kalibr, 3M14 Biryuza (Бирюза, turquoise), ( NATO reporting name SS-N-27 Sizzler and SS-N-30A) is a family of Russian cruise missiles developed by the Novator Design Bureau (OKB-8). There are ship-launched, submarine-launched and air-launched versions of the missile, and variants for anti-ship, anti-submarine and land attack use. Some versions have a second propulsion stage that initiates a supersonic sprint in the terminal approach to the target, reducing the time that target's defense systems have to react, while subsonic versions have greater range than the supersonic variants. The missile can carry a warhead weighing up to of explosive or a thermonuclear warhead. Design The missile is a modular system with five versions: two anti-shipping types, one for land attack and two anti-submarine types. The missile is designed to share common parts between the surface and submarine-launched variants but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Strike Missile
The Naval Strike Missile (NSM) is an anti-ship and land-attack missile developed by the Norwegian company Kongsberg Defence & Aerospace (KDA). The original Norwegian name was Nytt sjømålsmissil (literally ''New sea target missile'', indicating that it is the successor of the Penguin missile). The English marketing name Naval Strike Missile was adopted later. According to Kongsberg the NSM/JSM is selected by Norway, Poland, Malaysia, Germany, the United States (as RGM-184), Japan, Romania, Canada, Australia and Spain as of 2022. The Joint Strike Missile (JSM) is a multi-role air-launched version of the NSM currently in development. Development The Naval Strike Missile's initial serial production contract was signed in June 2007. It has been chosen by the Royal Norwegian Navy for its s and s. In December 2008 the NSM was selected by the Polish Navy, which ordered fifty land-based missiles (including two for testing) in deals made in 2008 and 2011, with delivery planned fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |