|
Aiguillette
An aiguillette (, from '' aiguille'', "needle"), also spelled , or , is a cord with metal tips or lace tags, or the decorative tip itself. Functional or purely decorative fasteners of silk cord with metal tips were popular in the 16th and early 17th centuries, sometimes of gold set with gemstones or enameled, are generally called "aiglets", "aglets" or "points". In modern usage, an "aiguillette" is an ornamental braided cord with decorative metal tips worn on uniforms or as part of other costumes such as academic dress, where it will denote an honour. This usage of "aiguillette" derives from lacing used to fasten plate armor together. As such, a knot or loop arrangement was used which sometimes hung from the shoulder. These aiguillettes should not be confused with lanyards, which are cords also worn from the shoulder (or around the neck), but do not have the pointed aiguillette tips and are usually of fibre rather than gold or silver wire, and often not braided. The mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aglet
An aglet ( ) or aiglet is a small sheath, often made of plastic or metal, attached at each end of a shoelace, a cord, or a drawstring. An aglet keeps the fibers of the lace or cord from unraveling; its firmness and narrow profile make it easier to hold and easier to feed through eyelets, lugs, or other lacing guides. Etymology The word ''aglet'' and its variant ''aiglet'' come from the Middle French and Old French word ', the diminutive of ', meaning "needle, pin", which in turn comes from the Late Latin ' ("ornamental pin, pine needle"), diminutive of the Latin word for needle and pin, '.Picken, Mary Brooks: ''The Fashion Dictionary'', Funk and Wagnalls, 1957. (1973 edition ) History Aglets were originally made of metal, glass, or stone, and many were very ornamental. Wealthy people in the Roman era would have their aglets made out of precious metals such as brass or silver. Before the invention of buttons, they were used on the ends of the ribbons used to fasten clothi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Household Cavalry
The Household Cavalry (HCav) is made up of the two most senior regiments of the British Army, the Life Guards and the Blues and Royals (Royal Horse Guards and 1st Dragoons). These regiments are divided between the Household Cavalry Regiment stationed at Kiwi Barracks in Wiltshire and the ceremonial mounted unit, the Household Cavalry Mounted Regiment, garrisoned at Hyde Park Barracks (Knightsbridge Barracks) in London. The Household Cavalry is part of the Household Division and is the King's official bodyguard. Although the Household Cavalry Regiment is armoured, it is not part of the Royal Armoured Corps. Life Guards and Blues and Royals The British Household Cavalry is classed as a corps in its own right, and consists of two regiments: the Life Guards and the Blues and Royals (Royal Horse Guards and 1st Dragoons). They are the senior regular regiments in the British Army, with traditions dating from 1660, and act as the King's personal bodyguard. They are guards ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
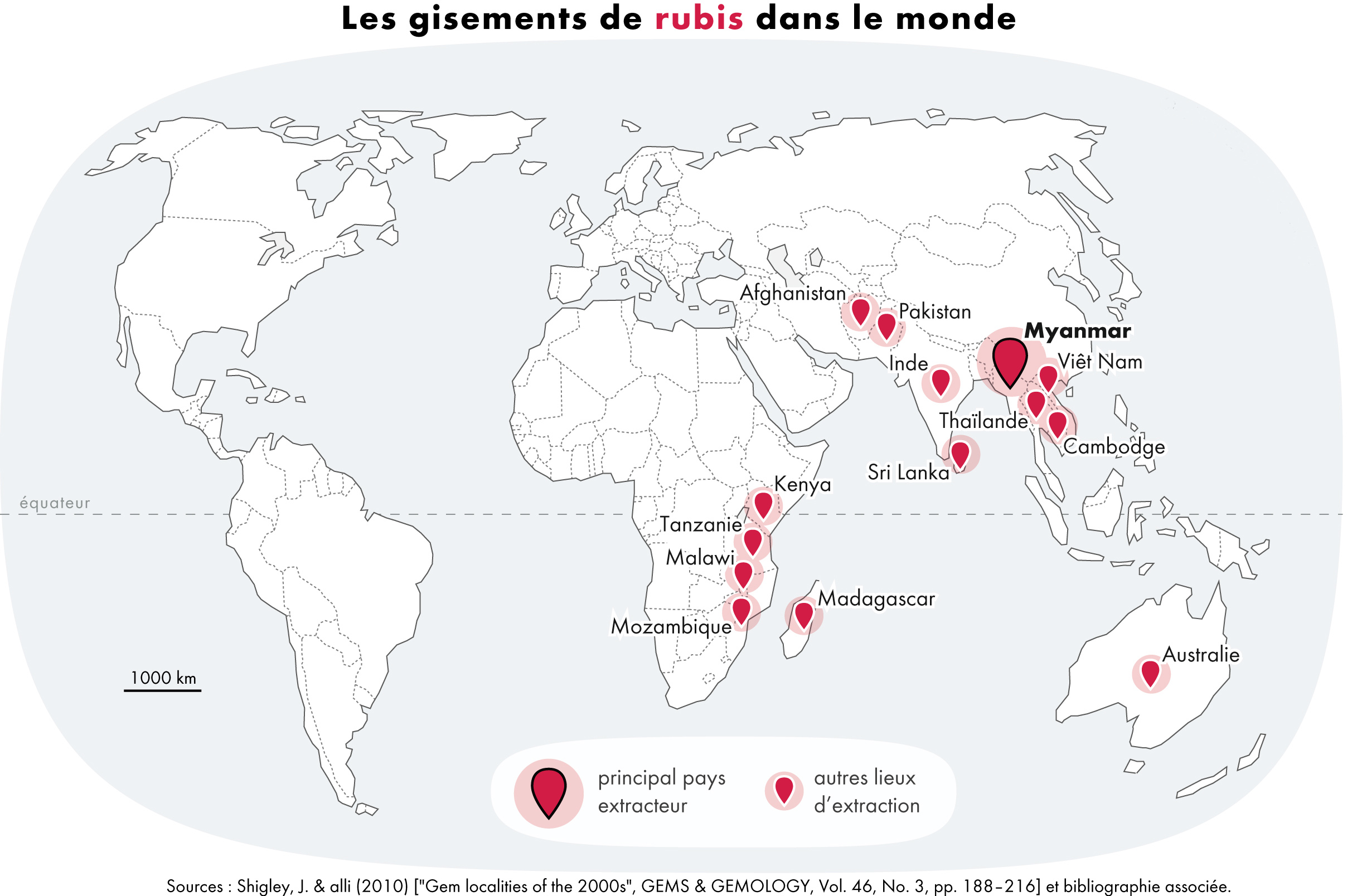
Rubies
A ruby is a pinkish red to blood-red colored gemstone, a variety of the mineral corundum ( aluminium oxide). Ruby is one of the most popular traditional jewelry gems and is very durable. Other varieties of gem-quality corundum are called sapphires. Ruby is one of the traditional cardinal gems, alongside amethyst, sapphire, emerald, and diamond. The word ''ruby'' comes from ''ruber'', Latin for red. The color of a ruby is due to the element chromium. Some gemstones that are popularly or historically called rubies, such as the Black Prince's Ruby in the British Imperial State Crown, are actually spinels. These were once known as "Balas rubies". The quality of a ruby is determined by its color, cut, and clarity, which, along with carat weight, affect its value. The brightest and most valuable shade of red, called blood-red or pigeon blood, commands a large premium over other rubies of similar quality. After color follows clarity: similar to diamonds, a clear stone will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentine Navy
The Argentine Navy (ARA; es, Armada de la República Argentina). This forms the basis for the navy's ship prefix "ARA". is the navy of Argentina. It is one of the three branches of the Armed Forces of the Argentine Republic, together with the Army and the Air Force. The Argentine Navy day is celebrated on May 17, anniversary of the victory in 1814 at the Battle of Montevideo over the Spanish fleet during the war of Independence. History 1810-1909 The Argentine Navy was created in the aftermath of the May Revolution of May 25, 1810, which started the war for independence from Spain. The navy was first created to support Manuel Belgrano in the Paraguay campaign, but those ships were sunk by ships from Montevideo, and did not take part in that conflict. Renewed conflicts with Montevideo led to the creation of a second fleet, which participated in the capture of the city. As Buenos Aires had little maritime history, most men in the navy were from other nations, such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-commissioned Officer
A non-commissioned officer (NCO) is a military officer who has not pursued a commission. Non-commissioned officers usually earn their position of authority by promotion through the enlisted ranks. (Non-officers, which includes most or all enlisted personnel, are of lower rank than any officer.) In contrast, commissioned officers usually enter directly from a military academy, officer candidate school (OCS), or officer training school (OTS) after receiving a post-secondary degree. The NCO corps usually includes many grades of enlisted, corporal and sergeant; in some countries, warrant officers also carry out the duties of NCOs. The naval equivalent includes some or all grades of petty officer. There are different classes of non-commissioned officers, including junior (lower ranked) non-commissioned officers (JNCO) and senior/staff (higher ranked) non-commissioned officers (SNCO). Function The non-commissioned officer corps has been referred to as "the backbone" of the arme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colegio Militar De La Nación
The National Military College ( es, Colegio Militar de la Nación) is the institution in charge of the undergraduate education of officers of the Argentine Army. It is located at El Palomar, Buenos Aires. Established on October 11, 1869, by President Domingo Sarmiento at the height of the Paraguayan War, its original quarters were opened in where the Parque Tres de Febrero stands today, with Col. Juan F. Czetz as the first superintendent. It was transferred to San Martín in 1892, and to its present location, the site of the 1852 Battle of Caseros that deposed mid-19th century strongman Juan Manuel de Rosas, in 1938. Its present facilities were inaugurated in 1937. ''El Palomar'' and ''La Casa de Caseros'', installations involved in the Battle of Caseros, were declared a National Historic Monument. Traditionally, most cadets belonged to high- or middle-class families, with many of them having a long military tradition. This has changed in recent years, the Corps of Cadets beco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regiment Of Mounted Grenadiers
The Regiment of Mounted Grenadiers ( es, Regimiento de Granaderos a Caballo) is the name of two Argentine Army regiments of two different time periods: a historic regiment that operated from 1812 to 1826, and a modern cavalry unit that was organized in 1903. The first Regiment of Mounted Grenadiers, formed in 1812, fought in the Argentine War of Independence under José de San Martín, and the Cisplatine War, subsequently becoming the Presidential bodyguard in 1825. Refusing to replenish its membership with soldiers who had not fought in the Argentine War of Independence, the regiment disbanded in 1826. The second Regiment of Mounted Grenadiers was formed in 1903, and serves as the national ceremonial unit. It claims the original regiment of 1812 as its heritage, but has no direct link or lineage. This incarnation of the regiment is also known as the ''General Jose de San Martin Cavalry Regiment''. As a unit, it has never been in combat, although ten members of the regiment w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Defense (Argentina)
The Ministry of Defense ( es, Ministerio de Defensa; MINDEF) of Argentina is a ministry of the national executive power that oversees and advises on matters of national defense, including overseeing the Argentine Armed Forces. The Ministry of Defense is one of the oldest ministries in the Argentine government, having existed continuously since the formation of the first Argentine executive in 1854, in the presidency of Justo José de Urquiza (then known as the Ministry of War). The incumbent minister is Jorge Taiana, who has served since 10 August 2021 in the cabinet of Alberto Fernández. History Traditionally the minister of Defense, as the Joint chiefs of Staff (Spanish: ''Estado Mayor Conjunto'') which traces back its origin to 1948 had a minor role in all armed forces activities, relegating key decisions to the respectives chiefs of staff. A major change came into effect on 12 June 2006 when President Néstor Kirchner brought into effect the Defense Law, which had bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Fiennes De Clinton, Earl Of Lincoln
Edward is an English given name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortune; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”. History The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-Saxon England, but the rule of the Norman and Plantagenet dynasties had effectively ended its use amongst the upper classes. The popularity of the name was revived when Henry III named his firstborn son, the future Edward I, as part of his efforts to promote a cult around Edward the Confessor, for whom Henry had a deep admiration. Variant forms The name has been adopted in the Iberian peninsula since the 15th century, due to Edward, King of Portugal, whose mother was English. The Spanish/Portuguese forms of the name are Eduardo and Duarte. Other variant forms include French Édouard, Italian Edoardo and Odoardo, German, Dutch, Czech and Romanian Eduard and Scandinavian Edvard. Short forms include Ed, Eddy, Eddie, Ted, Teddy and Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hose (clothing)
Hose are any of various styles of men's clothing for the legs and lower body, worn from the Middle Ages through the 17th century, when the style fell out of use in favour of breeches and stockings. The old plural form of "hose" was "hosen". In German these terms (''Hose'', singular, and ''Hosen'', plural) remained in use and are the generic terms for trousers today. The French equivalent was ''chausses''. History Since the 13th century, hose were already known to have been worn in Europe; these were tights that stretch from waist to feet. The outline of the legs were conspicuously shown, with the groin area sometimes covered by a material called a codpiece. However, unlike modern tights, these hose were not elastic; they were held firm while laced to the doublet and tied from small holes. During the 14th century, medieval hoses were made of wool and were made to fit tightly. Towards the end of the century traders and shopkeepers wore coloured hoses. Some people did away with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doublet (clothing)
A doublet (/ˈdʌblɪt/; derived from the Ital. ''giubbetta'') is a man's snug-fitting jacket that is shaped and fitted to the man's body. The garment was worn in Spain, and spread to the rest of Western Europe, from the late Middle Ages up to the mid-17th century. The doublet was hip length or waist length and worn over the shirt or drawers. Until the end of the 15th century, the doublet was usually worn under another layer of clothing such as a gown, mantle, overtunic or jerkin when in public. Originally it was a mere stitched and quilted lining ("doubling"), worn under a hauberk or cuirass to prevent bruising and chafing. Doublets were sometimes opened to the waistline in a deep V. The edges might be left free or laced across the shirt front. If there was space left it might be filled with a stomacher. By the 1520s, the edges of the doublet more frequently met at the center front. Then, like many other originally practical items in the history of men's wear, from the late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
